LinX Series Linear Motor - User Guide
36 D-000168 Rev 02 ANCA Motion
Appendix 9
Motor Selection Guide 9.1
Application Continuous Force Calculation 9.1.1
Example
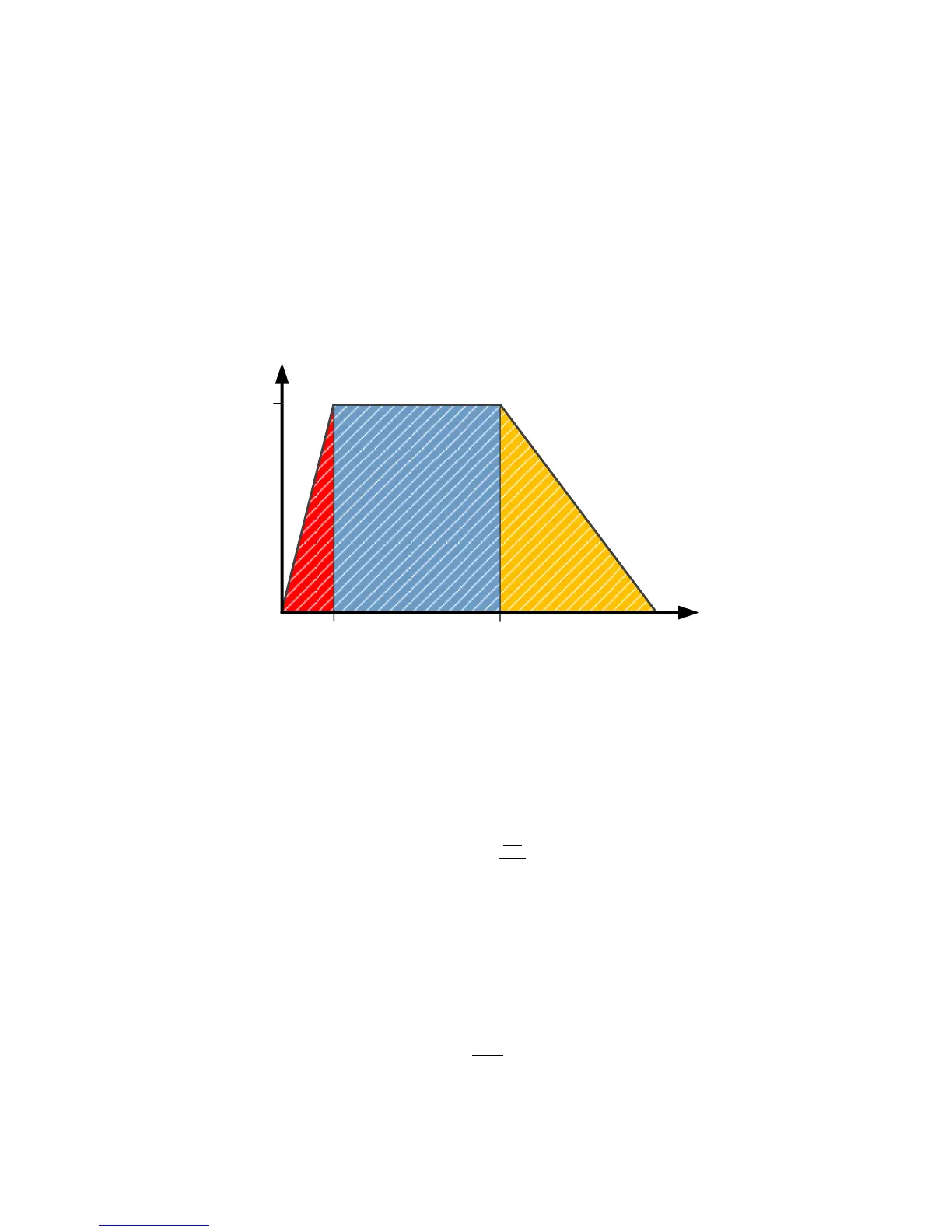
The following example demonstrates calculation of a motor duty cycle simple positioning move with a trapezoidal
velocity profile. The profile is broken up into sections i.e. acceleration, constant velocity and deceleration in order
to determine the RMS force and duty cycle.
Acceleration
Deceleration
Constant Velocity
Velocity
Time
1 m/s
0.2 sec 1.2 sec
2.2 sec
Load Mass = 90kg
Forcer Mass = 10kg
Coefficient of Friction (µ) = 0.005
Friction Force = 10N
Figure 9-1 - Positioning example velocity profile
In this example, friction is taken as a combination of the Coefficient of Friction (µ) and a constant force.
Referring to Figure 9-1, the positioning move can be broken down into the following segments:
Acceleration:
Constant Velocity:
Deceleration:

 Loading...
Loading...