ECM SYSTEM
WG1605-G-E3,WG1605-L-E3,WG1605-GL-E3, DM
1-35
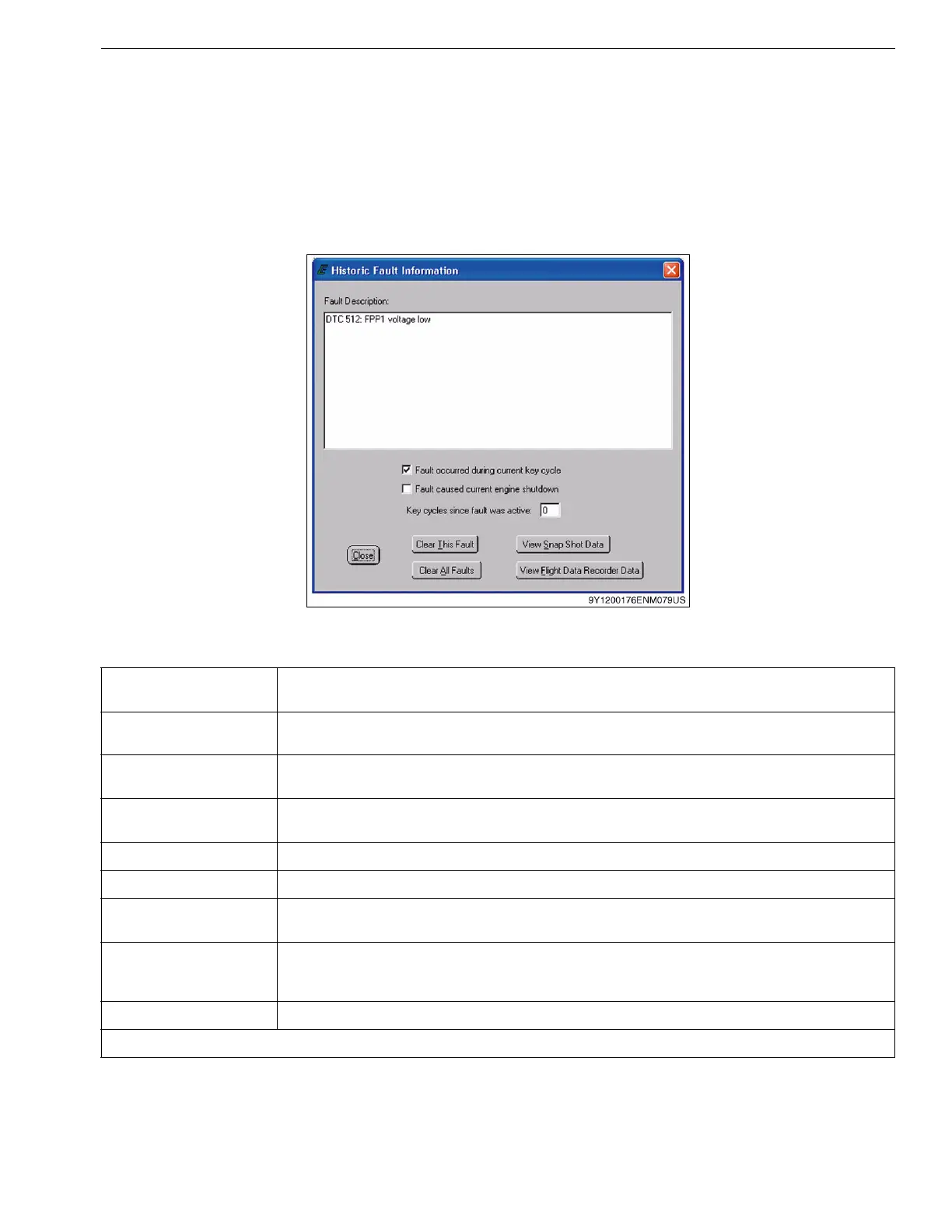
Accessing fault information is accomplished through
a double left-click of the fault LED in the historic fault list.
This produces the Historic Fault Information interface
shown in Figure 4. From this interface the user can
interpret a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) message,
identify whether or not the fault occurred during the
current key cycle, identify if the fault caused the engine
to shutdown, determine how many key cycles have
occurred since the fault was last active, clear selected or
all historic faults, and view snapshot and flight data.
Table 3 outlines the options displayed in the Historic
Fault Information screen. Historic faults are not
overwritten if the same fault becomes active, storing
data from the original active fault.
Figure 4: Historic Fault Information Interface
Historic Fault Information Interface Functions
Fault Description Message
Box
Customized text that references the DTC flash code and describes the fault.
Fault During Key Cycle
Checkbox
Informs that the fault occurred during the current key-on event.
Fault Caused Engine
Shutdown Checkbox
Informs that the fault caused the engine to shutdown.
Key Cycles Since Fault
Active Indicator
Displays the amount of key-on events since the fault was last active.
Clear This Fault Button* Erases the selected historic fault from the ECM.
Clear All Faults Button* Erases all historic faults from the ECM.
View Snap Shot Data Button
Retrieves a data “snap shot” from the ECM for variables defined in the base and custom snapshot variable
definition lists. An example of a fault snap shot is shown in Figure 5.
View Flight Data Recorder
Data Button
Retrieves a 10-second data strip chart (8 seconds prior, 2 seconds after fault trigger) from the ECM for
variables defined in the base and custom flight data recorder definition lists. An example of a fault snap shot is
shown in Figure 6.
Close Button Exits the Historic Fault Information interface. DOES NOT cancel or clear any faults.
* Snapshot and flight data recorder data for historic faults is erased after the prompt shown in Figure 7 is satisfied.

 Loading...
Loading...