31
VARIABLY SPACED HALF-BLIND DOVETAIL PROCEDURES
Chapter 9Super Jig-12-18-24 User Guide
9-3 Joint Fit and Depth of Cut
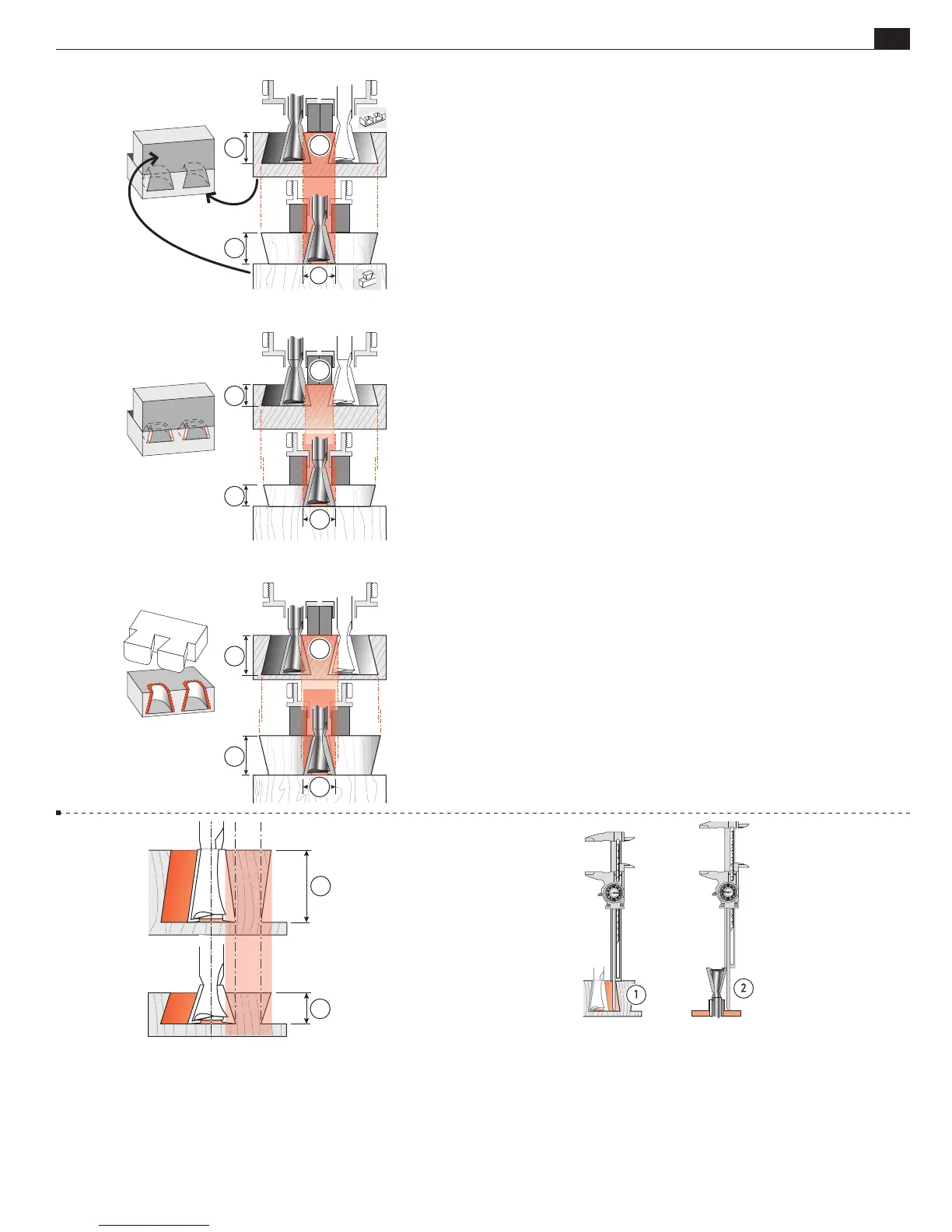
Here’s why the depth of cut
changes the fit in half-blind dove-
tails. Increasing or decreasing the depth of cut does not affect the
pin socket width
, but does affect the width of the pin
that
goes into the socket
.
1
3
2
1
1
3
2
1
PIN
2
1
3
1
9-4 Note that decreasing the bit depth
makes the pin
narrower while the pin socket
stays the same width, producing
a loose fit.
Decreasing the bit depth (i.e. raise the bit into the router) pro-
duces a looser fit.
9-5 Increasing the bit depth
makes the pin
larger while
the pin socket
stays the same width, producing too tight a fit.
Increasing the bit depth (i.e. lower the bit) produces a tighter fit.
9-6 Bit Angle and Depth of Cut Half-blind pins and tails
are routed with the same dovetail bit, the same guidebush, and
the same depth of cut. A different depth of cut requires a differ-
ent angled bit. Leigh offers five different angled dovetail bits for
a range of cut depths. A lesser angle, say 8˚, for a deeper cut
; a
greater angle, say 18˚, for a shallower cut
.
1
2
18˚
8˚
9-7 Cumulative plus/minus tolerances in routers, bits and
guidebushes, make it impossible to state exact bit depth for first-
time precision fit. All dovetail jigs require trial and error tests to
attain fine fitting joints. The good news; we give a starting depth
for each bit. Test and measure the successful ‘Best fit’ depth of
cut
or bit projection
. Record for future first-time fits.
 Loading...
Loading...