203
•
S
erial Number—Serial number of optical transceiver.
•
Data Ready—SFP is operational. Values are True and False
•
Loss of Signal—Local SFP reports signal loss. Values are True and False.
•
Transmitter Fault—Remote SFP reports signal loss. Values are True, False, and N
o
S
ignal (N/S).
•
Temperature—Temperature (Celsius) at which the SFP is operating.
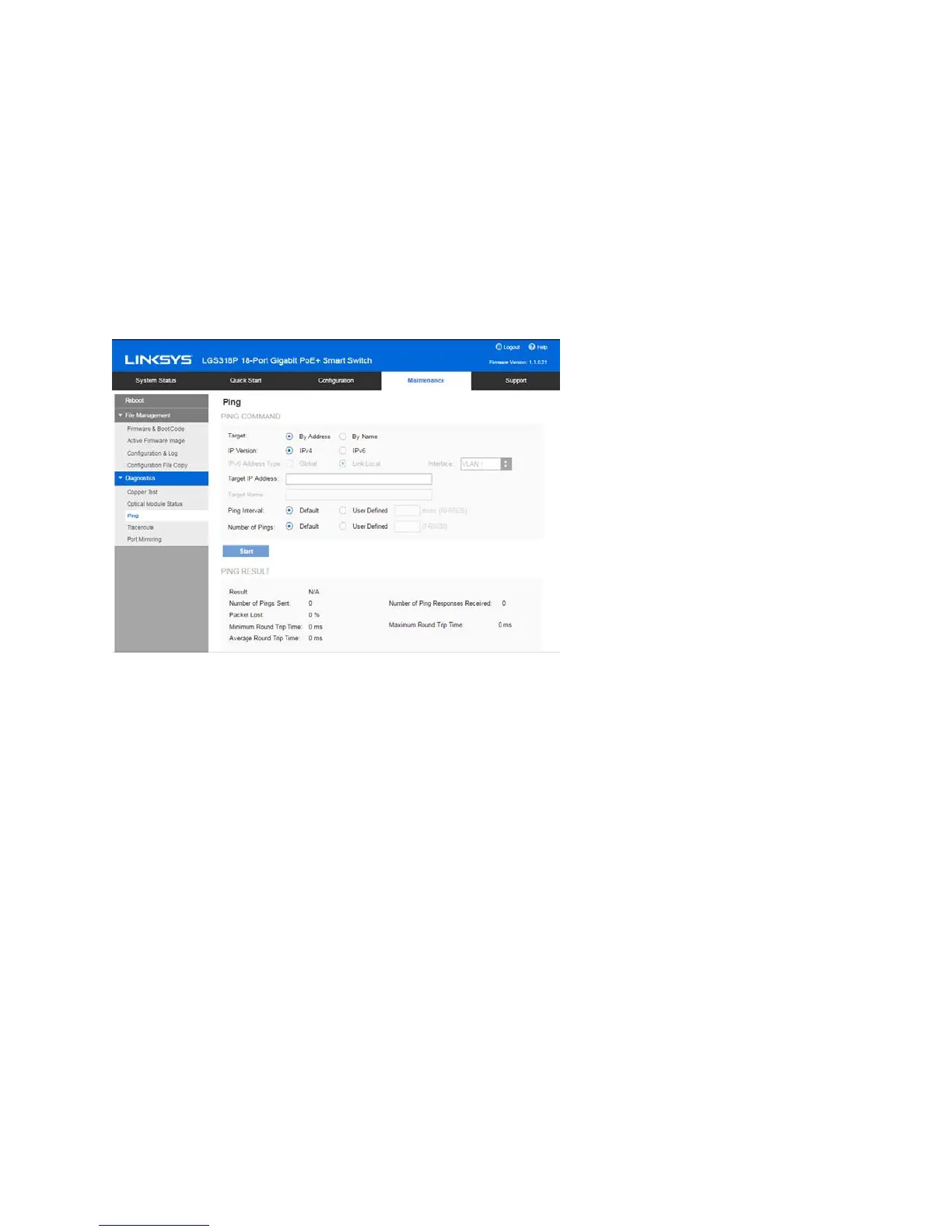
Ping
P
ing is a utility used to test if a remote host can be reached and to measure the round-trip time for
packets sent from the device to a destination device.
Ping operates by sending Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) echo request packets to the
target host and waiting for an ICMP response, sometimes called a pong. It measures the round-
trip time and records any packet loss.
To ping a host:
1. Click Maintenance > Diagnostics > Ping.
2. Configure ping by entering the fields:
•
Target—Select whether to specify the source interface by its IP address or name
.
T
his field influences the interfaces that are displayed in the Source IP field, a
s
d
escribed below.
•
IP Version—If the source interface is identified by its IP address, select either IPv4
or IPv6 to indicate that it will be entered in the selected format.

 Loading...
Loading...