Inverter Principle
- 7 -02.20 909.2710.1-06
3 Inverter Principle
A welding inverter is a electronically controlled welding power source. At conventional transformer based
machines, the mains voltage with 50/60 Hz is directly switched to the welding transformer. At a welding
inverter the mains voltage is rectified first and with electronic power switches (MOSFETs or IGBTs) chopped
into a frequency of 80 kHz. This allows a very small construction of the welding transformer, because it‘s
driven at this high frequency.
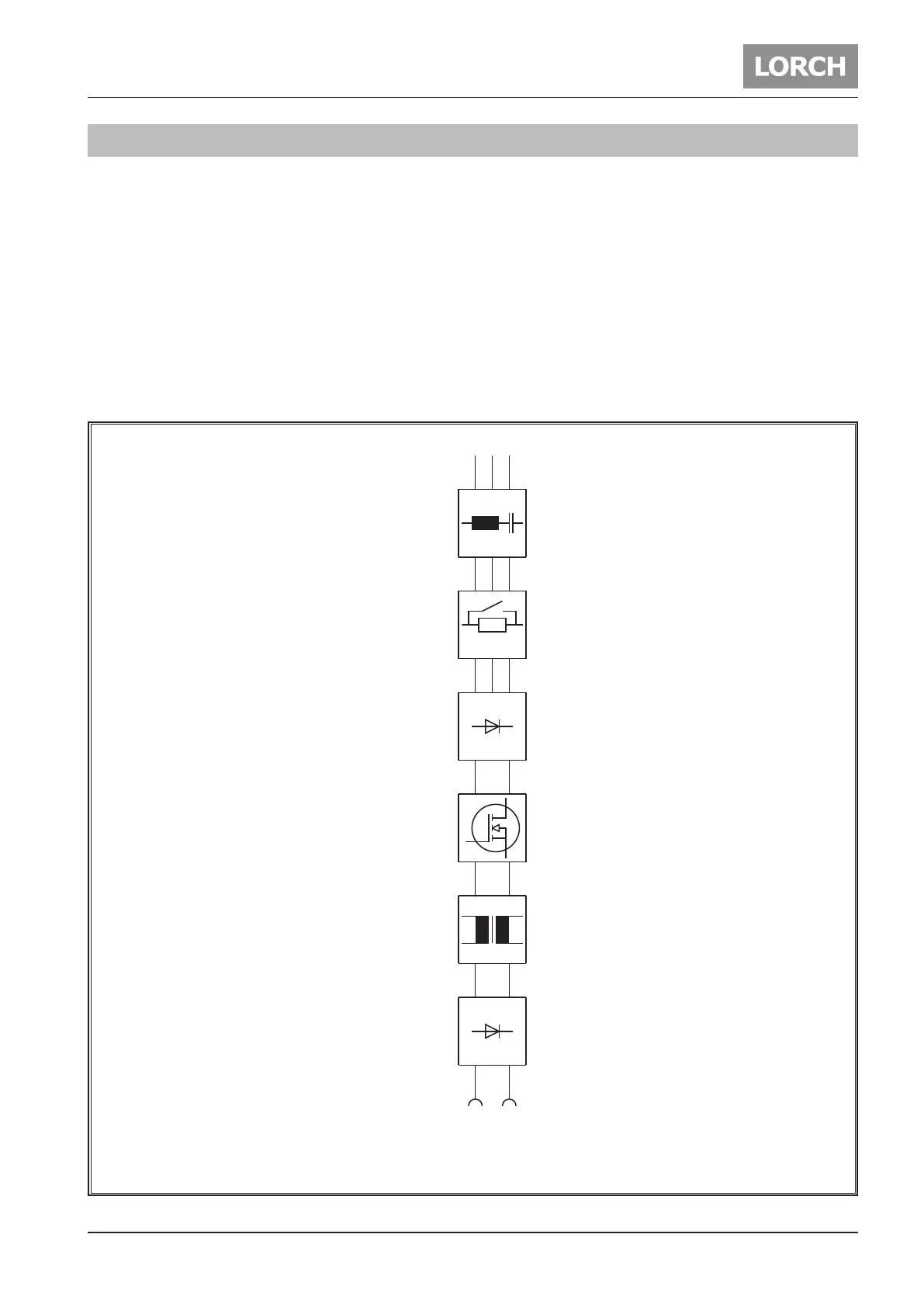
The basic structure of a welding inverter is always the same at Lorch power sources:
– mains filter
– power-up circuit
– mains rectifier
– primary inverter
– transformer
– secondary rectifier
mains
filter
3 phase mains
input
rectifier
primary
driver
transformer
secondary
rectifier
power
up
Fig. 3: Inverter principle
 Loading...
Loading...











