3.4.4 Power sharing mode
See figure 3-7. If the available power at the AC-input is
limited, and the load connected to the AC output increases,
the external AC circuit breaker may trip if nothing is done.
To avoid this, the Mass Combi Ultra can automatically
reduce the battery charger output, and thus the AC power
consumption.
The Power Sharing level should be set to match the value
of the external circuit breaker, which protects the incoming
AC power. For example, when the external AC power is
limited by a 6 A fuse, the Power Sharing level must be set
to 6 A. When the total connected AC load reaches the
level of the Power Sharing setting (6 A), there will be no
power left over to charge the battery. This means that the
charge current of the Mass Combi will be reduced to 0 A.
The Power Sharing level can be adjusted by means of the
DIP-switches locally on the Mass Combi Ultra. However,
we recommend the use optional remote control, like the
MasterView Easy.
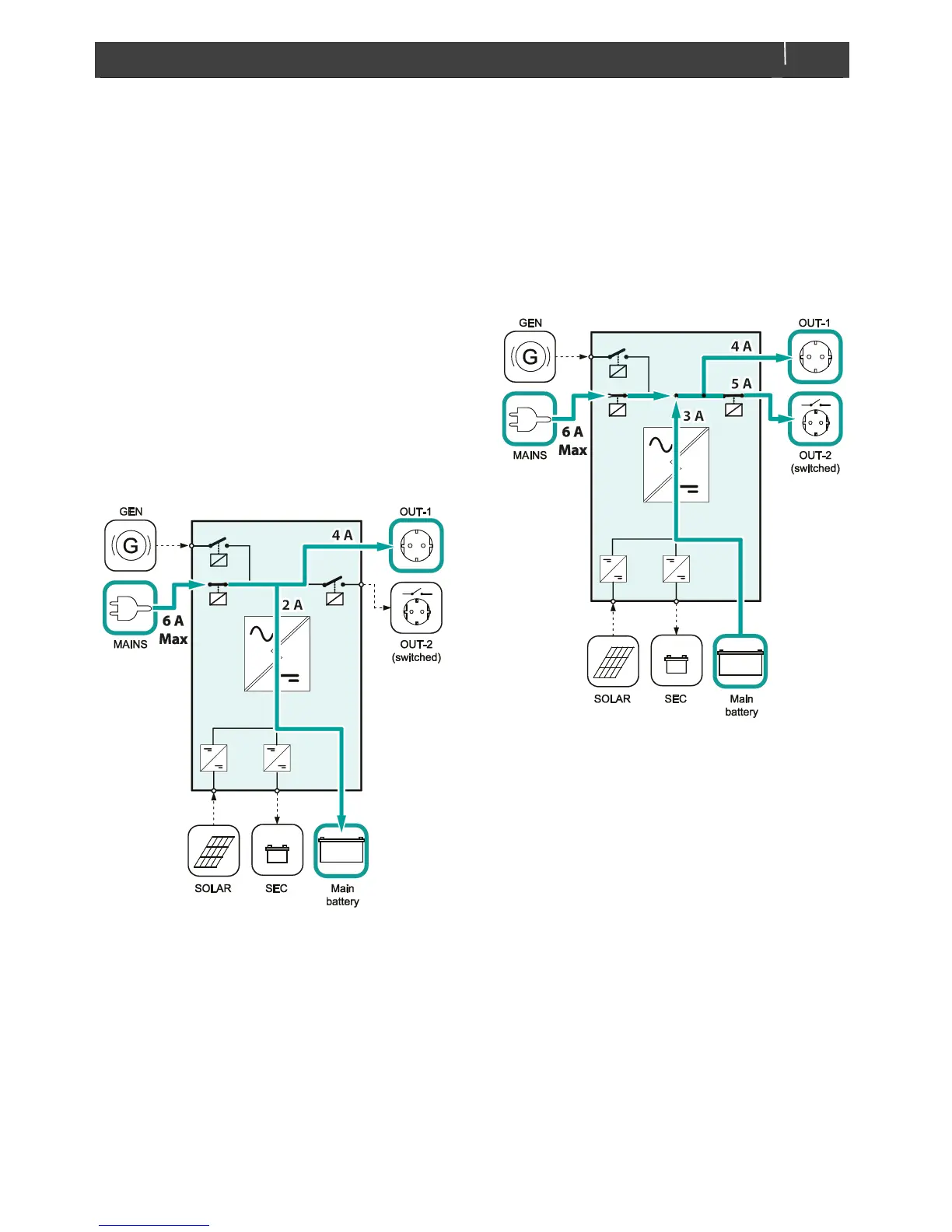
Figure 3-7: Power Sharing level is set to a 6 A while the AC
outputs consume a total of 4 A. This means that 6 – 4 = 2 A
is left over for charging.
3.4.5 Gen-/Mains support
See figure 3-8. If the demand for AC power is higher than
the available power at the AC–input, the external AC circuit
breaker may trip if nothing is done. This problem can be
solved by the Generator / mains support function. With the
Generator / mains support mode enabled, the inverter will
operate in parallel with the external AC power source. This
means that energy from the batteries is added to the AC-
output only.
Under no circumstances AC power from the inverter can be
fed back into the AC grid. Please mind that several
countries maintain different regulations with regard to AC-
sources operating in parallel with the AC-grid. This may
mean that in some situations the use of the Generator /
Mains support function is not allowed. Please acquaint
yourself with local regulations on this issue. Never use the
Generator / Mains support mode if this is not allowed!
Figure 3-8: Example: The AC-input is limited to 6 A. This is
not enough to supply the total load (4 + 5 = 9 A) connected
to the AC outputs. The inverter will supply the remaining 9
– 6 = 3 A.

 Loading...
Loading...











