24
you see each day?
Planetary transits are another exciting feature to see when observing the Sun.
Although this event happens infrequently, it occurs when the planet Mercury or
Venus passes in front of the Sun. From your EclipseView telescope this would
look like a small black dot travelling very slowly across the face of the Sun.
These rare planetary transits are well known in advance and often mentioned
on the local news days before they occur.
Solar Eclipses occur when the Moon, during its monthly trip around the Earth,
passes between the Earth and the Sun. This causes the Moons shadow to be
cast onto a small part of the Earth. This shadow will have two distinct regions,
the innermost and darkest region called the umbra and the outer brighter region
called the penumbra. The dark umbra region is a very narrow region sometimes
60 - 100 miles wide. The penumbra region covers a much larger area and can
be almost 4,000 miles wide.
There are three different types of solar Eclipses:
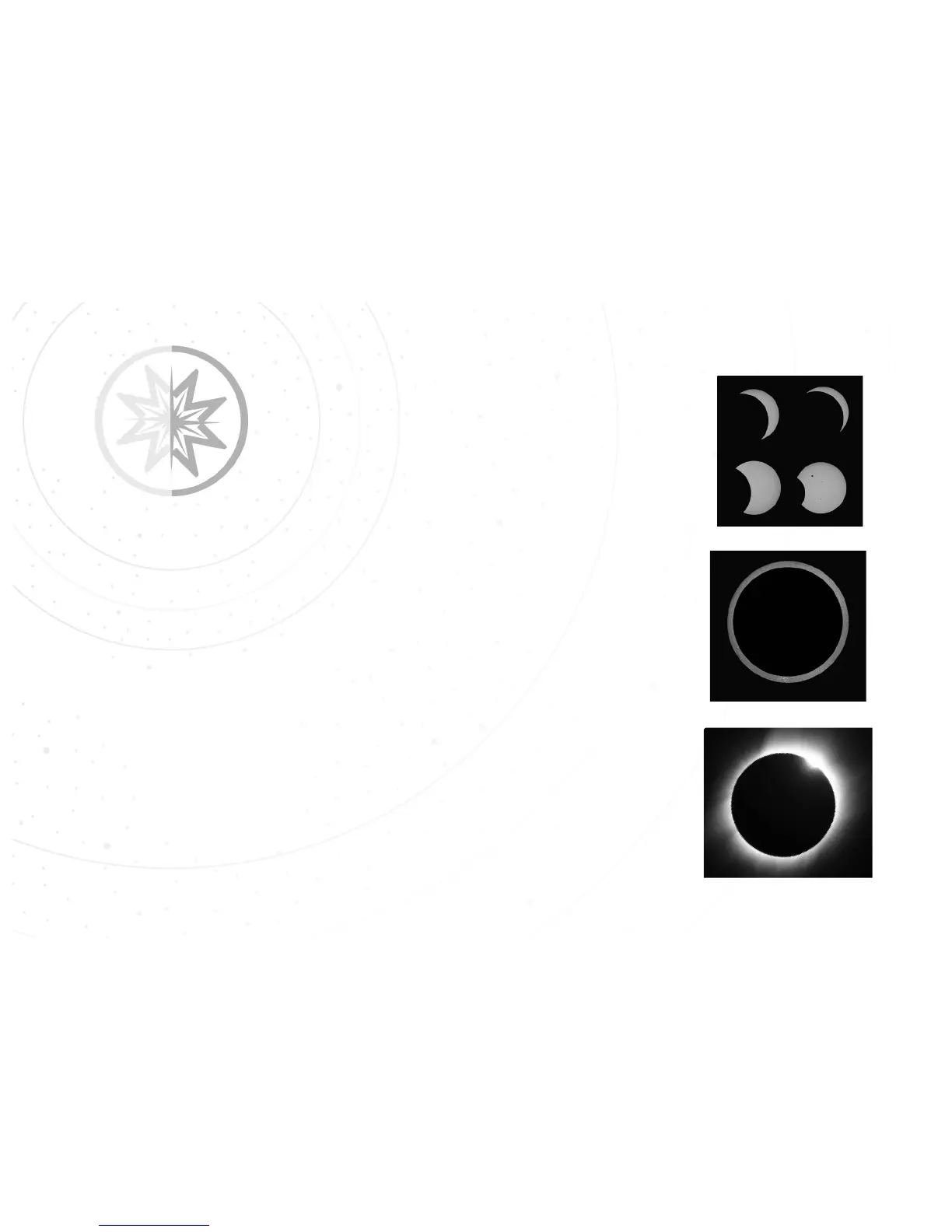
A Partial Solar Eclipse occurs when the Moon passes in front of the Sun and
blocks only a portion of the Sun. This is the most common type of solar eclipse.
The Sun will look like a bite has been taken out of it.
An Annular Solar Eclipse occurs when the Moon passes directly in front
of the Sun, but only blocks the central portion of the Sun. During this
Annular Solar Eclipse
23
Partial Solar Eclipse
Total Solar Eclipse
 Loading...
Loading...











