21
SATURO
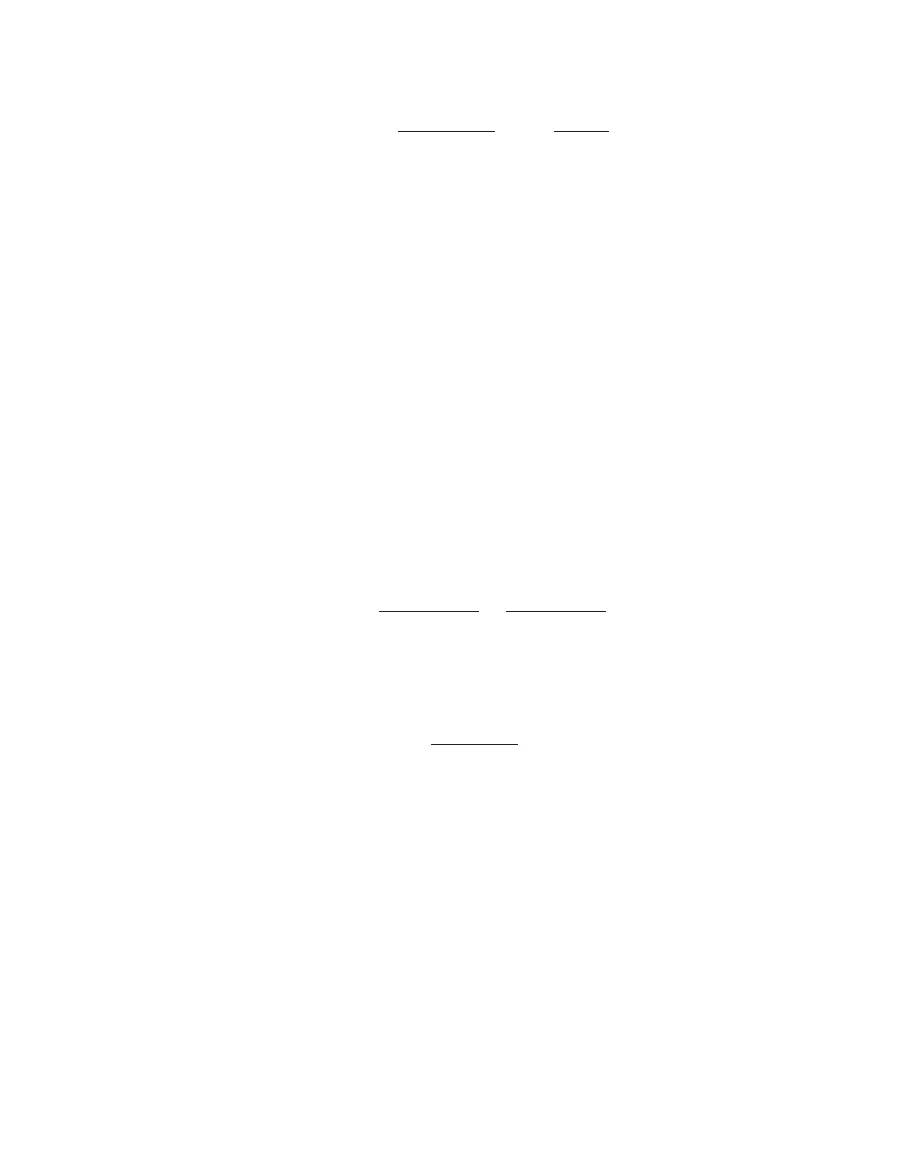
Nimmo et al. (2009) gives F as shown in Equation 2
F
Cd Cb
12
D
=+
+
=+
Equation 2
where
D
is the ponding depth (cm)
d
is the insertion depth of the infiltrometer (cm)
b
is the radius of the infiltrometer (cm)
∆
is the constant for a given infiltrometer geometry; C
1
d + C
2
b (cm)
C
1
is 0.993
C
2
is 0.578
λ
is the reciprocal of the Gardner ∝, which is a characteristic of the soil and its initial
water content (cm)
In Equation 2, ∆ is simply Equation 36 of Reynolds and Elrick (1990) multiplied by bπ, which
allows Figure2 and Equation 2 to be reconciled with Equation 37 of Reynolds and
Elrick(1990).
For two ponding depths, use Equation 3:
Equation 3
Rearranging one of the right terms to solve for λ in terms of K
fs
, substituting this for λ in the
other right term, and simplifying yields
Equation 4
where
D
1
is the actual high pressure head
D
2
is the actual low pressure head
∆
is 0.993d + 0.578b (cm)
i
1
is infiltration rate at the high pressure head
i
2
is infiltration rate at the low pressure head
For ∆, d is the infiltrometer insertion depth and b is the infiltrometer radius. For the SATURO
5-cm insertion ring, d = 5 cm and b = 7.5 cm, so ∆ = 9.3 cm. For the 10-cm insertion ring,
d=10 cm and b = 7.5 cm, so ∆ = 14.3 cm.
 Loading...
Loading...