Do you have a question about the Miller Bobcat 250 and is the answer not in the manual?
Explains safety symbols used throughout the manual.
Details potential dangers associated with arc welding processes.
Defines safety symbols specific to CE products.
Defines general symbols used throughout the manual.
Indicates where to find serial and rating plate information.
Technical specifications for CH730 engine models.
Technical specifications for ECH730 engine models.
Details operating and storage temperature ranges.
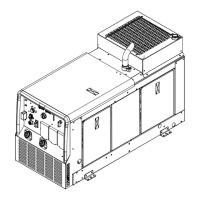
Instructions for mounting and securing the welder/generator unit.
Overview of the welder's front panel controls.
Details the available generator power receptacles and their ratings.
Schedule and tasks for routine maintenance.
List of recommended spare parts with part numbers and descriptions.
The main electrical circuit diagram for the unit.
Guidance on selecting auxiliary equipment for use with the generator.
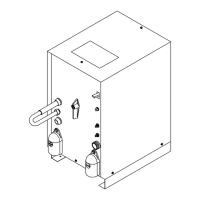
Procedures for safely grounding the generator to a vehicle frame.
Step-by-step guide for performing stick welding.
Connections for MIG welding with a voltage-sensing wire feeder.
Details the terms and conditions of the limited warranty.
| Rated Output | 250 A at 25 VDC, 100% Duty Cycle |
|---|---|
| Generator Power | 11, 000 Watts Peak, 9, 500 Watts Continuous |
| Engine | Kohler CH730 |
| Fuel Type | Gasoline |
| CC/CV | CC/CV |
| Phase | Single-phase |
| Frequency | 60 Hz |
| Type | Engine Driven Welder |
| Welding Processes | Stick (SMAW), MIG (GMAW), Flux-Cored (FCAW), TIG (GTAW) |
| Fuel Tank Capacity | 12 gallons |
| Welding Amperage Range | 40 - 250 A |
| Open Circuit Voltage | 80 VDC |
| Voltage | 120/240 V |
| Outlet Types | 120V 20A Duplex, 240V 50A |