7-20 | ni.com
Chapter 7 Counters
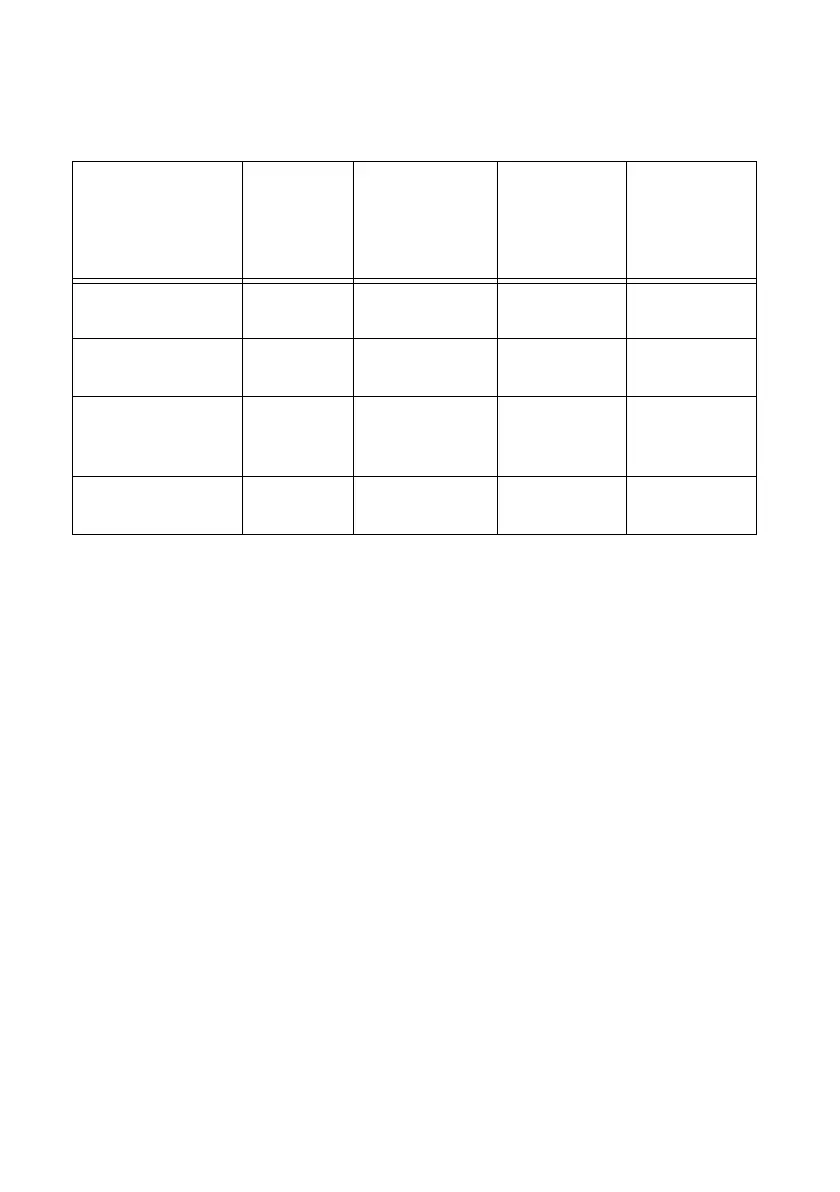
Table 7-5 summarizes some of the differences in methods of measuring frequency.
For information about connecting counter signals, refer to the
Default Counter/Timer Pins
section.
Period Measurement
In period measurements, the counter measures a period on its Gate input signal after the counter
is armed. You can configure the counter to measure the period between two rising edges or
two falling edges of the Gate input signal.
You can route an internal or external periodic clock signal (with a known period) to the Source
input of the counter. The counter counts the number of rising (or falling) edges occurring on the
Source input between the two active edges of the Gate signal.
You can calculate the period of the Gate input by multiplying the period of the Source signal by
the number of edges returned by the counter.
Period measurements return the inverse results of frequency measurements. Refer to the
Frequency Measurement section for more information.
Table 7-5. Frequency Measurement Method Comparison
Method
Number of
Counters
Used
Number of
Measurements
Returned
Measures
High
Frequency
Signals
Accurately
Measures
Low
Frequency
Signals
Accurately
Low frequency with
one counter
1 1 Poor Good
High frequency with
two counters
1 or 2 1 Good Poor
Large range of
frequencies with
two counters
2 1 Good Good
Sample clocked
(averaged)
1 1 Good Good

 Loading...
Loading...











