Serial Interface
6
Section 6 - Serial Interface
The DP606A and DP612A uses the Modbus/RTU interface as described in MODBUS
APPLICATION PROTOCOL SPECIFICATION (V1.1b3).
The Modbus specification allows accessing to up 65535 internal ‘holding’ registers
using register READ, register WRITE and WRITE MULTIPLE commands. Each
Modbus holding register is defined as a 16 bit entity structured as BIG ENDIAN
values (most significant byte always presented first).
Modbus is structured using a MASTER-SLAVE topology, in which there is one
MASTER device and up to 247 slave devices. All transactions are initiated by the
MASTER device. The DP606A and DP612A acts as a slave device, with a device
address in the range 1 to 247.
Modbus slave devices are individually accessed using a one byte SLAVE address.
The MASTER device initiates a transaction by sending a request packet to a specific
slave. The SLAVE device processes the transaction and returns either response
packet indicating success or failure.
Address 0 is reserved as a ‘broadcast’ address, in which all slave devices will accept
and process the transaction but will not send a response.
Section 6.1 - Modbus Functions
The DP606A and DP612A Modbus interface supports the following Modbus
FUNCTION requests.
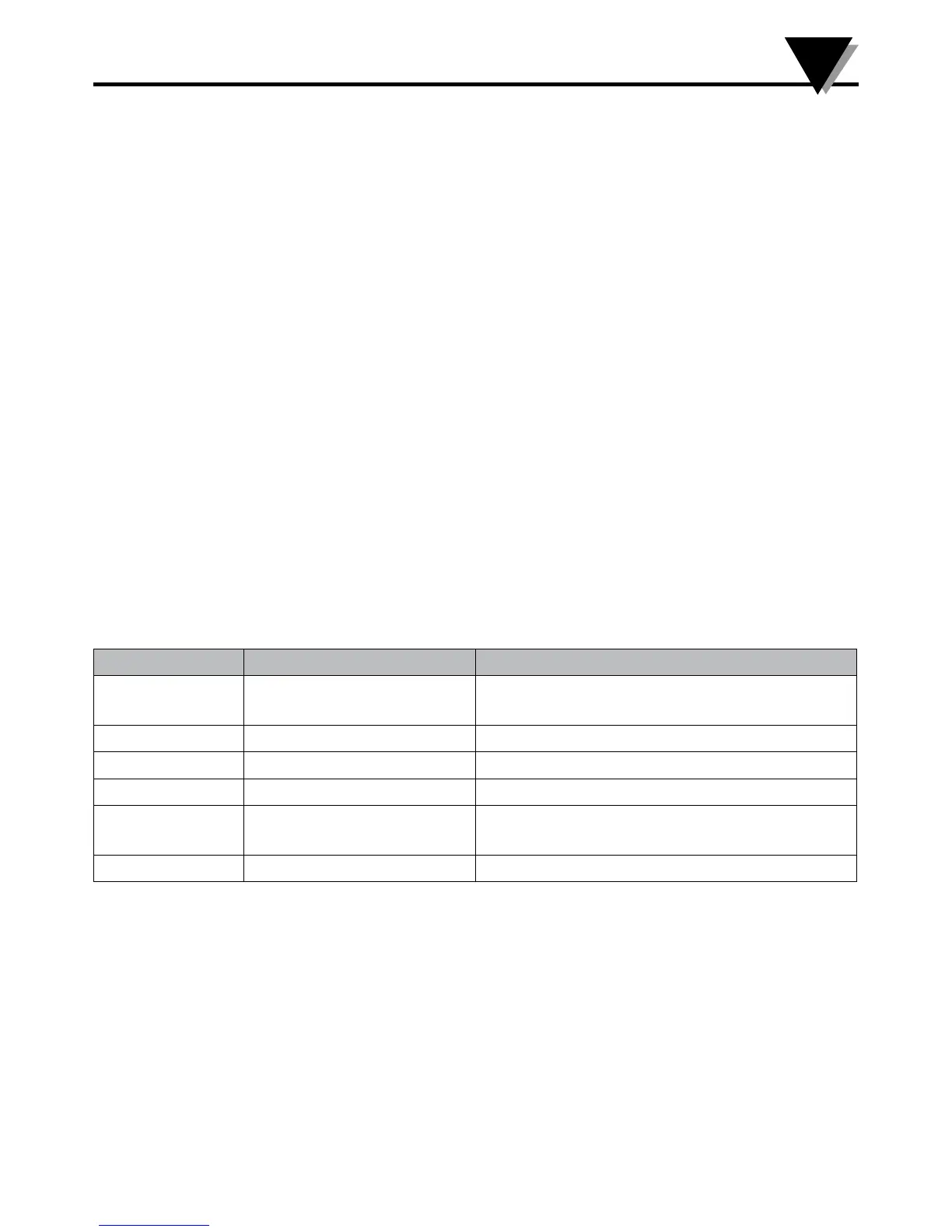
Function Code Mnemonic Description
0x03 Read Holding Register Reads one or more consecutive 16 bit
holding registers
0x06 Write Single Register Writes a specific 16 bit holding register
0x07 Read Exception status Reads structured status information
0x08 Reserved
0x10 Write Multiple Registers Write one or more consecutive 16 bit
holding registers
0x0b Get Comm events Read communication event counters
Table 8 - Modbus Functions
20
 Loading...
Loading...