302
CPU Processing Modes Section 6-8
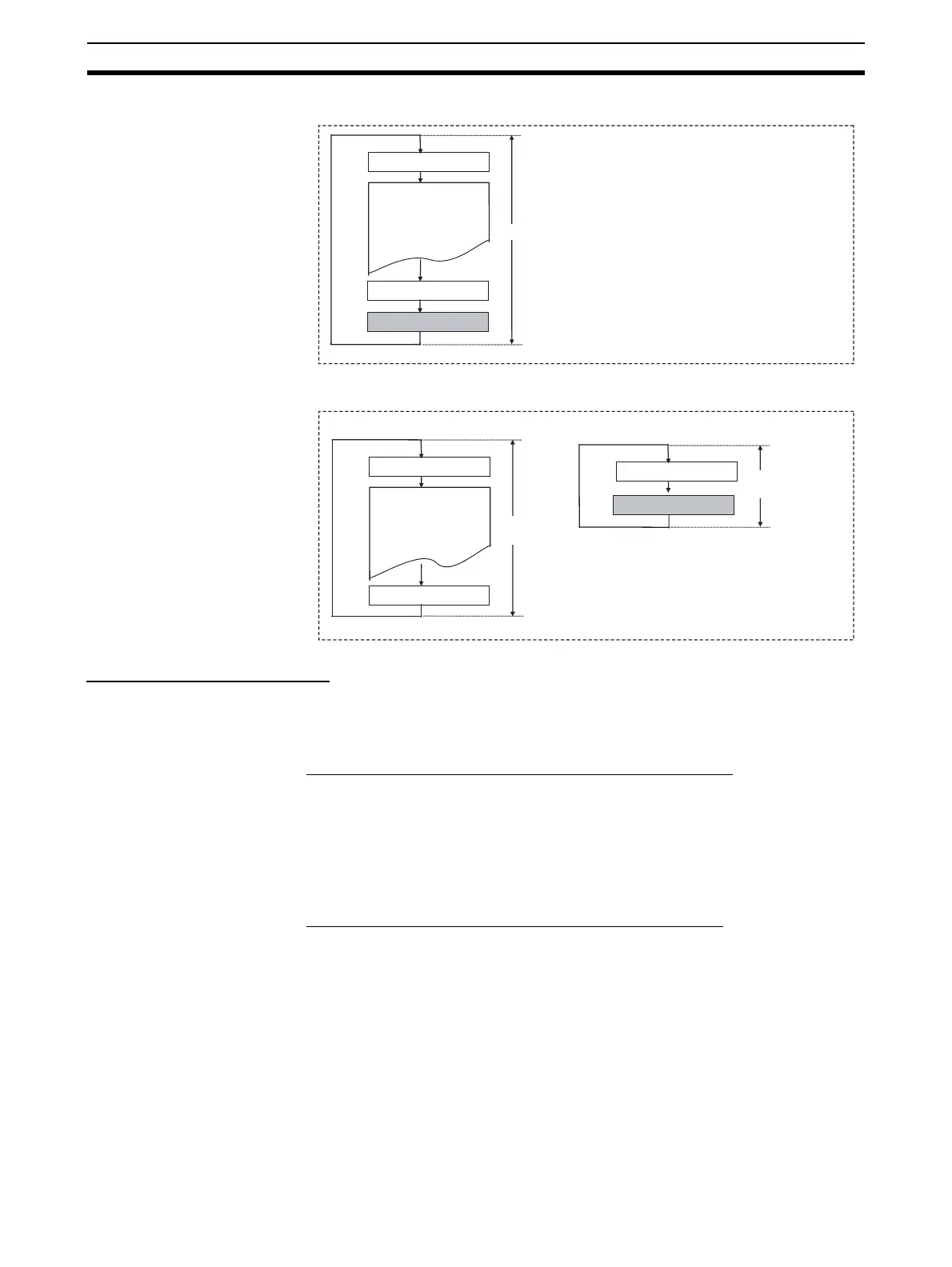
Normal Mode
Parallel Processing Modes
Parallel Processing Modes
There are two different Parallel Processing Modes: Parallel Processing with
Synchronous Memory Access and Parallel Processing with Asynchronous
Memory Access.
■ Parallel Processing with Asynchronous Memory Access
In this mode, I/O memory access for peripheral servicing is not synchronized
with I/O memory access for program execution. In other words, all peripheral
servicing is executed in parallel with program execution, including memory
access. This mode will provide the fastest execution (compared to the other
modes) for both program execution and event processing when there is a
heavy peripheral servicing load.
■ Parallel Processing with Synchronous Memory Access
In this mode, I/O memory access for peripheral servicing is not executed in
parallel with program execution, but rather is executed following program exe-
cution, just like it is in the normal execution mode, i.e., following the I/O
refresh period. All other peripheral servicing is executed in parallel with pro-
gram execution.
This mode will provide faster execution that the normal execution mode for
both program execution and event processing. The program execution cycle
time will be longer than that for Parallel Processing with Asynchronous Mem-
ory Access by the time required to refresh I/O for peripheral servicing.
The cycle times and peripheral servicing responses for Normal, Parallel Pro-
cessing with Asynchronous Memory Access, and Parallel Processing with
Synchronous Memory Access are listed in the following table. (These values
Overseeing processing
Program execution
I/O refreshing
Peripheral Servicing
Cycle time
Overseeing processing
Program execution
I/O refreshing
Peripheral servicing
Cycle time for
program execution
Overseeing processing
Cycle time for
peripheral servicing
Program Execution Cycle Peripheral Servicing Cycle

 Loading...
Loading...











