User Manual Chapter 1
GFK-2749A Jan 2020
PSM Module Description and Specifications 8
1.8.1 Autonomous Operation
The PSM is a semi-autonomous module running on the RX3i backplane. If the PLC goes to
Stop Mode, or the CPU is lost due to over temperature or a watchdog timeout, the PSM
continues to operate with the last directive received from the CPU. If the CPU had requested
the synchronization of Grid 1 and Grid 2, when all sync parameters are met, the PSM will
assert RelayCloseOK and close its relay output contacts, even when the PLC is in Stop Mode.
Care must be taken to leave the Sync request in a known state when transitioning to stop
mode.
When Grid 1 and Grid 2 are synchronized, the PSM cannot be reset or cleared, and it will not
accept a new hardware configuration from the CPU. Once synchronized, the PSM can only
be cleared in preparation for receiving a new configuration by first commanding the PSM to
release the grid synchronization (simultaneously set %Q offset 16 to 1, and clear %Q offset
32 to 0), or by removing power from the PSM module. Mission Critical applications must
have a redundant PSM system to take over the grid synchronization from the Primary PSM
if the primary controller can no longer perform its function.
1.8.2 Frequency Measurement
Healthy three-phase power systems produce three almost identical sinusoidal voltage
waveforms that swing from positive to negative voltage at a frequency of either 50 or 60
times per second (50–60Hz).
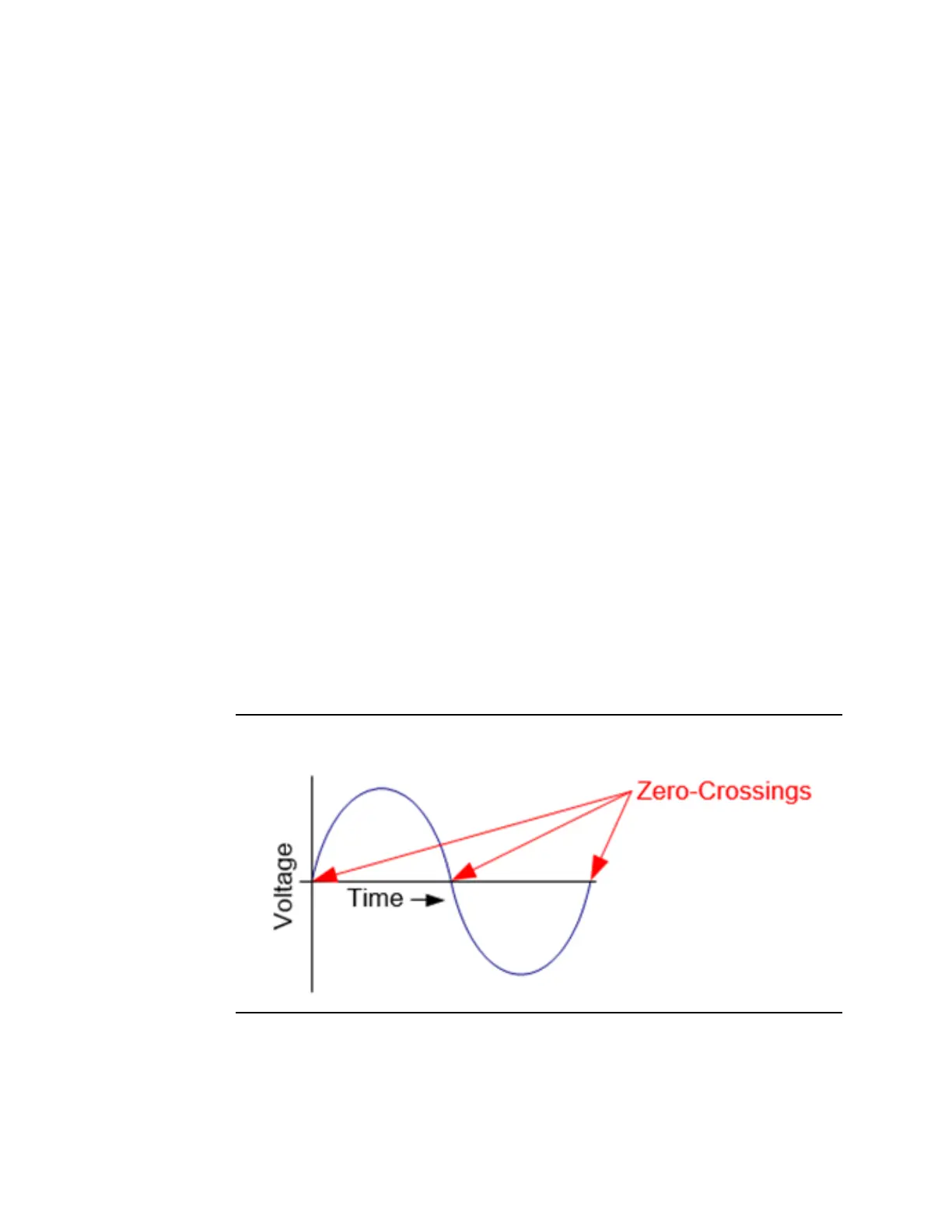
The PSM determines the frequency of the power line by looking for the zero crossings, which
are places where the voltage crosses zero volts going from positive to negative or from
negative to positive. Only phase A voltages are used for the zero-crossing detection, so
phase A must be always present on one or the other grid.
Figure 4
 Loading...
Loading...