5.0/5.7/6.0L/8.1L ECM and Sensors 2 - 7
MEFI 4 - PCM
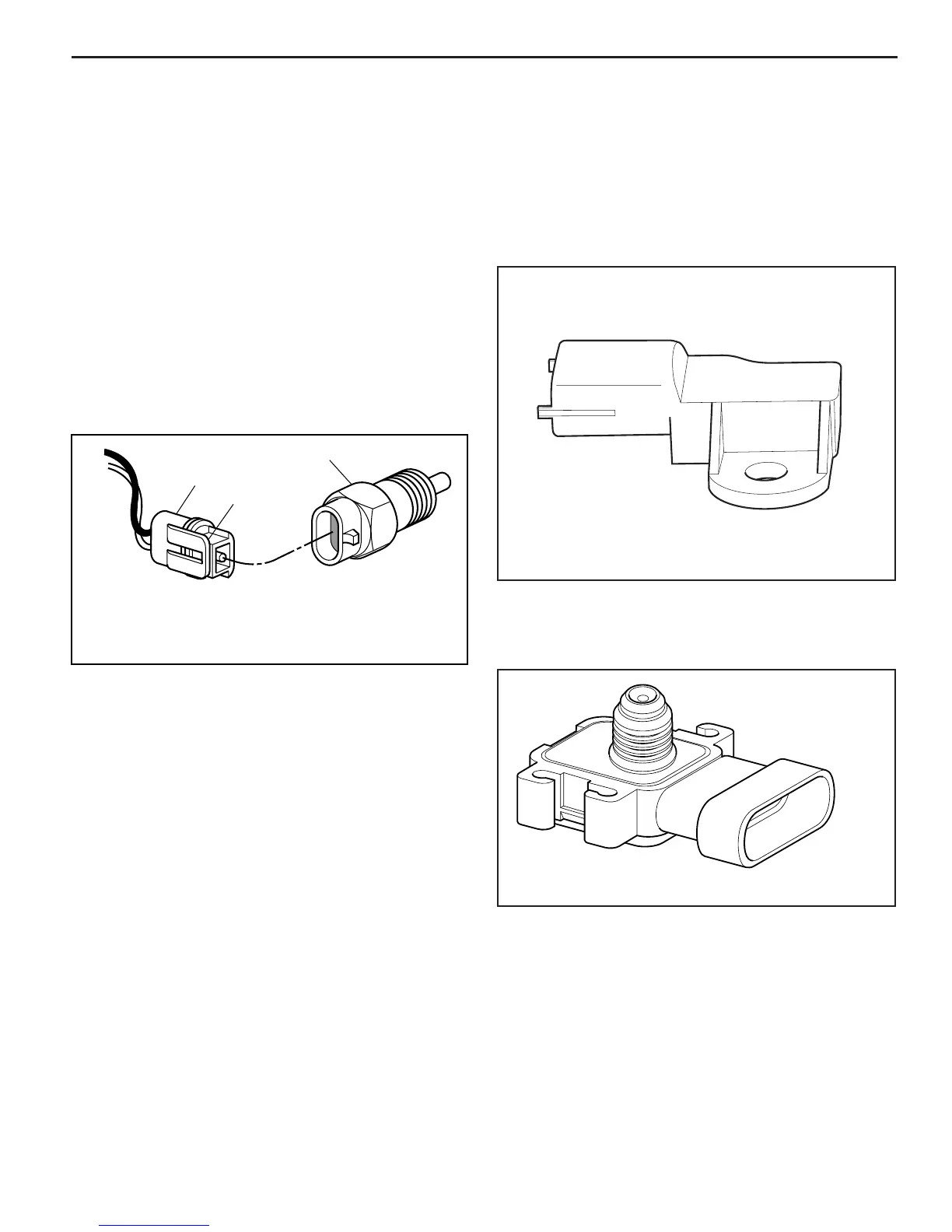
Figure 2-6 - Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
1HARNESS CONNECTOR
2LOCKING TAB
3SENSOR
8-24-94
RS 22189
1
2
3
Figure 2-7 - Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor/
Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
(Used On 5.0/5.7L Engines)
Figure 2-8 - Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
(Used On 6.0/8.1L Engines)
I 22312
The ECM supplies a 5 volt reference voltage to the MAP
sensor. As the manifold pressure changes, the electrical
resistance of the MAP sensor also changes. By monitoring
the sensor output voltage, the ECM knows the manifold
pressure. A higher pressure, low vacuum (high voltage)
requires more fuel. A lower pressure, high vacuum (low
voltage) requires less fuel. The ECM uses the MAP sensor
to control fuel delivery and ignition timing. A failure in the
MAP sensor circuit should set a DTC 33 or DTC 34.
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
The Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor is a
pressure transducer that measures the changes in the
intake manifold pressure. The pressure changes as a result
of engine load and speed change, and the MAP sensor
converts this into a voltage output.
A closed throttle on engine coastdown would produce
a relatively low MAP output voltage, while a wide open
throttle would produce a high MAP output voltage. This
high output voltage is produced because the pressure
inside the manifold is almost the same as outside the
manifold, so you measure almost 100% of outside air
pressure. MAP is the opposite of what you would measure
on a vacuum gauge. When manifold pressure is high,
vacuum is low, causing a high MAP output voltage.
The MAP sensor is also used to measure barometric
pressure under certain conditions, which allows the ECM
to automatically adjust for different altitudes.
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
The engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor is a
thermistor (a resistor which changes value based on
temperature) mounted in the engine coolant stream. Low
coolant temperature produces a high resistance (100,000
ohms at -40°C/-40°F) while high temperature causes low
resistance (70 ohms at 130°C/266°F).
The ECM supplies a 5 volt signal to the ECT sensor
through a resistor in the ECM and measures the voltage.
The voltage will be high when the engine is cold, and low
when the engine is hot. By measuring the voltage, the ECM
calculates the engine coolant temperature. Engine coolant
temperature affects most systems the ECM controls.
A hard fault in the engine coolant sensor circuit should
set DTC 14 or DTC 15; an intermittent fault may or may
not set a DTC. The DTC “Diagnostic Aids” also contains
a chart to check for sensor resistance values relative
to temperature.
 Loading...
Loading...