7.2.1 Standard Diaphragm Replacement
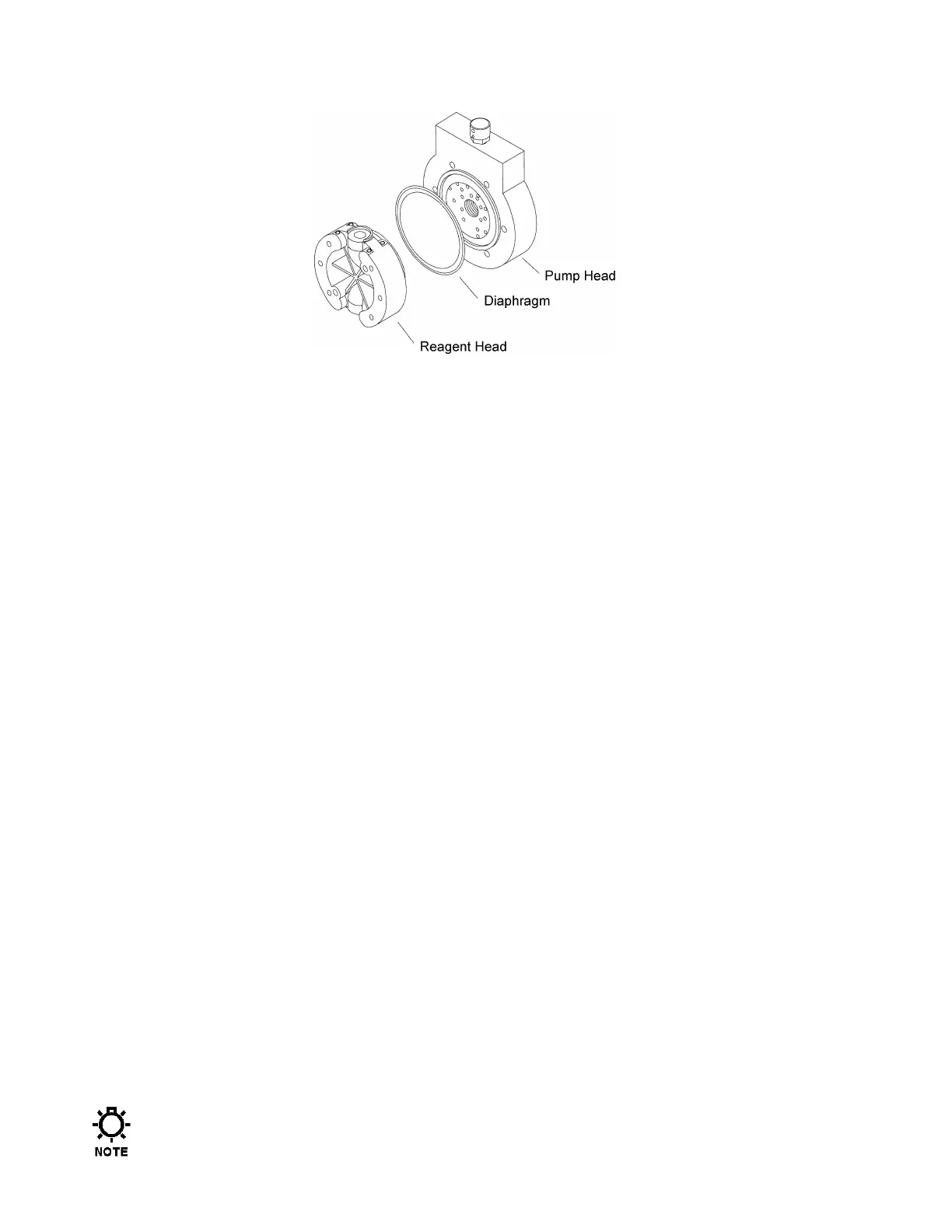
Figure 14
PULSAR diaphragms do not have a specific cycle life; however, the accumulation of foreign
material or the entrapment of sharp particles between the diaphragm and dish cavity can
eventually cause failure. Failure can also occur as a result of hydraulic system malfunction or
chemical attack. Periodic diaphragm inspection and replacement are recommended.
Diaphragm Replacement Procedure:
1. Disconnect the power source to the drive motor
2. Relieve all pressure from the piping system.
3. Take all precautions to prevent environmental and personnel exposure to hazardous
materials.
4. Close the inlet and outlet shutoff valves.
5. Place a suitable container underneath the pump head to catch any liquid leakage.
6. Disconnect piping to the reagent head and drain any process liquid, following material safety
precautions described.
7. Remove all but one top reagent head bolt. Oil will leak out between the pump head and
reagent head as the bolts are loosened.
8. Tilt the head and pour out any liquids retained by the check valves into a suitable container,
continuing to follow safety precautions as appropriate.
9. Remove the final bolt and rinse or clean the reagent head with an appropriate material.
10. Remove and inspect the diaphragm. It may have taken a permanent convex/concave set as
a result of normal flexure and conformance to the dishplate. This condition is normal and is
not cause for replacement. The diaphragm must be replaced if it is deformed, dimpled, or
obviously damaged.
11. To install a diaphragm, first ensure that the critical sealing areas of diaphragm, reagent
head, and pump head are clean and free of debris. Set the diaphragm in place on the
reagent head and ensure seating of the diaphragm sealing ring into the mating groove in the
reagent head.
12. Install the reagent head bolts and tighten in an alternating pattern to ensure an even seating
force. Torque to the values recommended in Appendix IV.
13. Re-prime the pump head, see Section 7.2.2.
When reinstalling a used diaphragm, it is not necessary to maintain the previous
orientation relative to the reagent head or pump head hole pattern.
 Loading...
Loading...