32 RD1000™ Operation Manual
Section 4 Surveying Techniques
4.1 Cross and mark
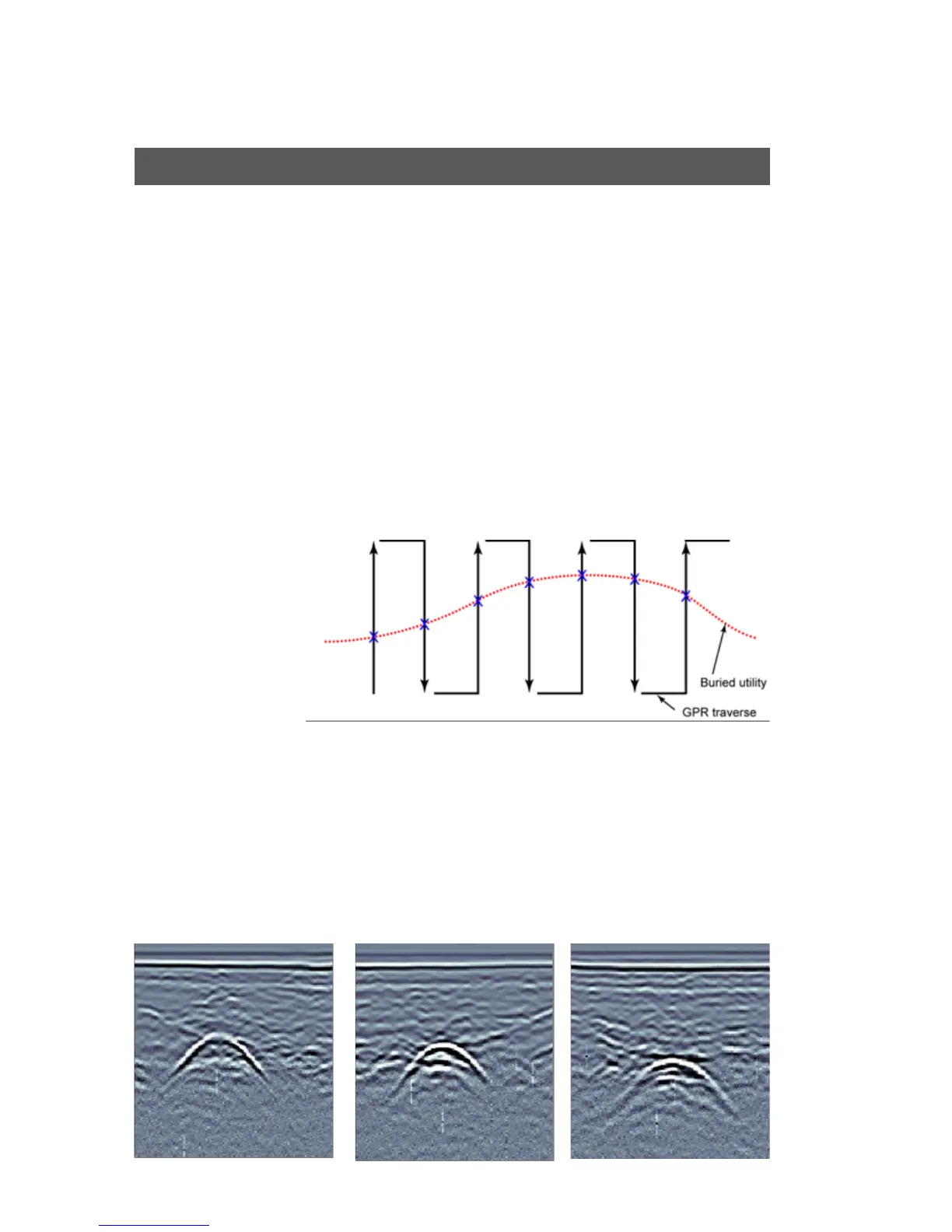
The most common method of locating is cross and mark as you
go. This method works well in favourable soils and uncluttered
settings. Cross and mark is very similar to the use of traditional
current tracking utility detectors. The Cart is moved along sweeps
perpendicular to the anticipated utility axis (see figure below). When
the GPR sensor crosses the utility, the image shows an arch. The
top of the arch is the position of the utility. The depth to the top of
the arch is an estimated depth.
By moving the GPR back and forth and marking the ground where
the top of the arch is observed, the alignment of the subsurface
utility can be traced out as the X’s in the figure indicate.
For example, a concrete storm sewer alignment was located under
the road in the figure and data images of lines 1, 2 and 3 below.
The target arch visible on each scan clearly identifies the pipe
alignment.
Figure 4.1:
cross and mark
surveying
Figure 4.2: locating a concrete pipe
 Loading...
Loading...