201.028 REV 1 Date of Issue: 18 June 2018
2 Low Pressure, Off-Line Operation
Figure 6.9 CMS working pressure generated by hydraulic component
3 Very Low Flow Systems
Figure 6.10 Entire system flow rate is within the range of the CMS
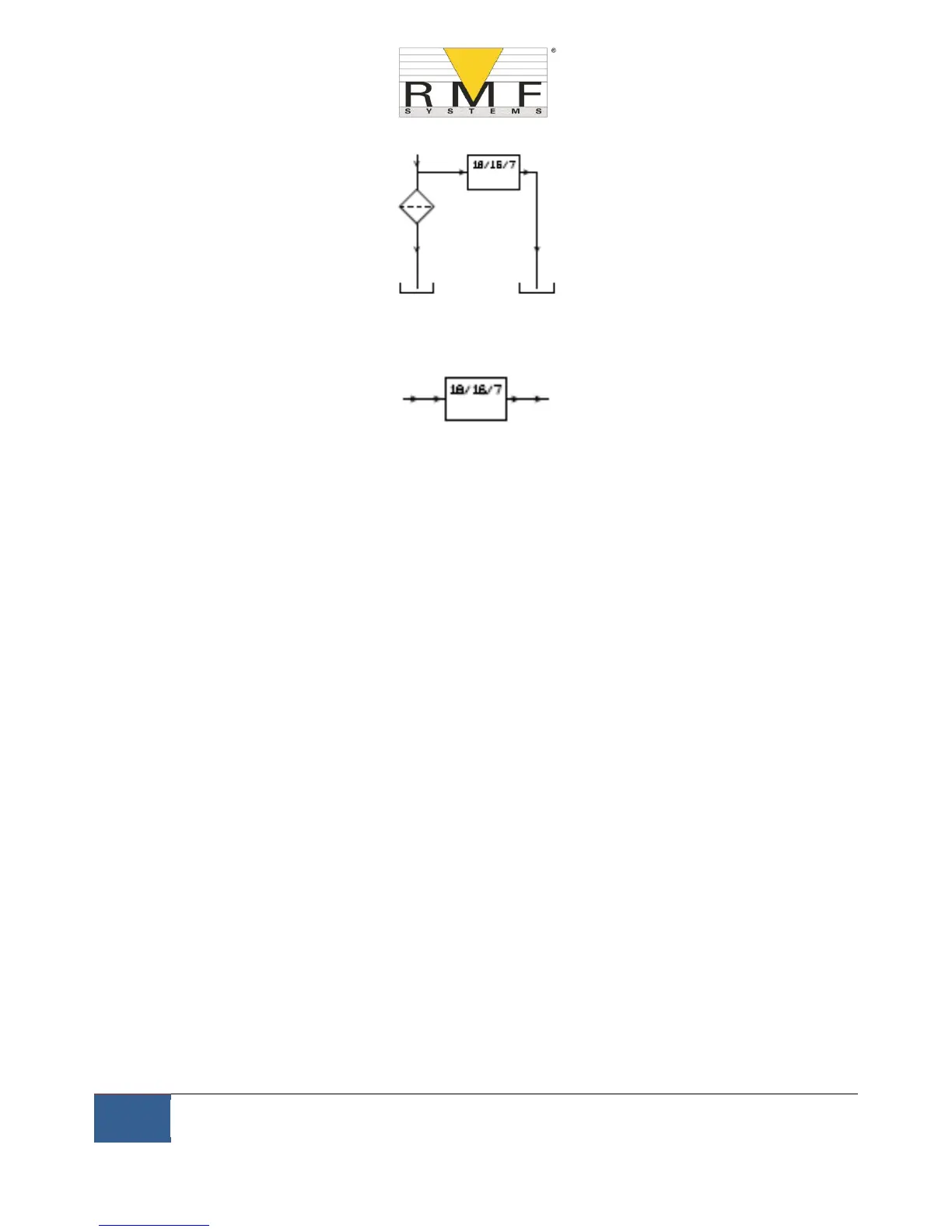
6.1.3.1 Flow Rate
For the majority of systems, a differential pressure of a few Bar will generate an in-range flow for a CMS
connected using two 1.5 meter lengths of microbore pressure hose. The required differential pressure can be
obtained by taking advantage of an existing pressure drop within the system. Alternatively one can be created by
inserting a check valve. The CMS can then be connected across this differential pressure source.
6.1.3.1.1 Detailed Calculations
In general the flow rate of fluid through the CMS needs to be kept within the range of the unit (see hydraulic
specification 3.2). The CMS measures the flow during operation, so this can be used to check that the flow is
correct.
A flow that is out of range will be indicated by a fault code (see section 7.2).
Note: Results taken with out-of-range flows are not logged.
The flow is entirely generated by the differential pressure between the ends of the pipes used to connect the
CMS. The pressure needed to generate an in-range flow can be estimated by assuming a target flow, and
determining the resulting pressure drop across the CMS and connection piping. Use Figure 6.10 on page 24 to
lookup the CMS pressure drop, and manufacturers’ data to lookup the piping pressure drop at the desired flow.
The sum of these two pressures is the pressure needed.
The user connects the CMS between two points in the hydraulic circuit that have this pressure difference.
In order to use the graph:
− Determine the working viscosity of the fluid, e.g. 30 cSt
− Decide on a desired flow rate. 200ml/minute is normally used since this is in the middle of the CMS flow
range. But 100ml/minute is also suitable and uses less oil
 Loading...
Loading...