76 Rockwell Automation Publication 750-RM100A-EN-P - August 2019
Chapter 9 Reference Motion Planners
Note the following relationships:
• Acceleration Limiting trades maximum jerk for lower maximum
acceleration
• Acceleration Limiting automatically induces acceleration dwells with
smooth transitions, which extends the move time
• Acceleration Limiting does not affect energy directly
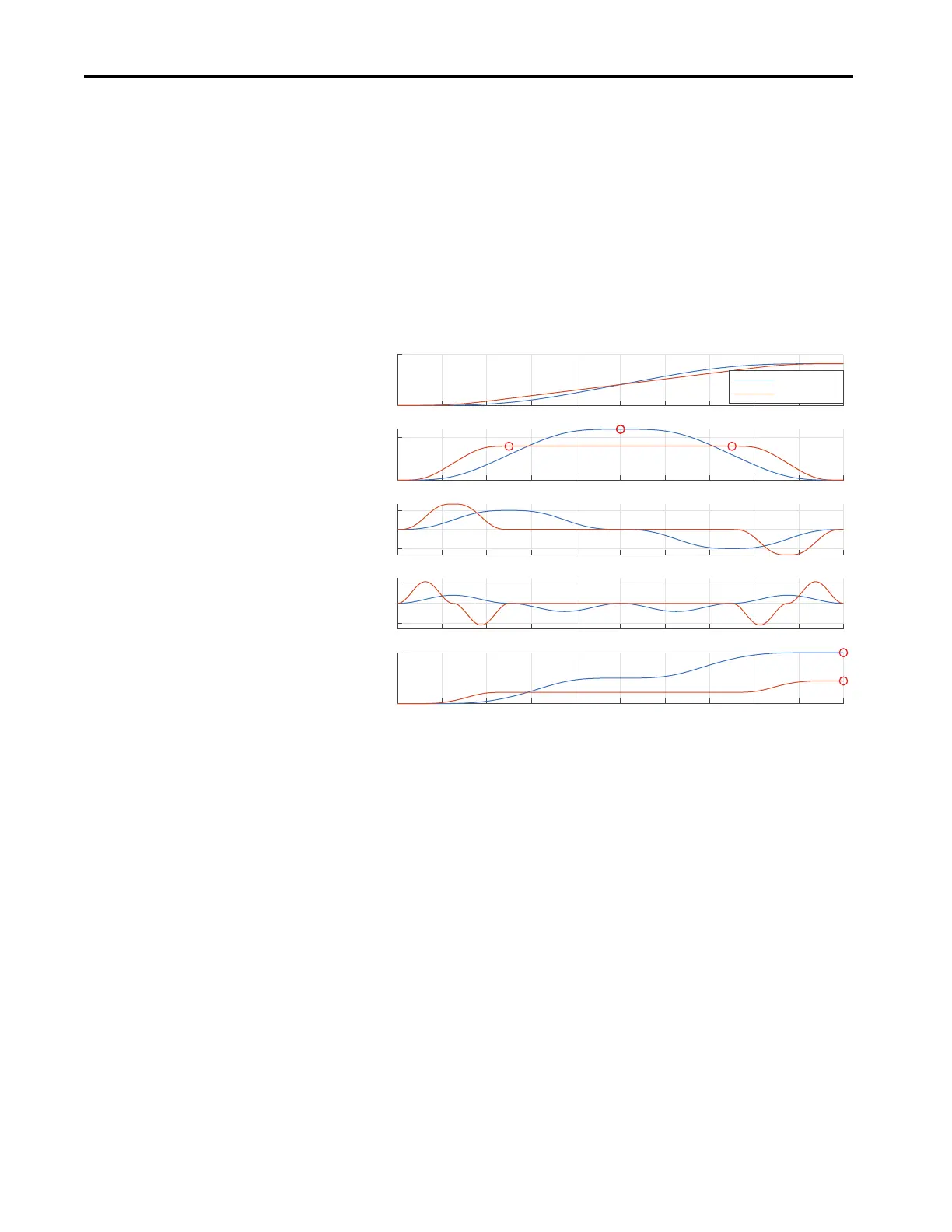
The following example shows what happens when velocity limits are lowered below what
is required by an unconstrained move with adjusted acceleration and deceleration times.
Figure 23 - Velocity Limiting with Adjusted Times
Note the following relationships:
• Velocity Limiting trades maximum acceleration and jerk for lower
maximum velocity and energy
• Velocity Limiting automatically induces a velocity dwell with a smooth
transition, which extends the move time
• Velocity Limiting affects energy directly
The following example shows the effect of Energy Balance.
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2
0
5000
Not Limitied
Vel Lim = 40
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2
0
50
Vel
[RPM]
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2
-2
0
2
Accel
[rev/sec
2
]
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2
-20
0
20
Jerk
[rev/sec
3
]
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2

 Loading...
Loading...
















