Storage Concept and Startup Types
8.1 Overview of the memory concept of S7-400 CPUs
S7-400 Automation System, CPU Specifications
8-2 Manual, 10/2006, 6ES7498-8AA04-8BA0
Important note for CPUs with selectable allocation of the work memory
If you change the work memory allocation by modifying parameters, this work memory is
reorganized when you load system data into the CPU. The result of this is that data blocks
that were created with SFC are deleted, and the remaining data blocks are assigned initial
values from the load memory.
The usable size of the working memory for logic or data blocks is changed when loading the
system data if you change the following parameters:
● Size of the process image (byte-oriented; in the "Cycle/Clock Memory" tab)
● Communication resources (S7-400 only; "Memory" tab)
● Size of the diagnostic buffer ("Diagnostics/Clock" tab)
● Number of local data for all priority classes ("Memory" tab)
Basis for Calculating the Required Working Memory
To ensure that you do not exceed the available amount of working memory on the CPU, you
must take into consideration the following memory requirements when assigning parameters:
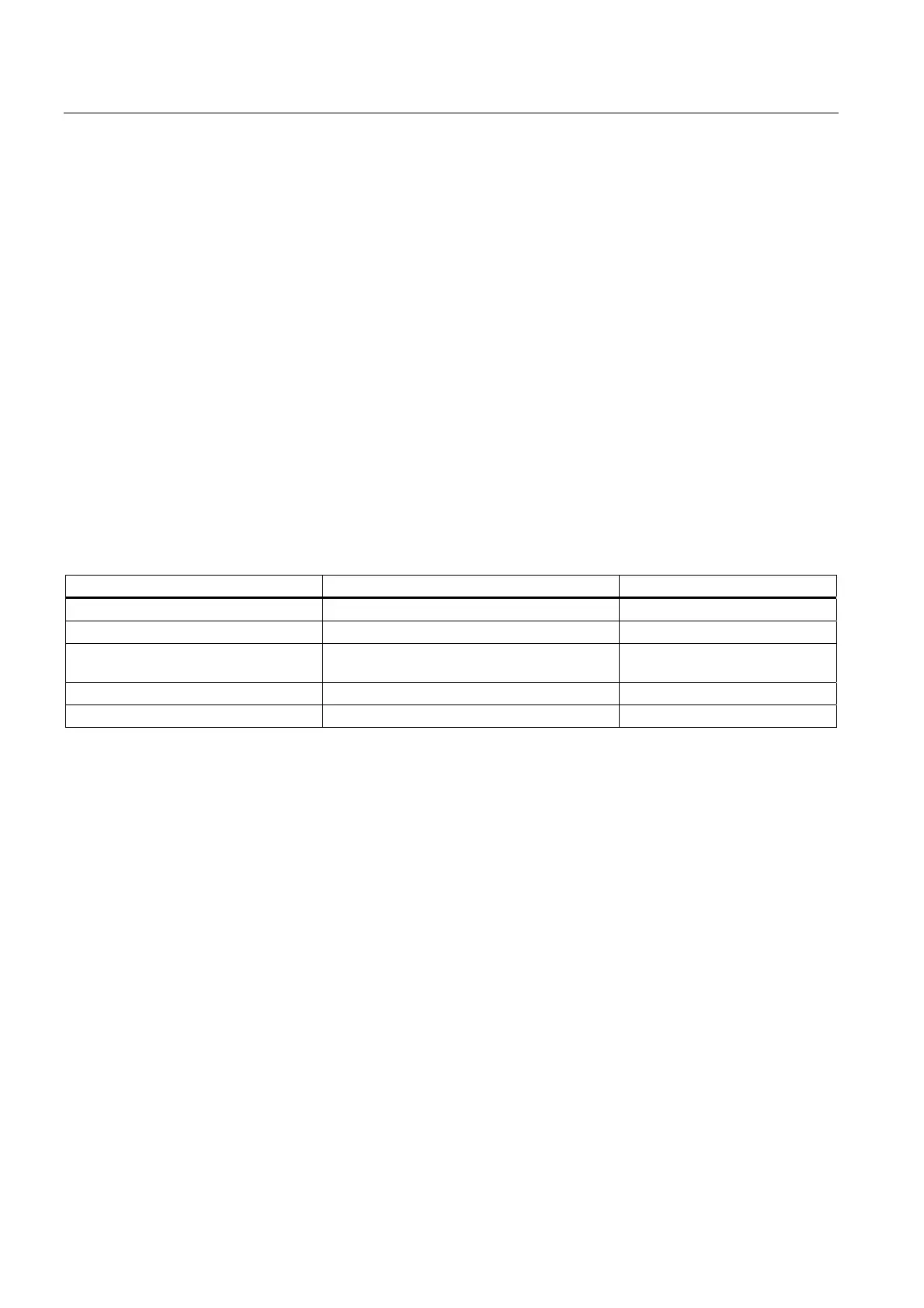
Table 8-1 Memory requirements
Parameters Required working memory In code/data memory
Size of the process image (inputs) 12 bytes per byte in the process input image Code memory
Size of the process image (outputs) 12 bytes per byte in the process output image Code memory
Communication resources
(communication jobs)
72 bytes per communication job Code memory
Size of the diagnostic buffer 32 bytes per entry in the diagnostic buffer Code memory
Quantity of local data 1 byte per byte of local data Data memory
Memory Types in S7-400 CPUs
● Load memory for project data, such as blocks, configuration and parameter assignment
data, including symbols and comments as of version 5.1.
● Work memory for the runtime-relevant blocks (logic blocks and data blocks).
● System memory (RAM) contains the memory elements that each CPU makes available to
the user program, such as bit memory, timers and counters. System memory also
contains the block stack

 Loading...
Loading...




















