Setting Example
General
The following examples describe the most important settings for the protection of explosion-proof motors
with type of protection increased safety e.
Motor Data
Take the following motor data as an example:
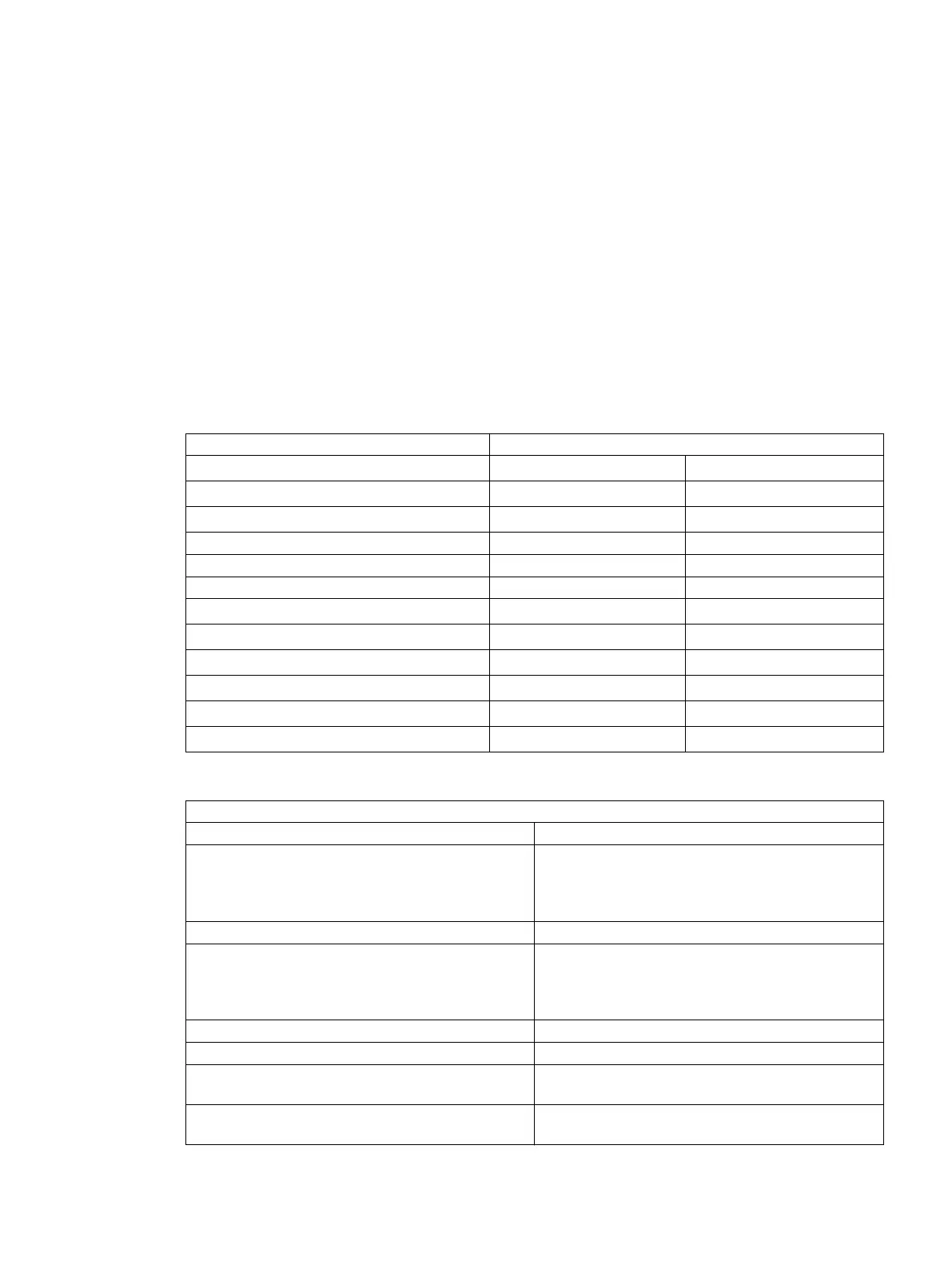
Type of motor Explosion-proof motor
Rated power P
rated, motor
1400 kW
Rated voltage V
rated, motor
6 kV
Rated current I
rated, motor
160 A
Power factor cosφ 0.84
Frequency f 50 Hz
Speed n 2980 r/min
Starting current/motor rated current I/I
rated, motor
5.2
Locked-rotor time t
E
8.2 s
Primary transformer rated current I
rated, CTprim
200 A
Permissible number of cold starts n
cold
2
Permissible number of warm starts n
warm
1
Transformation ratio Ratio
Tr
200/1
Step 1: Motor Differential Protection
I-DIFF
(_:11041:3) Threshold = 0.20 I/IrObj The pickup threshold for the differential current
(_:11041:100) Slope 1 = 0.30 The slope value 1 to avoid the overfunction of the
differential protection with external low-current faults
as a consequence of current-transformer transmission
faults
(_:11041:101) Intersection 1 Irest = 0.67 I/IrObj The restraint current 1
(_:11041:102) Slope 2 = 0.70 The slope value 2 to avoid the overfunction of the
differential protection with external high-current
faults as a consequence of current-transformer trans-
mission faults
(_:11041:103) Intersection 2 Irest = 2.50 I/IrObj The restraint current 2 from which the slope 2 begins
(_:11041:108) Factor increasing char. = 2.0 The factor to increase the threshold and the slope 1
(_:11041:110) Factor increasing char. DC = 2.3 The factor to increase the threshold and the slope 1
caused by the DC components
(_:11041:128) Threshold add-on stabiliz. = 2.00 I/
IrObj
The pickup threshold for the additional stabilization
4
SIPROTEC 5, Additional Information on the Protection of Explosion-Proof Motors with Type of Protection Increased Safety e,
Manual
25
C53000-H5050-C078-1, Edition 03.2019

 Loading...
Loading...











