2.4 Time Overcurrent Protection for Phase and Residual Currents
159
7UT613/63x Manual
C53000-G1176-C160-2
Overcurrent Protection“. The alternative pickup values themselves can be set for each
of the stages of the time overcurrent protection.
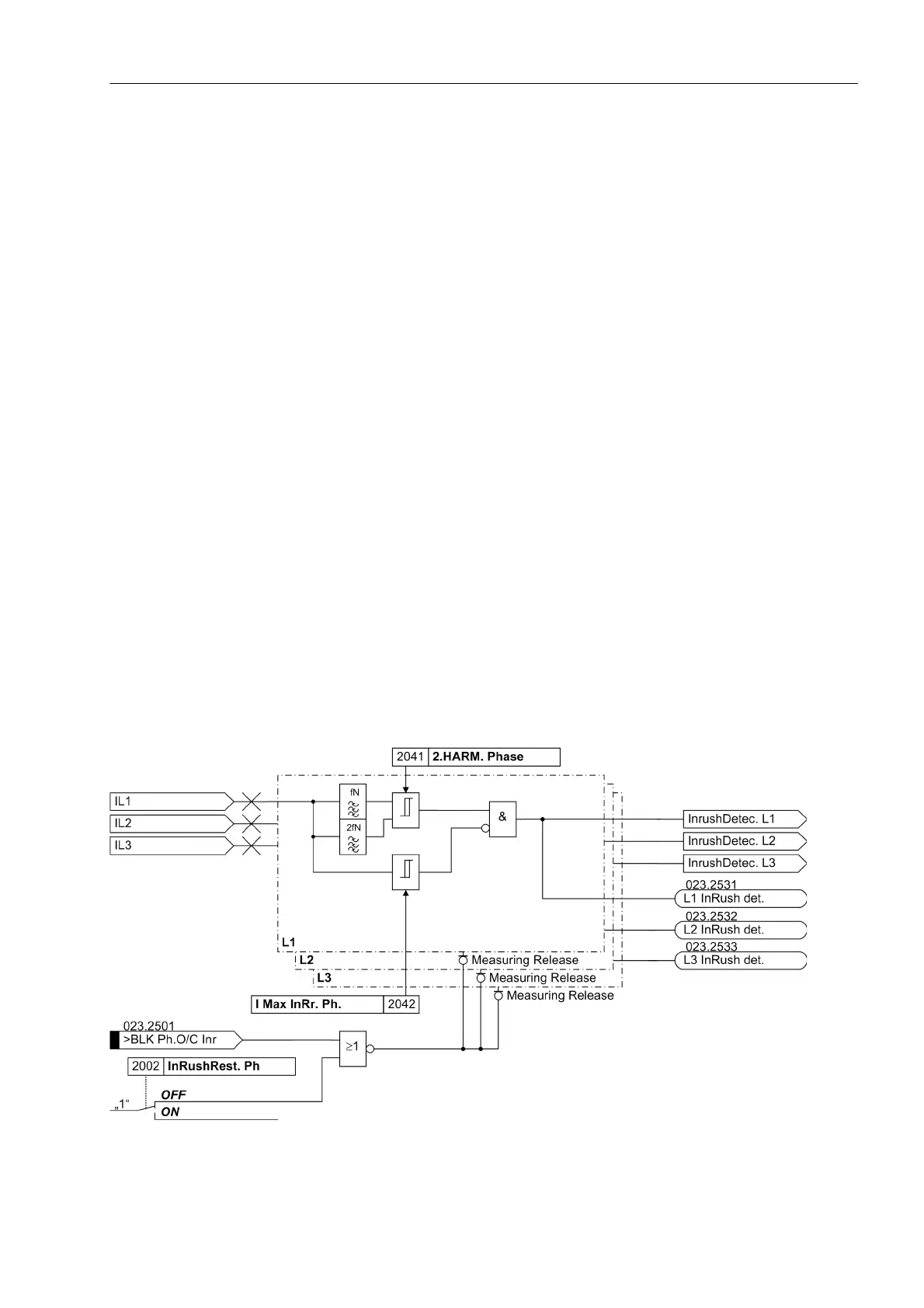
2.4.1.5 Inrush Restraint
When switching unloaded transformers or shunt reactors on a live busbar, high mag-
netising (inrush) currents may occur. These inrush currents may be several times the
nominal current, and, depending on the size and design of the transformer, may last
from several ten milliseconds to several seconds.
Although overcurrent detection is based only on the fundamental harmonic compo-
nent of the measured currents, false pickup due to inrush might occur since the inrush
current may even contain a considerable component of fundamental harmonic.
The time overcurrent protection provides an integrated inrush restraint function This
blocks the „normal“ pickup of the I> or I
p
stages (not I>>) for phase and residual cur-
rents in cash of inrush detection. After detection of inrush currents above a pickup
value special inrush signals are generated. These signals also initiate fault annuncia-
tions and start the assigned trip delay time. If inrush current is still detected after expi-
ration of the delay time, an annunciation is output only reporting that time elapsed but
tripping is suppressed.
The inrush current is characterised by a considerable 2nd harmonic content (double
rated frequency) which is practically absent in the case of a short-circuit. If the second
harmonic content of a phase current exceeds a selectable threshold, trip is blocked for
this phase. The same applies to the zero sequence current.
The inrush restraint has an upper limit: if a certain (adjustable) current value is exceed-
ed, it will no longer be effective, since there must be an internal current-intensive short-
circuit. The lower limit is the operating limit of the harmonic filter (0.1 I
N
).
Figure 2-72 shows a simplified logic diagram.
Figure 2-72 Logic diagram of the inrush restraint feature — example for phase currents (simplified)
 Loading...
Loading...











