The area number is specified by bits An, the row number within an area by bits Rn, the
pixel line number within a row by bits Ln and the column number by bits Cn. It can be
seen that the lower 8 bits are identical between the display file and the attributes file,
and this approach was used since it simplified the picture generation logic inside the
ULA. Note that the A0 and A1 bits never both hold a value of 1, and thus the display
file and the attributes file can never overlap.
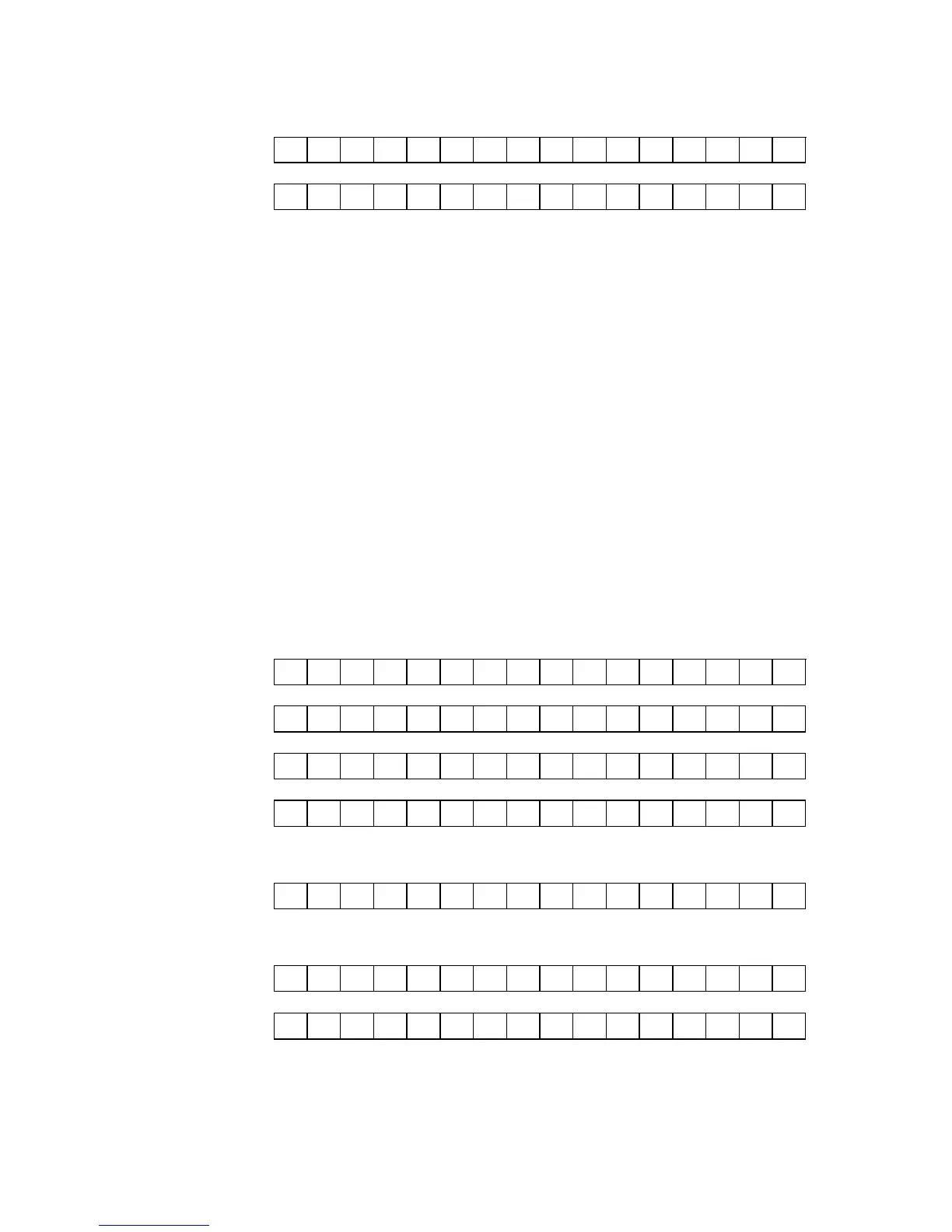
The new attribute modes provided by the SPECTRA interface use an addressing
scheme for the display file that is identical to that used by the standard Spectrum
screen. However, the addressing schemes used for the various display mode attribute
files are different. A relationship between them and the display file can be seen by
examining address lines A8 to A12, which shift by one bit position to the left each time
the vertical colour resolution is doubled. It becomes clear that although the standard
attributes file (row mode) visually appears to be a logical progression, it can actually be
thought of as an extreme case of the ‘odd’ sequence seen in the display file. The
addressing schemes for the new attribute modes are shown below.
 Loading...
Loading...