1 System integration
The LPS22HB/LPS25HB pressure and temperature sensors' integration in application
systems such as portable devices like smartphones, wearable devices, weather stations or
industrial equipments shall be implemented without compromising the sensor
performances. The system integration can be done by looking at the main mechanical and
geometrical parameters and the factors that influence the sensor performance and thus
optimizing those.
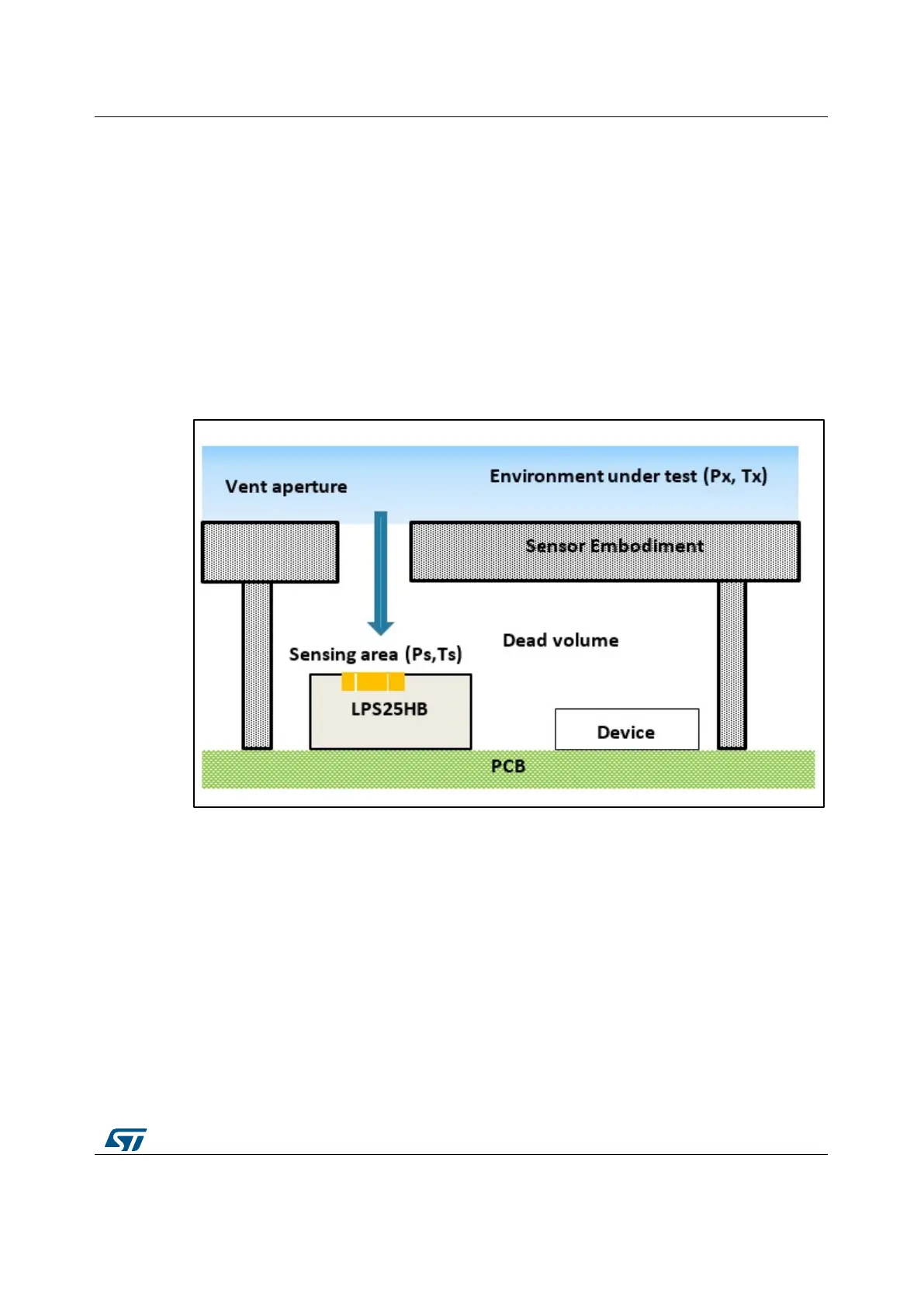
The typical sensor integration scenario is described in Figure 1: "Pressure sensor system
integration" where the embodiment of the sensor has to be designed in order to get as
much as possible the correspondence between the pressure (Px) and temperature (Tx)
conditions of the environment under test, and (Ps, Ts) that represent the conditions around
the sensor sensing area, nearby the air inlet houses.
Figure 1: Pressure sensor system integration
Therefore, in order to get a reliable and consistent measurement, all the parameters
involved in the mechanical design must be dimensioned to get the maximum sensor
exposition to the external environment, to get a faster response time, in terms of pressure
and temperature, compatible with the required design specifications.
Every change in the condition under test must be reflected as a sensor consistent
measurement, also in the case of fast pressure and temperature variations. Therefore, the
integration design must guarantee the environment conditions matching with the sensing
area conditions not only in “steady-state” (static conditions) but also in dynamic conditions.
Deviations between the conditions under test and the conditions around the sensing area
are also influenced by heating sources, like other devices close the sensing area, the self-
heating of the sensor. Changes in temperature are critical because not only the
temperature is influenced but, changes in temperature will also determine pressure
deviations and, as a consequence, a slower response of the system.

 Loading...
Loading...