From a physical point of view, these local sources act like a thermal capacitor placed in
parallel to the thermal model of the LPS25HB and they can give a contribution to the local
temperature that is different from the environmental one.
Depending on the heat sources location and the heating mechanism propagation, we can
distinguish the propagation related to different mechanisms as described below.
Heating convection
Local thermal sources around the sensor can modify the pressure and temperature
measurement by heating radiation.
Typical sources are as follows:
other sensors and devices like close the pressure sensor
power management devices
processors and microcontrollers
LCD displays that, in particular provide a significant temperature gradient between the
environment and the dead volume inside the system
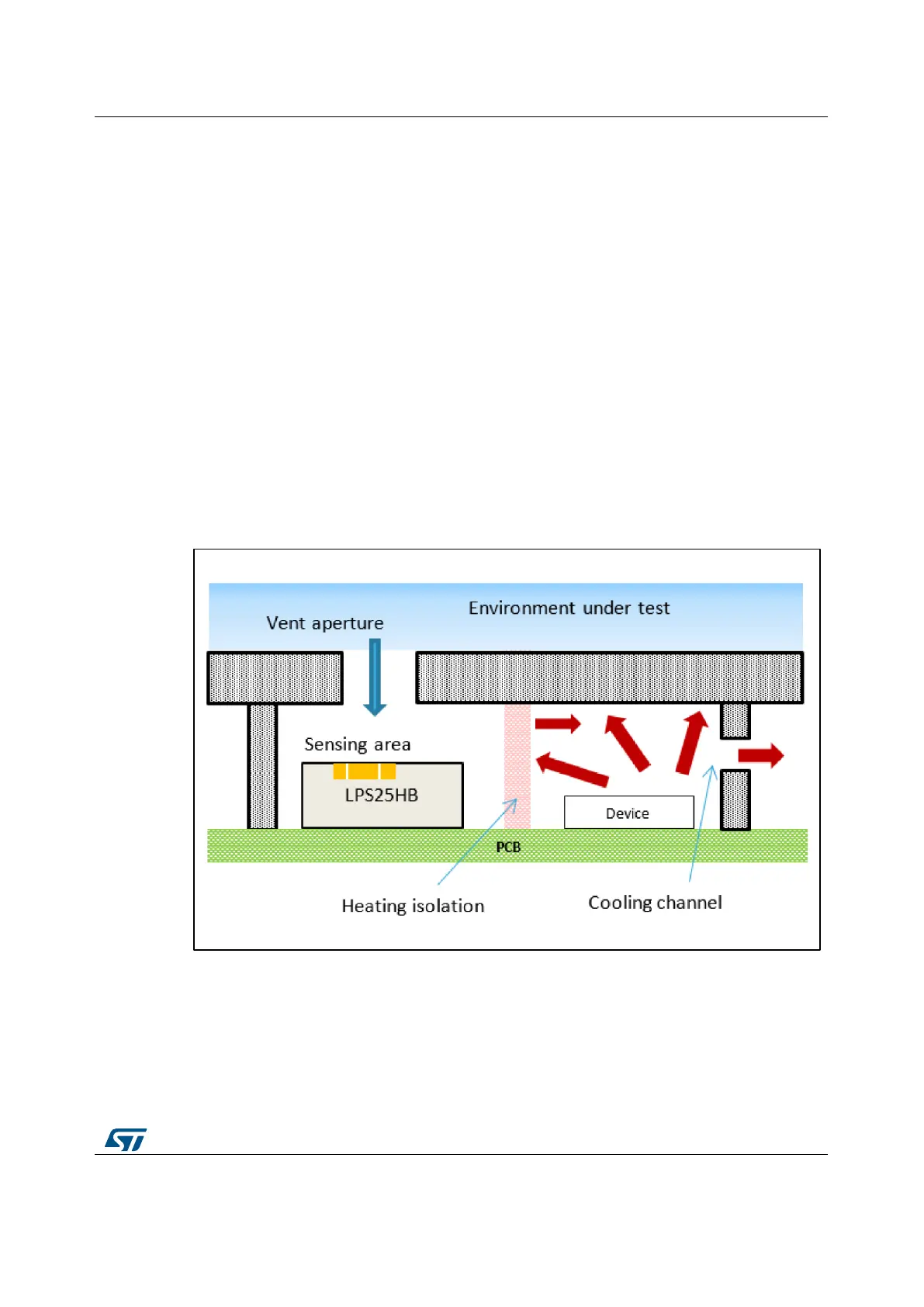
Therefore the sensor has to be placed at the correct distance from these sources, and to
guarantee the appropriate isolation, it is recommended to adopt inside the embodiment,
heating isolation structures as described in Figure 4: "Heating isolation implemented for
protecting the sensor". It also suggested, according to the specific layout to implement as
well vent aperture close the heat source, acting as cooling channels.
Figure 4: Heating isolation implemented for protecting the sensor
Looking at a section of the sensor housing, Figure 5: "Top view of the sensor housing: on
the left a correct design with the heat isolation, on the right a wrong design" shows a good
design with the heating isolation structure on the left; the heat source is far from the sensor
and a thermal protection structure is placed in the middle. On the right, a wrong design is
described, determining the sensor heating because of the heat radiation coming from the
component nearby.

 Loading...
Loading...