4 5
1. Safety Precautions and Warnings 2. General Information
To prevent personal injury or damage
to vehicles and the scan tool,read
this user manual first carefully
and observe the following safety
Precautions at a minimum whenever
working on a vehicle:
Always perform automotive testing in a safe
environment.
Do not attempt to operate or observe the tool
while driving a vehicle. Operating or observing
the tool will cause driver distraction and could
cause a fatal accident.
Wear safety eye protection.
Keep clothing,hair,hands,tools,test
equipment,etc. Away from all moving or hot
engine parts.
Operate the vehicle in a well-ventilated work
area: Exhaust gases are poisonous.
Put blocks in front of the drive wheels and
never leave the vehicle Unattended while
running tests.
Use extreme caution when working around
1iie ignition coil,distributor cap,ignition wires
and spark plugs. These components create
hazardous voltages when the engine is
running.
Put the transmission in P(for A/T)or N(for M/T)
and make sure the parking brake is engaged.
Keep a fire extinguisher suitable for gasoline/
chemical/electrical fires nearby.
Don’t connect or disconnect any test
equipment while the ignition is on or the
engine is running.
Keep the scan tool dry,clean,free from oil/
water or grease. Use a mild detergent on a
clean cloth to clean the outside of the scan
tool when necessary.
2.1 On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) II
The OBD II system is designed to monitor
emission control systems and Key engine
components by performing either continuous
or periodic Tests of specific components
and vehicle conditions. When a problem
is detected,the OBD II system turns on a
warning lamp(MIL)on the Vehicle instrument
panel to alert the driver typically by the
phrase Of “Check Engine” or “Service Engine
Soon”. The system will also Store important
information about the detected malfunction
so follow Three pieces of such valuable
information.
1) Whether the Malfunction Indicator Light
(MIL) is commanded “on” Or “off”
2) Which,if any, Diagnostic Trouble Codes
(DTCs) are stored;
3) Readiness Monitor Status.
2.2 Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
OBD n Diagnostic Trouble Codes are codes
that are stored by the On-Board computer
diagnostic system in response to a problem
found In the vehicle. These codes identify a
particular problem area and Are intended to
provide you with a guide as to where a fault
might Be occurring within a vehicle.OBD n
Diagnostic Trouble Codes Consists of a five-
digit alphanumeric code. The first character,a
Letter,identifies which control system sets
the code. The other Four characters,all
numbers,provide additional information on
Where the DTC originated and the operating
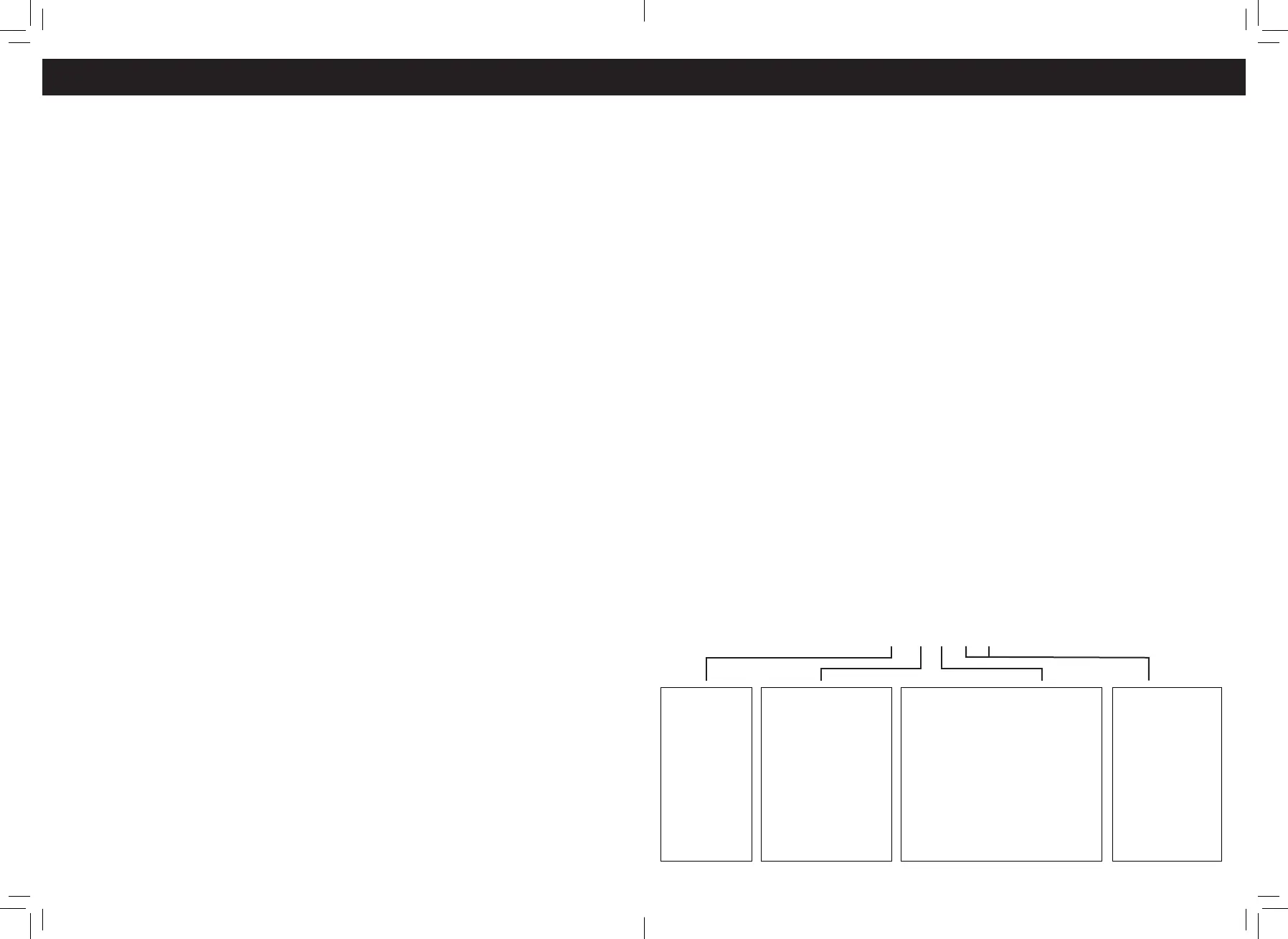
conditions that caused It to set. Here below
is an example to illustrate the structure of the
digits.
Systems
B=Body
C=Chassis
P=Powertrain
U=Network
Identify specific
malfunctioning
sections of the
system
Code Type
Generic (SAE):
P0,P2,P34^P39
B0.B3
CO, C3
U0,U3
Manufacturer specific:
PI, P30-P33
B1,B2
C1,C2
U1,U2
Sub-systems
1=Fuel and Air Metering
2=Fuel and Air Metering
3=Ignition System or Engine Misfire
4=Auxiliary Emission Controls
5=Vehicle Speed Control and Idle
Controls
6=Computer Output Circuits
7=Transmission Controls
8=Transmission Controls
DTC EXAMPLE
P0202

 Loading...
Loading...