Page 6.7
Follow the procedure step by step to correctly diagnose the problem. Take particular care with the
checks highlighted by circled numbers, which are described in detail below:
(1) Place the tester probes between the orange (positive) and black (negative) cables on the
alternator. Select the “Manual Training” function on the display and start exercising on the
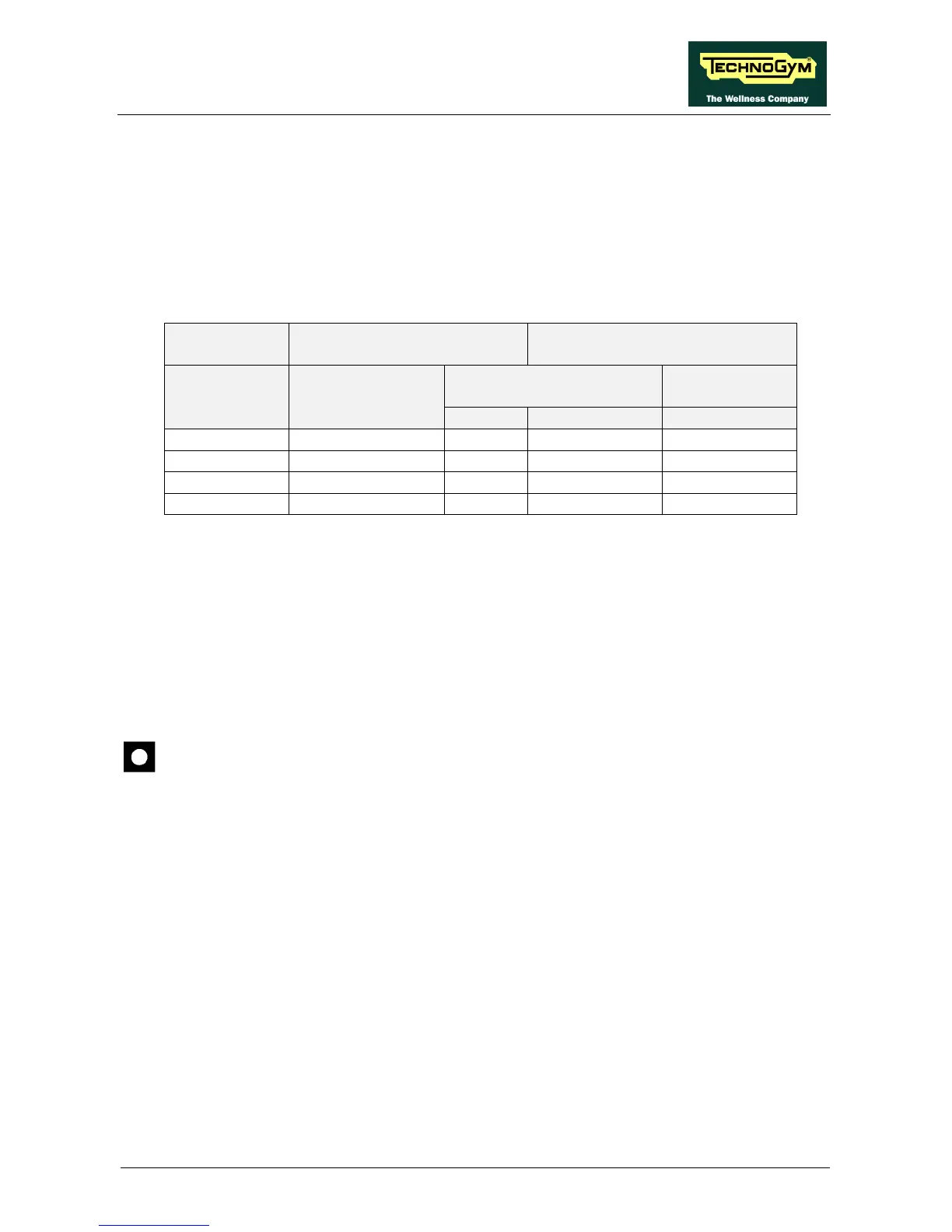
machine. When the level of difficulty is varied, maintaining the speed indicated in Table
6.3-1, the excitation voltage should vary as shown in the same table:
RPM = 70 EXCITATION VOLTAGE
(VDC)
WAVEFORM FREQUENCY
(Hz)
ALTERNATOR
INTERFACE BOARD
CPU BOARD DIFFICULTY
LEVEL
ALTERNATOR
4-5/CN2 6-3/CN1 6-3/CN1
1 1.5 1.5 155 155
3 2.3 2.3 250 250
6 3.2 3.2 360 360
9 4.6 4.6 510 510
Table 6.3-1
The voltages and frequencies quoted above are nominal values.
(2) As for step (2) but with the tester between pins 4 and 5 of connector CN2 on the alternator
interface board.
(3) Disconnect all the cables from the 2 power resistor terminals. Place the tester probes on the 2
terminals and measure the value of the resistance. The correct value for the power resistor is
approximately 0.5 Ω.
BE AWARE: Because all tester probes have a non zero internal resistance, which varies
depending on the model and may be in the same order of magnitude as the quantity
being measured, the following procedure is recommended:
1. Measure the internal resistance of the probes by short-circuiting them with each
other;
2. Measure the resistance of the power resistor.
3. The true resistance value is obtained by subtracting the short-circuit resistance of
the probes from the measured value.
(4) As for step (2) but with an oscilloscope between pins 6 and 3 of connector CN1 on the
alternator interface board.
(5) As for step (2) but with the oscilloscope between pins 6 and 3 of connector CN1 of the display
CPU board.
 Loading...
Loading...