Force known load current
End
ccDelta = ccGain * 1,193,046
Typically 1000 mA
The signs of the variables are very
important. and
should be positive. ccOffset should be
treated as a 16-bit signed integer and
boardOffset should be an 8-bit signed
integer.
current avgRawCurrent
current = forced load current
Obtain CC Offset and Board offset
from DF
Obtain avgRawCurrent
The sign of current should be positive. Raw
current samples are positive in discharge
mode. This ensures that ccGain is positive.
Convert ccGain and ccDelta to
Gauge’s floating point
representation and write to DF
ccGain = current /(avgRawCurrent-(ccOffset + boardOffset) / 16)
Current Calibration
www.ti.com
16
SLUUBH1C–August 2016–Revised March 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2016–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Factory Calibration
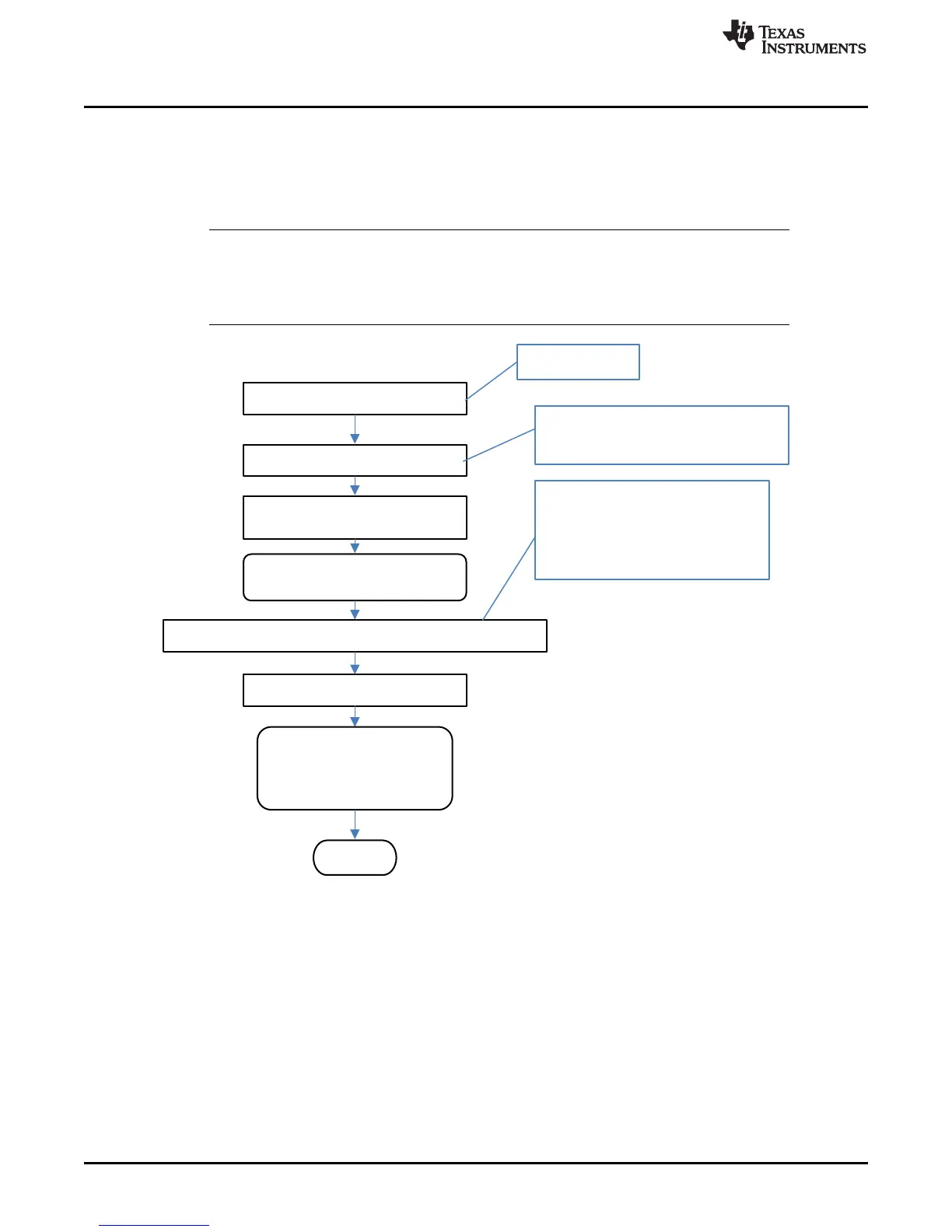
3.8 Current Calibration
CC Gain and CC Delta are two calibration parameters of concern for current calibration. A known load,
typically 1000 mA, is applied to the device during this process. Details on converting the CC Gain and CC
Delta to floating point format are in Floating Point Conversion. The host system must ensure that the fuel
gauge is UNSEALED.
NOTE: The step labeled Obtain avgRawCurrent refers to Section 3.7, Obtain Raw Calibration
Data.
The step labeled Convert ccGain and ccDelta to Gauge’s floating point representation
and write to DF refers to Section 3.10, Floating Point Conversion.
Figure 3-6. Current Calibration Flow
 Loading...
Loading...