val < 0
mod _val = val
False
True
mod_val = val x (-1)
tmpVal = mod _val
False
True
byte2 = tmpVal LHS* of decimal
tmpVal = 2
8
× (tmpVal ± byte2)
False
byte1 = tmpVal LHS* of decimal
True
tmpVal = 2
8
× (tmpVal
± byte1)
decrement exp by 1
byte0 = tmpVal LHS* of decimal
False
True
True
Byte 2 OR with 0x80
False
True
False
rawData[byte0] = exp + 128
rawData[byte1] = byte2
rawData[byte2] = byte1
rawData[byte3] = byte0
exp < í128
End
val = read in value
Create integer, set to 0
exp = 0
tmpVal = tmpVal × (1+2
±25
)
tmpVal < 0.5
tmpVal < 0.5
multiply tmpVal by 2
tmpVal > = 1.0
tmpVal > = 1.0
divide tmpVal by 2
increment exp by 1
exp > 127
exp = 127
Write rawData [0-3] to
corresponding DF location
val < 0
tmpVal = 2
(8 ± exp)
× mod_val ± 128
exp í128
Floating Point Conversion
www.ti.com
18
SLUUBH1C–August 2016–Revised March 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2016–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Factory Calibration
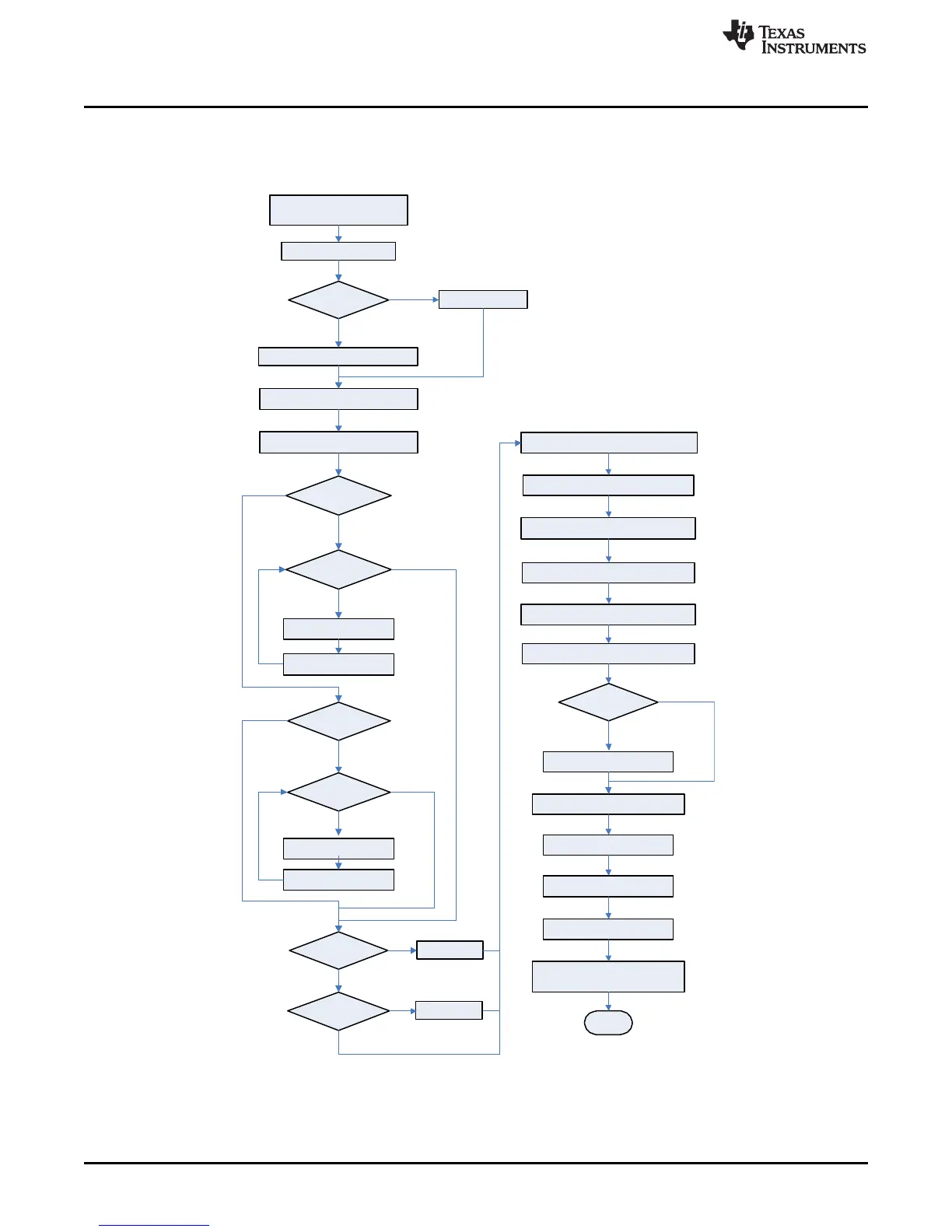
3.10 Floating Point Conversion
This section details how to convert the floating point CC Gain and CC Delta values to the format
recognized by the gauge.
* LHS is an abbreviation for Left-Hand Side. This refers to truncating the floating point value by removing anything to
the right of the decimal point.
Figure 3-8. Floating Point Conversion Flow
 Loading...
Loading...