1
SDA LINE
START
MSB
LSB
1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
WRITE
ACK
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 00
0
00 0
0
ACK
1
RESTART
MSB
0 0 0
LSB
1 0
READ
ACK
ACK
NO ACK
STOP
Device
Address
Address
Pointer, MSB
Address
Pointer, LSB
ACK
Device
Address
DATA BYTE 1 DATA BYTE 2
I
2
C Boot Function
Arbitration, bus busy, and slave signals are not checked. Therefore, no other master is allowed to control
the bus during this initialization phase. If the application requires another master during I
2
C boot mode,
that master must be configured to hold off sending any I
2
C messages until the application software signals
that it is past the bootloader portion of initialization.
The nonacknowledgment bit is checked only during the first message sent to initialize the EEPROM base
address. This is to make sure that an EEPROM is present at address 0x50 before continuing. If an
EEPROM is not present, code will jump to the flash entry point. The nonacknowledgment bit is not
checked during the address phase of the data read messages (I2C_Get Word). If a non acknowledgment
is received during the data read messages, the I
2
C bus will hang. Table 2-7 shows the 8-bit data stream
used by the I
2
C.
Table 2-7. I
2
C 8-Bit Data Stream
Byte Contents
1 LSB: AA (KeyValue for memory width = 8 bits)
2 MSB: 08h (KeyValue for memory width = 8 bits)
3 LSB: I2CPSC[7:0]
4 reserved
5 LSB: I2CCLKH[7:0]
6 MSB: I2CCLKH[15:8]
7 LSB: I2CCLKL[7:0]
8 MSB: I2CCLKL[15:8]
... ...
... ...
17 LSB: Reserved for future use
18 MSB: Reserved for future use
19 LSB: Upper half of entry point PC
20 MSB: Upper half of entry point PC[22:16] (Note: Always 0x00)
21 LSB: Lower half of entry point PC[15:8]
22 MSB: Lower half of entry point PC[7:0]
... ...
... ...
Blocks of data in the format size/destination address/data as shown in the generic data stream
description.
... ...
... ...
n LSB: 00h
n+1 MSB: 00h - indicates the end of the source
The I
2
C EEPROM protocol required by the I
2
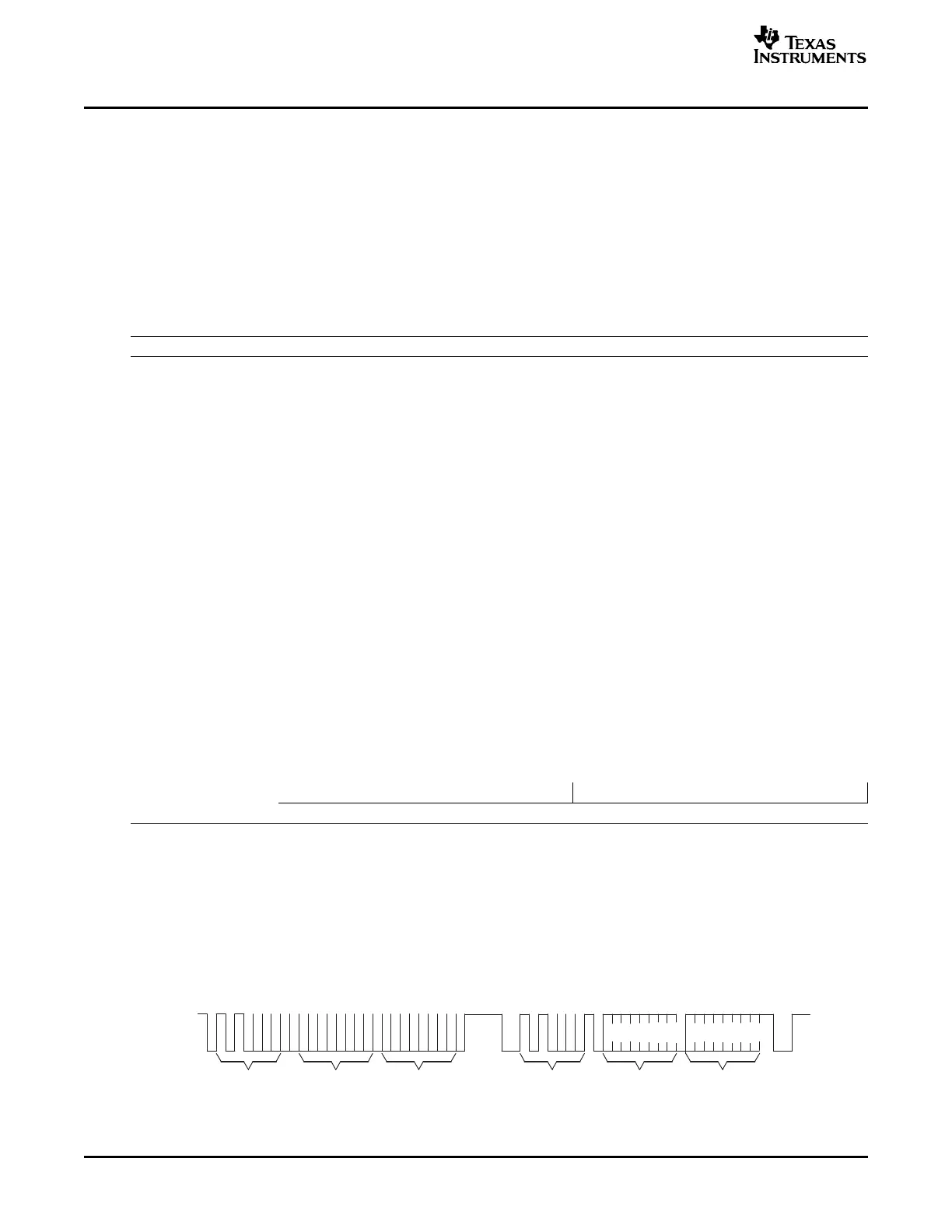
C bootloader is shown in Figure 2-24 and Figure 2-25 . The
first communication, which sets the EEPROM address pointer to 0x0000 and reads the KeyValue
(0x08AA) from it, is shown in Figure 2-24 . All subsequent reads are shown in Figure 2-25 and are read
two bytes at a time.
Figure 2-24. Random Read
44 Bootloader Features SPRU722C – November 2004 – Revised October 2006
Submit Documentation Feedback

 Loading...
Loading...











