- 48 -
Scaling, Reading Coordinates of 2 Points Method
A scaling method, where the low and high input values are determined from
actual signals. A known low signal is first applied to the meter, such as the
output of a pressure transducer at zero pressure. That signal is captured as the
low input value, and the desired low reading is entered. A known high signal is
then applied, such the output of a transducer for a know weight or pressure.
That signal is captured as the high input value, and the desired high reading is
entered. The meter then applies straight line fit. This scaling method has the
advantage of calibrating the transducer and meter as a system. The actual
voltage or current at either point does not need to be known. The decimal point
is set by the separate dEC.Pt menu item.
Setpoint A value compared to the reading to determine the state of a relay. Term often
used interchangeably with “alarm setpoint.” The relay action can by latching or
non-latching, utilize a hysteresis band, or utilize a deviation band. Hysteresis
bands and deviation bands are specified by two symmetrical limits around the
setpoint.
Span The number of counts corresponding to a given signal range.
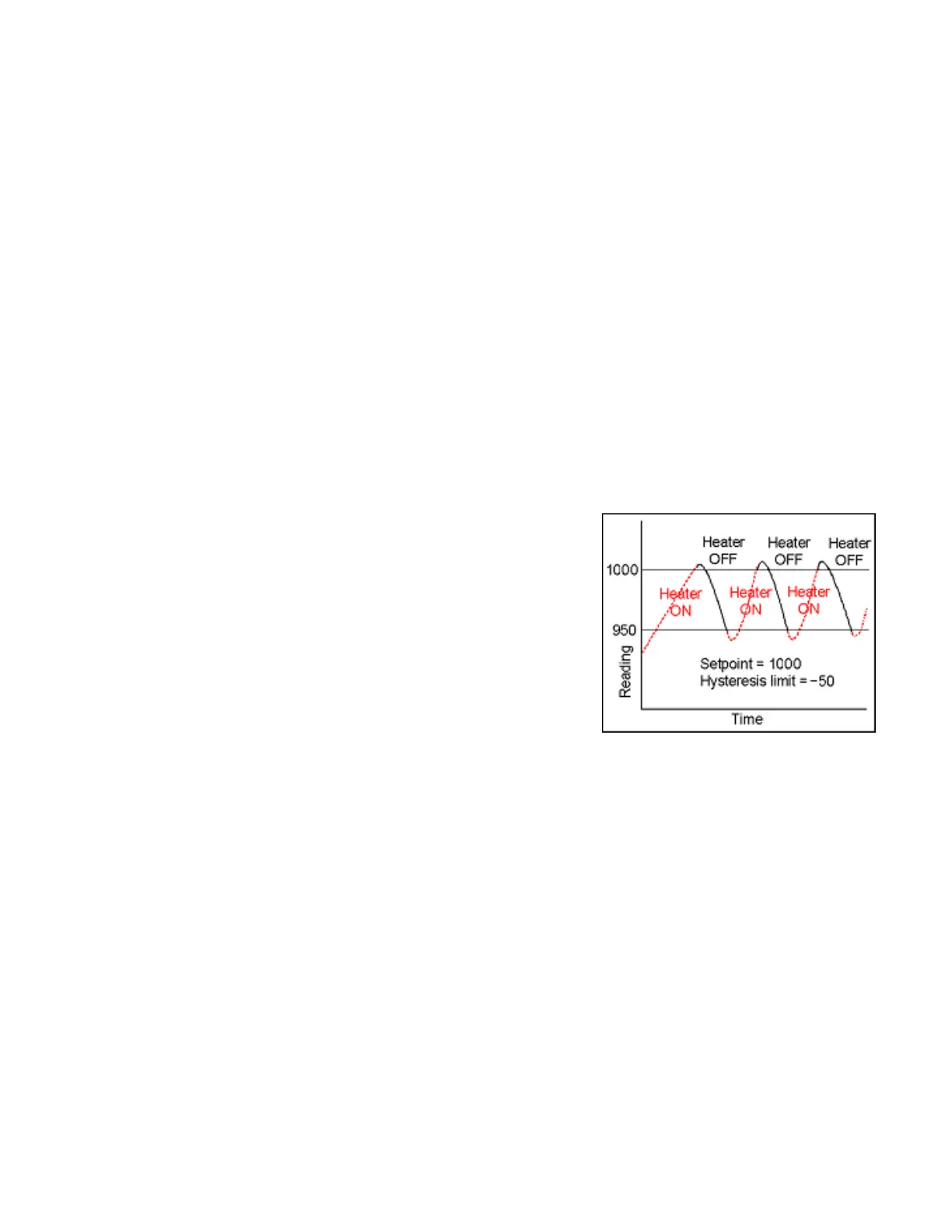
Split Hysteresis
A hysteresis mode where a setpoint and a
single-side hysteresis limit are entered. That
limit can be negative or positive. If the limit is
negative, the relay will close below the hys-
teresis limit, for example to turn on a heater,
and open when the setpoint is reached. If the
limit is positive, the relay will close when that
limit is reached, for example to turn on a
cooler, and open when the setpoint is
reached. Split hysteresis is an alternative to
normal hysteresis, where the setpoint is at
the center of a symmetrical hysteresis band.
Tare A rear panel input which causes the display to be set to zero when the input is
momentarily tied to logic ground by a switch or is held at 0V (logic level true).
When the input is allowed to float or is held at +5V (logic level false), the meter
displays readings relative to this new zero. A common application is in
weighing, where an external Tare button is pressed to read the weight of an
empty scale (tare), and tare is then automatically subtracted as a constant from
gross weight for display of net weight. Tare can also be used for other appli-
cations where a reading relative to starting point is desired.
TEDS 1451.4 TEDS, or Transducer Electronic Data Sheet, is a set of electronic data in a
standardized format defined within the IEEE 1451.4 standard that is stored in
EEPROM. This data specifies what type of sensor is present, describes its
interface, and gives technical information such as sensitivity, bridge type,
excitation, etc. With TEDS Plug and Play, the sensor and the meter are auto-
matically scaled as a system at power on.
 Loading...
Loading...