Thermostatic shower pole
4
Service
valves
Balanced cold mains supply
Cold mains supply
Shower pole
Expansion
vessel
Pressure
reducing
valves
Stop tap
Unvented
hot water
storage unit
Safety devices
not shown
Fig.3 (diagrammatic view – not to scale)
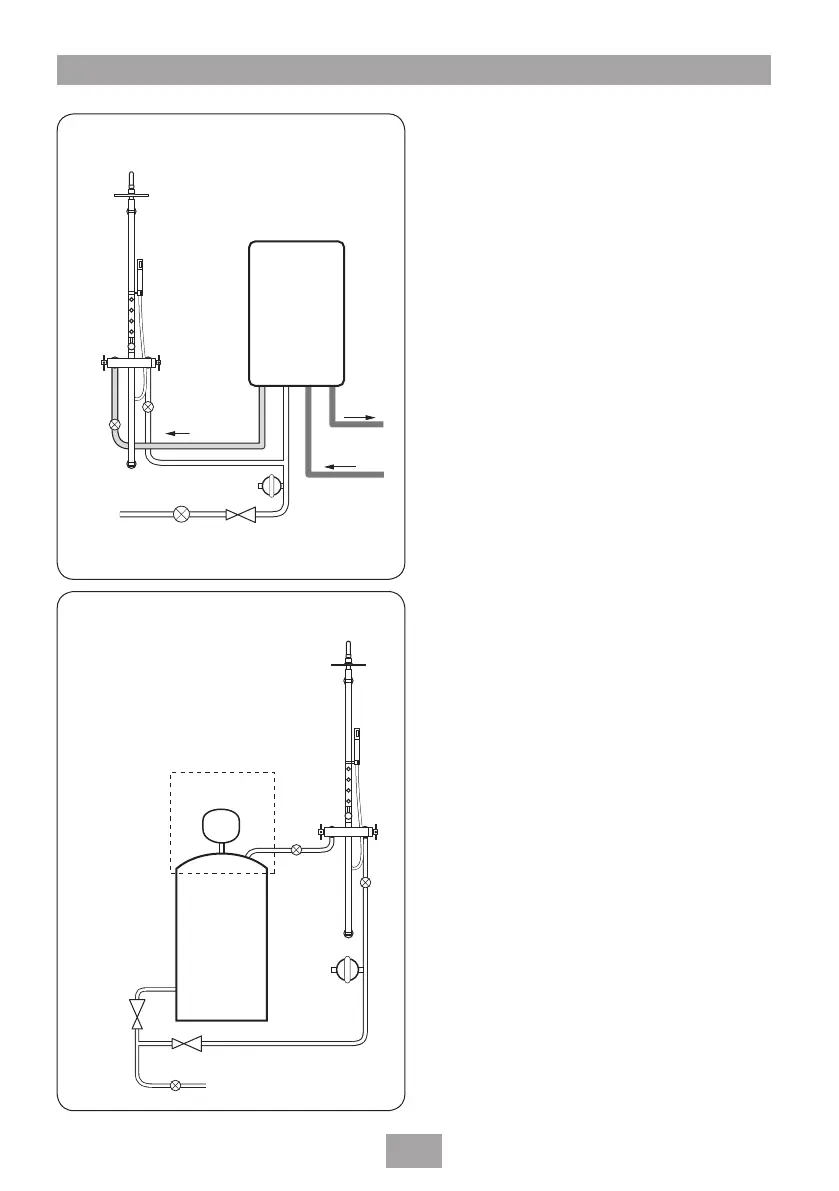
CH flow
Cold
mains
supply
Hot water
CH return
Service
valves
Shower pole
Stop
tap
Expansion
vessel
Pressure
reducing valve
Combination
boiler
Fig.2 (diagrammatic view – not to scale)
TYPICAL SUITABLE INSTALLATIONS
a) Instantaneous gas-heated systems,
e.g. combination boilers
(fig.2)
The shower MUST be installed with a multipoint
gas water heater or combination boiler of a fully
modulating design (i.e. to maintain relatively
stable hot water temperatures).
A drop tight pressure reducing valve MUST
be fitted if the supply pressures exceed 5 bar
running.
An expansion vessel (shown in fig.2) MUST be
fitted, and regularly maintained, to prevent the
shower being damaged by excess pressures. This
may already be installed within the boiler (check
with manufacturer) and is in addition to the
normally larger central heating expansion vessel.
The layout and sizing of pipework MUST be
such that nominally equal inlet supply pressures
are achieved and the effects of other draw-offs
are minimised. The hot supply temperature
MUST remain a minimum of 10°C hotter than
the required blend temperature for optimum
performance.
b) Unvented mains pressure systems
(fig.3)
The shower can be installed with an unvented,
stored hot water cylinder.
For systems with no cold water take off after the
appliance reducing valve, it will be necessary to
fit an additional drop tight pressure reducing
valve when the mains pressure is over 5 bar.
The drop tight pressure reducing valve must be
set at the same value as the unvented package
pressure reducing valve.
Note: An additional expansion vessel (fig.3)
may be required if a second pressure reducing
valve is installed. This does not apply to
packages with a cold take off after the pressure
reducing valve to the cylinder.
The layout and sizing of pipework MUST be
such that nominally equal inlet supply pressures
are achieved and the effects of other draw-offs
are minimised.

 Loading...
Loading...