Rx / Ry / Rz representation also, using 3 values to represent
the pose (but not three rotation angles), which is the product
of a three-dimensional rotation vector [x, y, z] and a rotation
angle [phi (scalar)].
The characteristics of the axis angle:
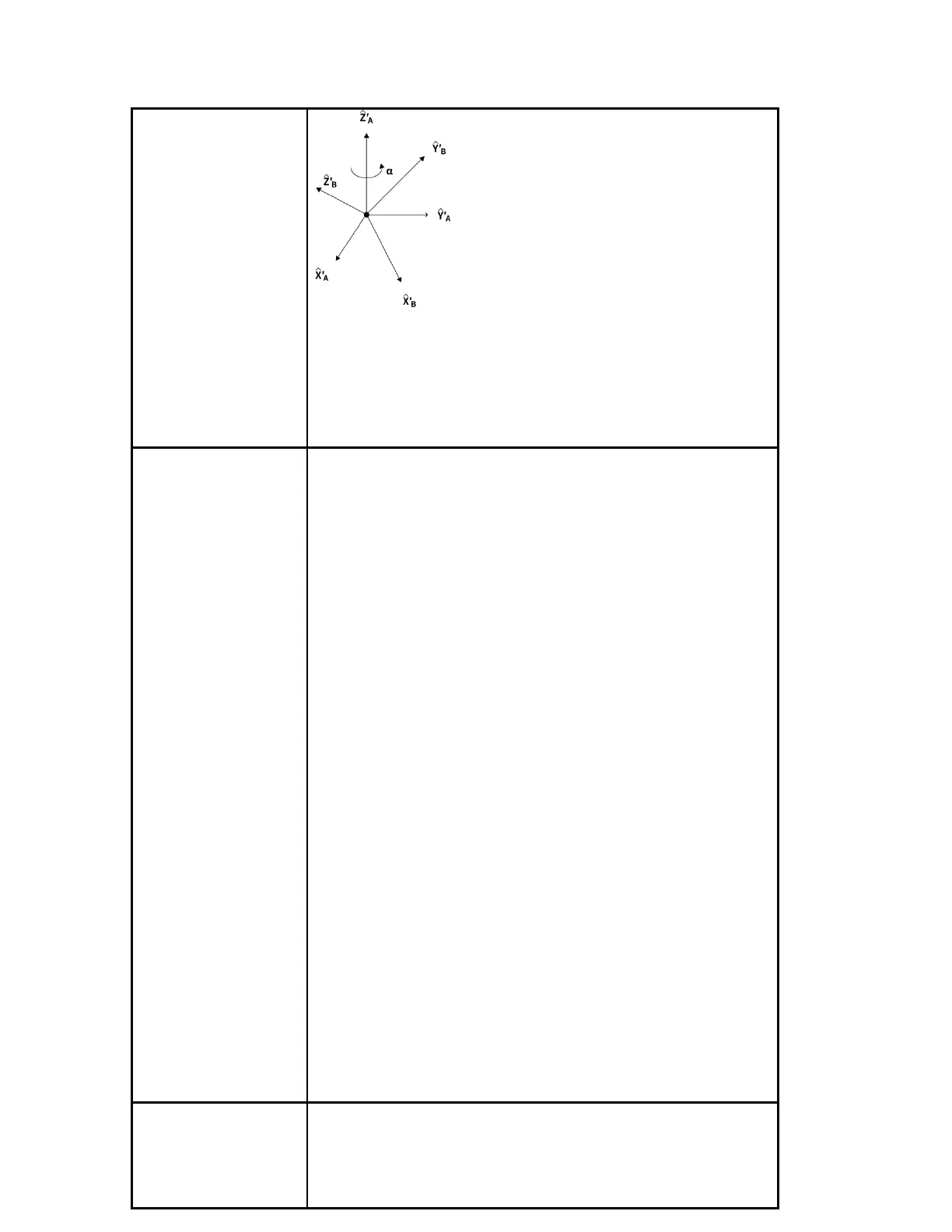
Assume the rotation axis is [x, y, z], and the rotation angle is
phi.
Then the representation of the axial angle:
[Rx, Ry, Rz] = [x * phi, y * phi, z * phi]
Note:
1. [x, y, z] is a unit vector, and phi is a non-negative value.
2. The vector length (modulus) of [Rx, Ry, Rz] can be used to
estimate the rotation angle, and the vector direction is the
rotation direction.
3. If you want to express reverse rotation, invert the rotation
axis vector [x, y, z], and the value of phi remains unchanged.
4. Using phi and [x, y, z] can also derive the attitude
representation as unit quaternion q = [cos (phi / 2), sin (phi /
2) * x, sin (phi / 2) * y, sin (phi / 2) * z].
For example:
The vector of the rotation axis represented by the base
coordinate system is [1, 0, 0], and the rotation angle is 180
degrees (π), then the axis angle representation of this pose is
[π, 0, 0].
The rotation axis is [0.707, 0.707, 0] and the rotation angle is
90 degrees (π / 2), then the axis angle posture is [0.707 * (π
/ 2), 0.707 * (π / 2), 0].
 Loading...
Loading...