109
current joint and its degree.
Operation mode:
Click 【+】 or【-】 for the step angles, users can set the step angle in 【Settings】 -
【Motion Settings】 -【Joint Motion】 -【Joint Step 】.
Press-and-hold【+】or【-】for continuous joint motion in a positive or negative
direction, which will stop when the mouse is released.
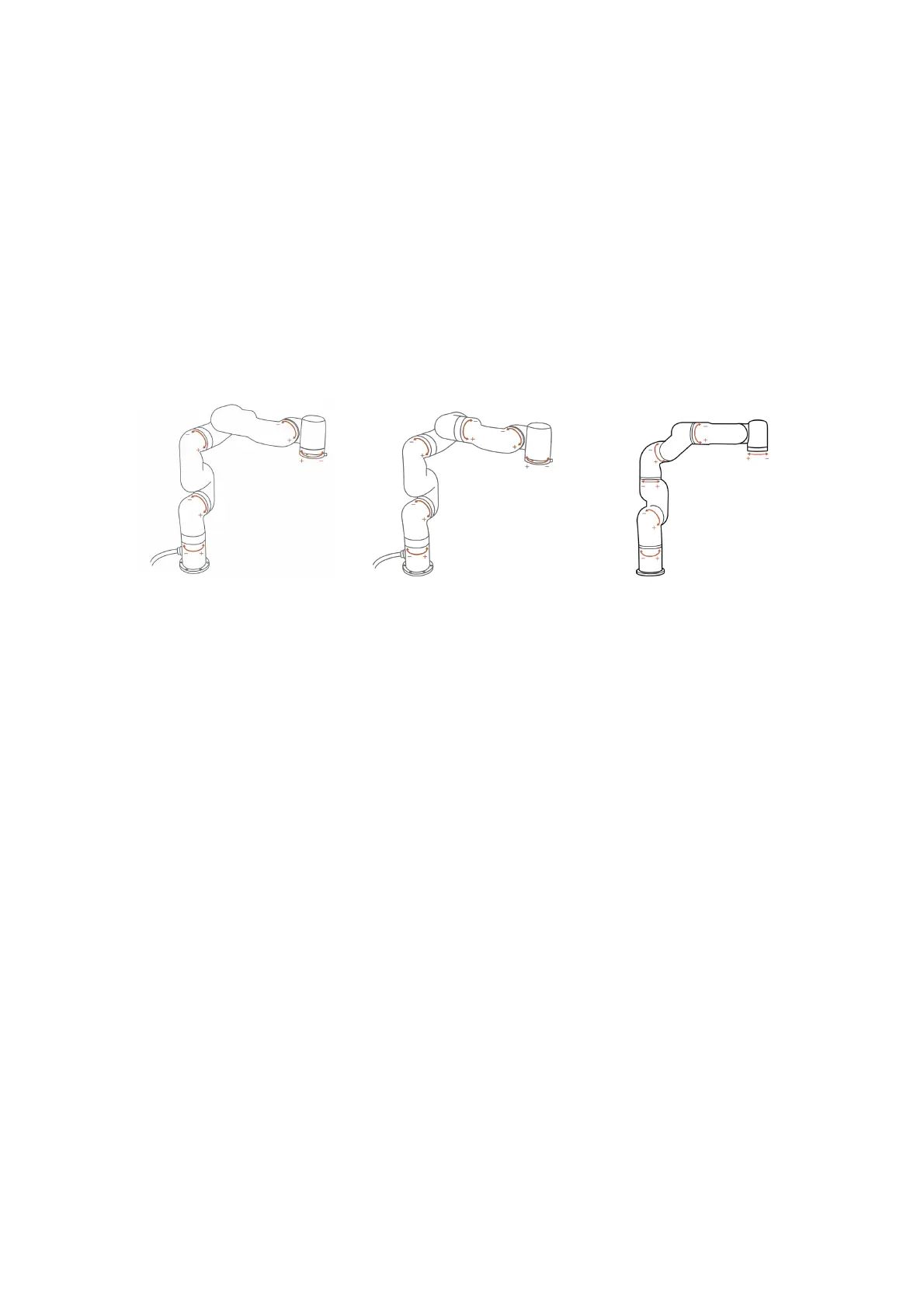
To confirm the direction of joint rotation, please refer the figure below:
xArm 5 xArm 6 xArm 7
1.5.6 Linear Motion
1.5.6.1 Introduction
Users can control the motion of the robotic arm based on the base coordinate system
and TCP coordinate system. The trajectory of tool center point in the Cartesian space
is a straight line. Each joint performs a more complex movement to keep the tool in a
straight path. The TCP path is unique once the target point is confirmed, and the
corresponding posture in the execution process is random.
X, Y, and Z control the position of TCP in base or tool coordinate system, in the unit
of mm. While Roll/Pitch/Yaw controls the TCP orientation in the unit of degree.
Linear motion and arc linear motion belong to the Cartesian space trajectory planning,
which needs to be solved by inverse kinematics. Therefore, there may be no solution,
multiple solutions, and approximated solutions; and due to the nonlinear relationship
between the joint space and Cartesian space, the joint motion may exceed its
maximum speed and acceleration limits.
 Loading...
Loading...