VWR Rotary Vane Pump ver 1.3 23.11.2020
8.30 Function
8.31 Working Principle
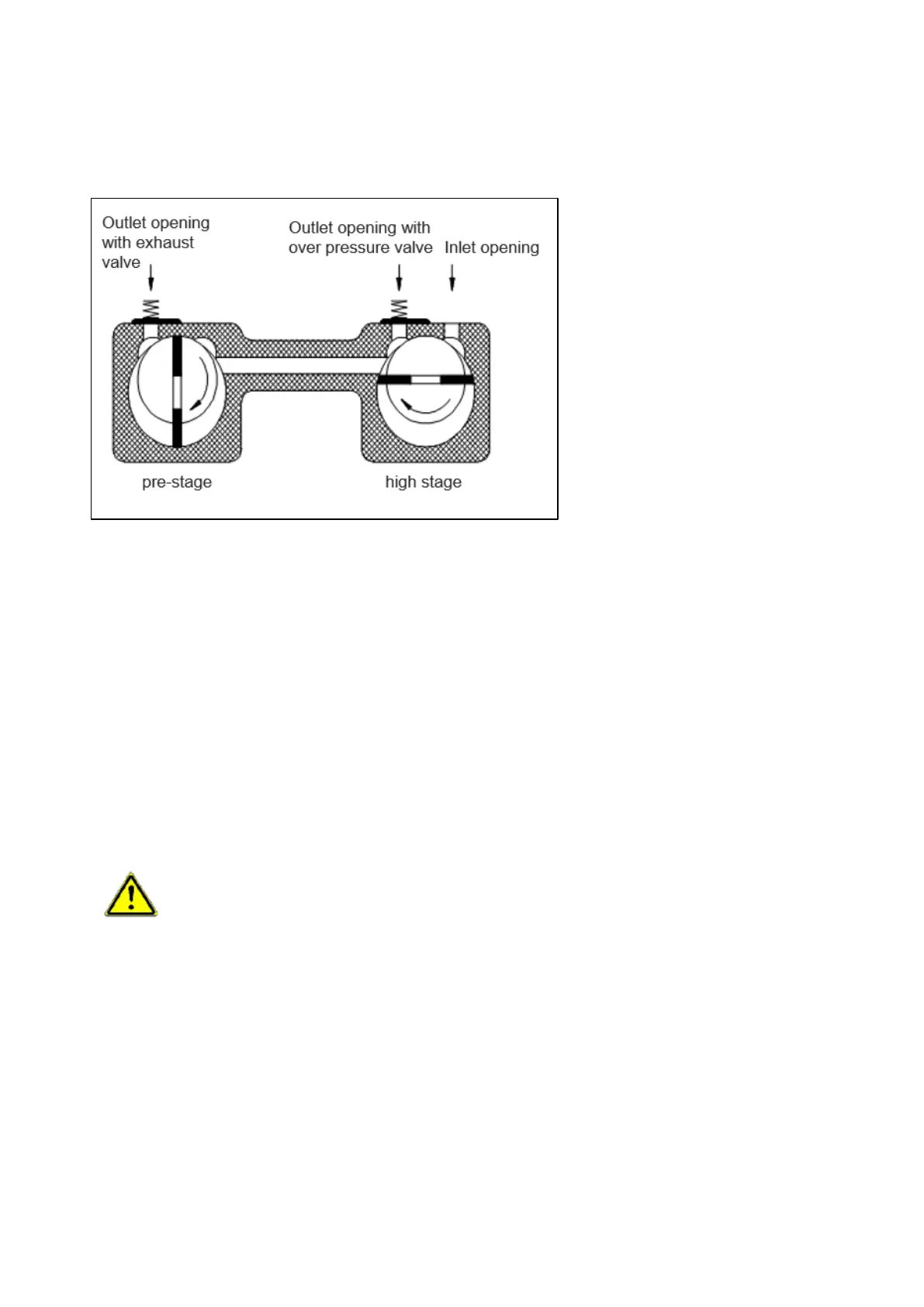
Two pump stages (fore-stage and high-stage) are arranged in series in order to improve the end pressure
and the pumping speed at lower pressures. The intake takes place in the first stage (high-stage), the
compression and the outlet in the second stage (fore-stage).
Fig. 8: Pre-stage / high-stage
The pump body is subdivided into several chambers by the eccentrically arranged rotor which has two
radically sliding vanes. The volume of each chamber changes cyclically as the rotor turns. This sucks the
gas into the intake opening. The gas flows through the dirt filter, which is connected to the centring ring, into
the pump body. After the intake opening is closed by the vane, the gas is transported onwards and
compressed.
A dosed quantity of air (gas ballast) can be let into the pump body during the compression by opening the
gas ballast valve. This prevents vapours condensing in the vacuum pump. Oil is injected into the pump body
for sealing and lubrication. An oil pump pumps oil out of the oil reservoir into a pressure oil lubrication
system that feeds all the bearings. The low-mounted oil suction pipe achieves a large usable oil reserve.
At the outlet valve, the compressed gas is pumped out of the pump body through the exhaust port. The oil
carried along with the gas is separated out by a filter (accessory).
8.32 Gas ballast
WARNING!
Condensable vapours may only be extracted when the gas ballast valve is open, when
the vacuum pump is at operating temperature and within the limits of the maximum
tolerance of water vapour pressure! Condensation occurs if the maximum water vapour
pressure tolerance is exceeded.
When pumping condensable vapours, they may be compressed during the compression phase above the
saturated vapour pressure and condense.
This causes considerable deterioration in the vacuum pump’s performance:
- ultimate pressure is not achieved
- corrosion occurs
- heavy oil contamination and formation of emulsions
When the gas ballast valve opens (to the left) air flows into the compression space. The air flowing in keeps
the partial pressure of the condensable medium so low that the pressure needed to open the outlet valve is
reached before the medium condenses.
 Loading...
Loading...