Functional Software description
70 DCS 500 Software Description
Q
act
time
A
B
C
D
E
F
H
Accel. Constant speed Decel. Standstill Accel.
100%
Motor’s thermal capacity
Q
k
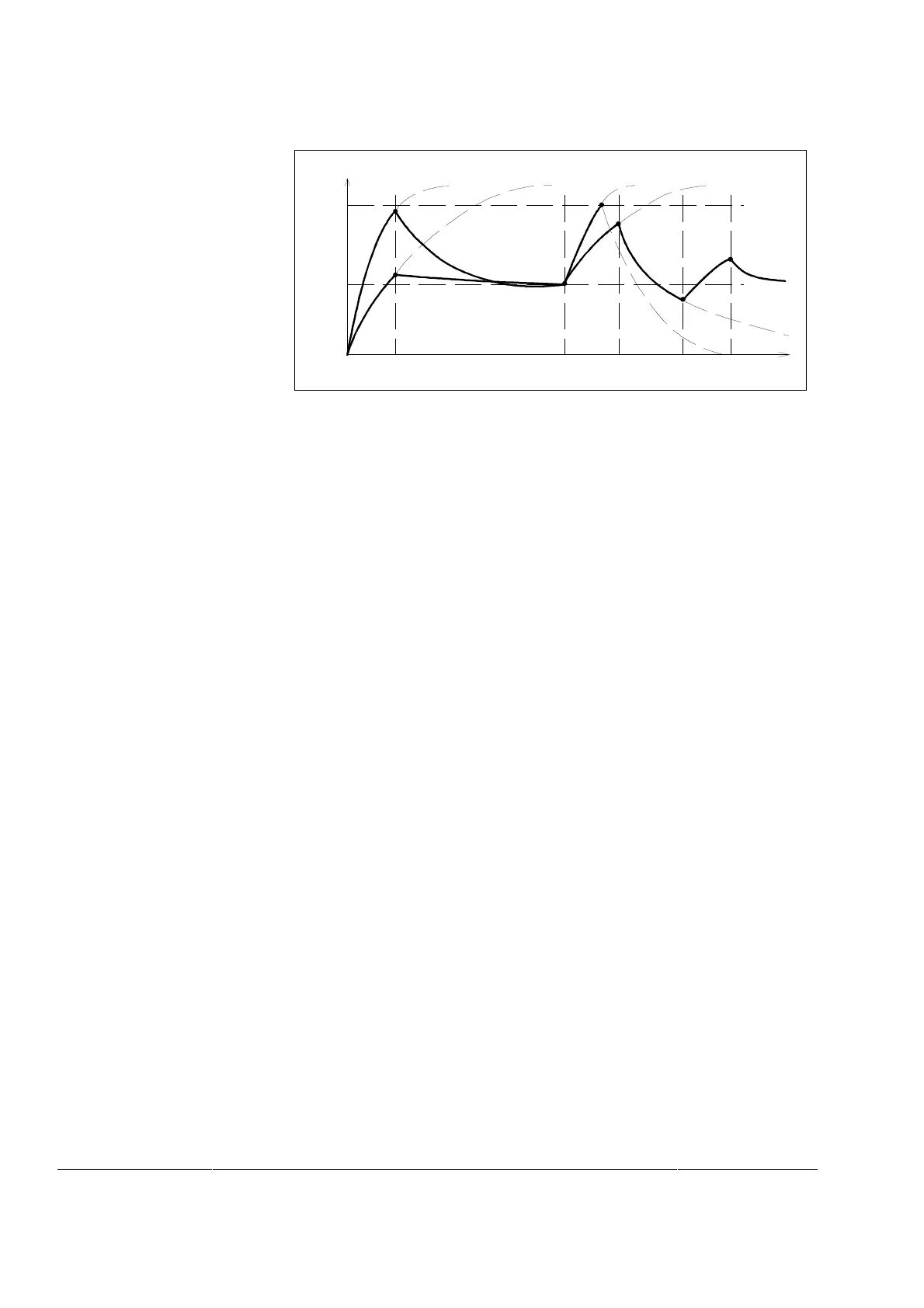
Figure 49 Q
act
as a function of different loads
Previous figure shows how Q
ACT
(motor’s thermal capacity) is for-
med of rising and falling sections of the time constant function. On
curve 0-A-C-D an overload trip occurs at point D owing to a too
short time constant even though the heating up clearly does not
reach the limit Q
ACT
= 100% which corresponds to the motor’s
thermal capacity.
In point A acceleration does not yet cause a trip because a cold
start was made
On curve 0-B-C-E-F-H the desired loading cycle can be repeated as
many times as necessary because its time constant is sufficiently
long.
The temperature rise of the motor behaves as a time constant
which is proportional to the motor current in power of two.
I
act
2
Q
act
= * ( 1 - e
-t/τ
) * 100 (1)
I
ref
2
where:
Q
act
thermal value
I
act
motor current actual
I
ref
reference current, normally rated current of motor
τ temperature time constant.
100 scaling factor
t time
 Loading...
Loading...