• The defective operation of the automatic voltage regulator when the generator
is in isolated operation.
• Operation under manual control with the voltage regulator out of service. A
sudden variation of load, in particular the reactive power component, gives rise
to a substantial change in voltage because of the inherent large voltage
regulation of a typical alternator.
• Sudden loss of load due to the tripping of outgoing feeders, leaving the
generator isolated or feeding a very small load. This causes a sudden rise in the
terminal voltage due to the trapped field flux and overspeed.
If a load sensitive to overvoltage remains connected, it leads to equipment damage.
It is essential to provide power frequency overvoltage protection, in the form of
time delayed element, either IDMT or DT to prevent equipment damage.
4.5.1.7 Signals
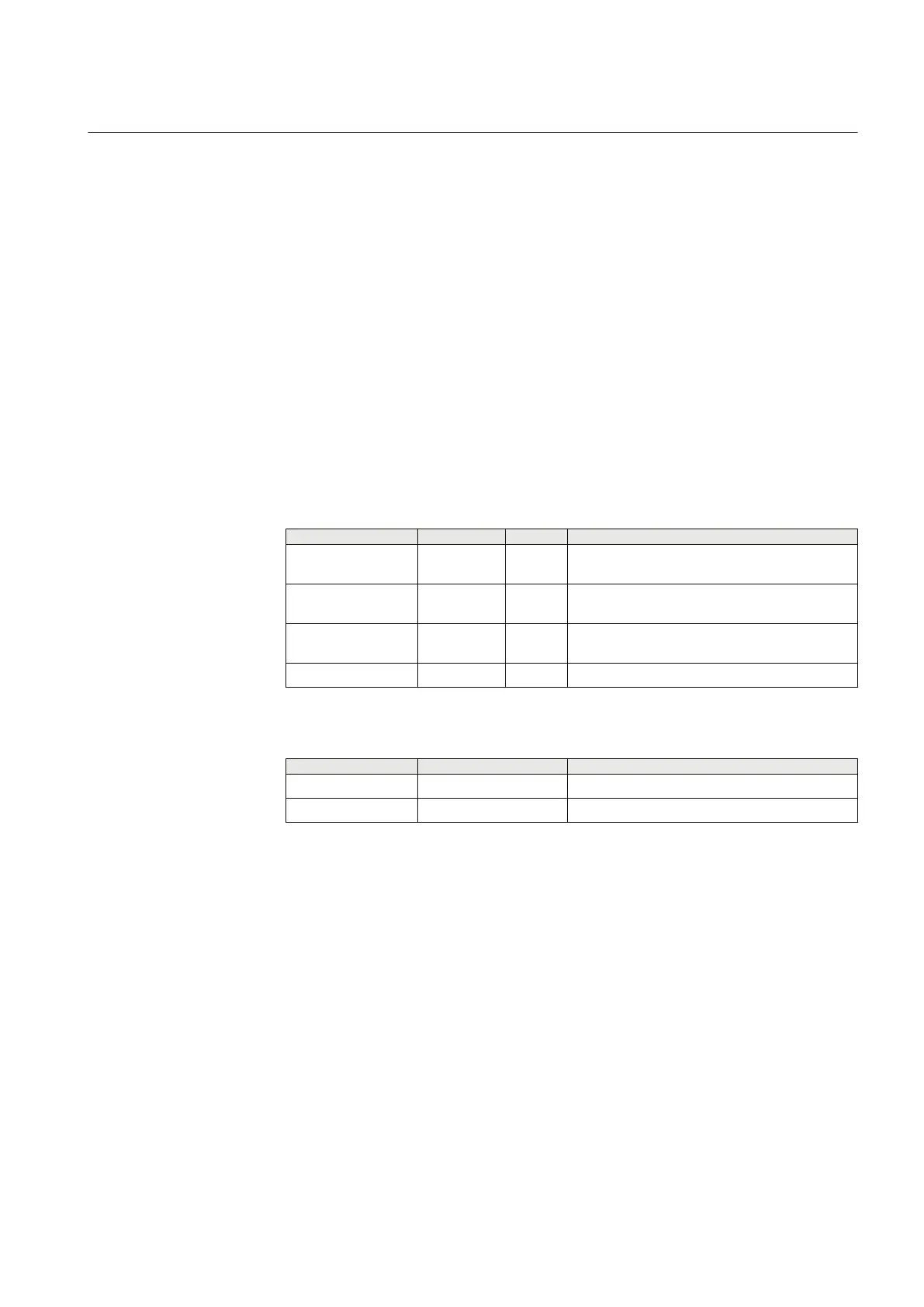
Table 385: PHPTOV Input signals
Name Type Default Description
U_A_AB SIGNAL 0 Phase to earth voltage A or phase to phase
voltage AB
U_B_BC SIGNAL 0 Phase to earth voltage B or phase to phase
voltage BC
U_C_CA SIGNAL 0 Phase to earth voltage C or phase to phase
voltage CA
BLOCK BOOLEAN 0=False Block signal for activating the blocking mode
Table 386: PHPTOV Output signals
Name
Type Description
OPERATE BOOLEAN Operate
START BOOLEAN Start
1YHT530004D05 D Section 4
Protection functions
615 series 471
Technical Manual
 Loading...
Loading...