30 Advanced Operation
3 Method Development
Rearranging provides:
where:
K is the partition coefficient (or distribution coefficient),
C
L
/C
G
at equilibrium
V
G
/V
L
is also called the phase ratio
The equation shows two important points:
• For consistent results, the ratio V
G
/V
L
must remain
constant. This means that the sample amount and vial
size need to be kept the same.
• Minimizing the partition coefficient, K, provides higher
concentration of sample vapor in the headspace volume.
• A smaller V
G
/V
L
ratio yields a greater concentration of
volatile of interest in the headspace volume
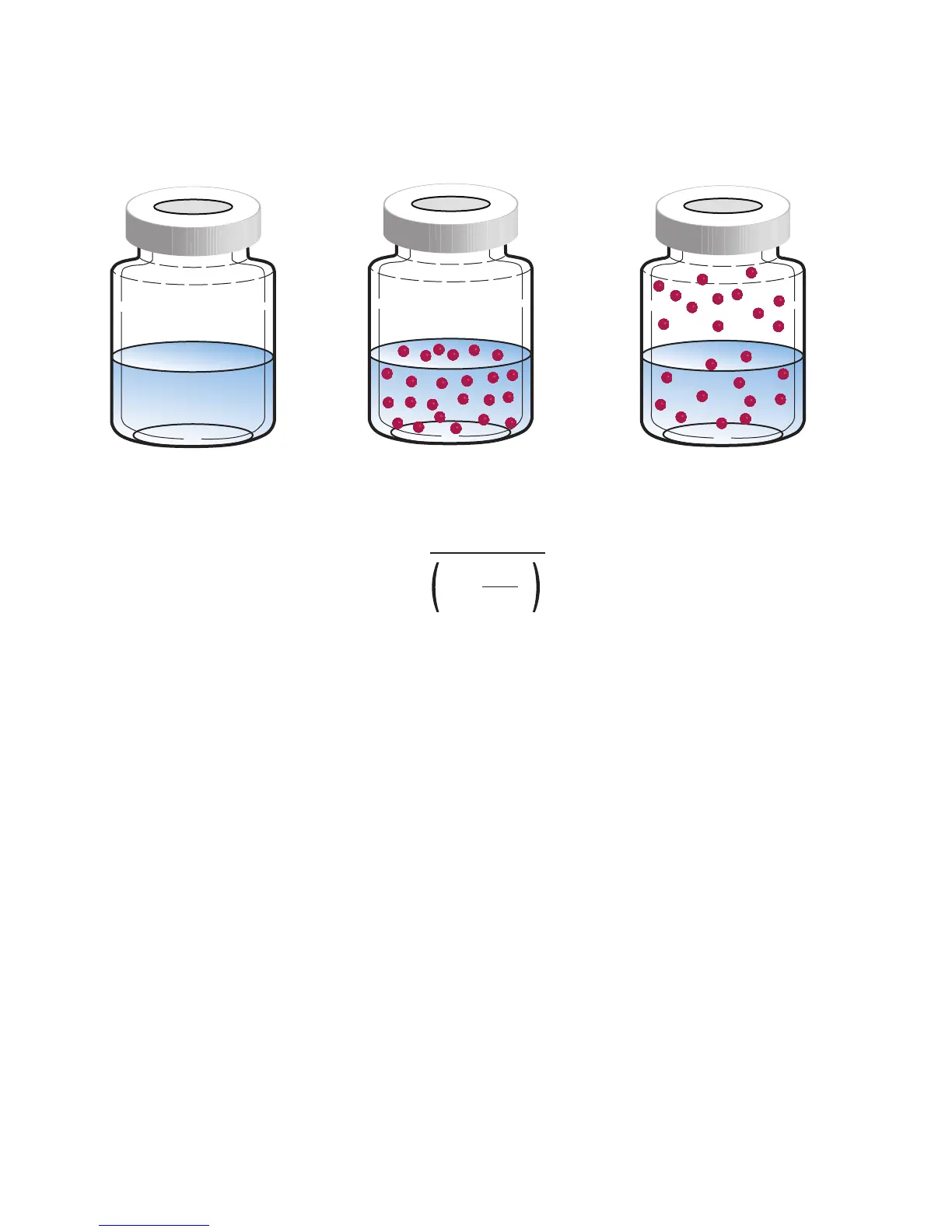
Impact of K and phase ratio
The concentration of analyte in the headspace volume
depends on many factors, including: sample amount, original
concentration of analyte in the sample, available headspace
volume, temperature, and total pressure in the vial. Some
factors are manipulated in the sample and in the matrix,
while others can be controlled using the headspace sampler.

 Loading...
Loading...



