124 Chapter 3
Programming the Status Register System
Status Byte Group
Status Byte Register
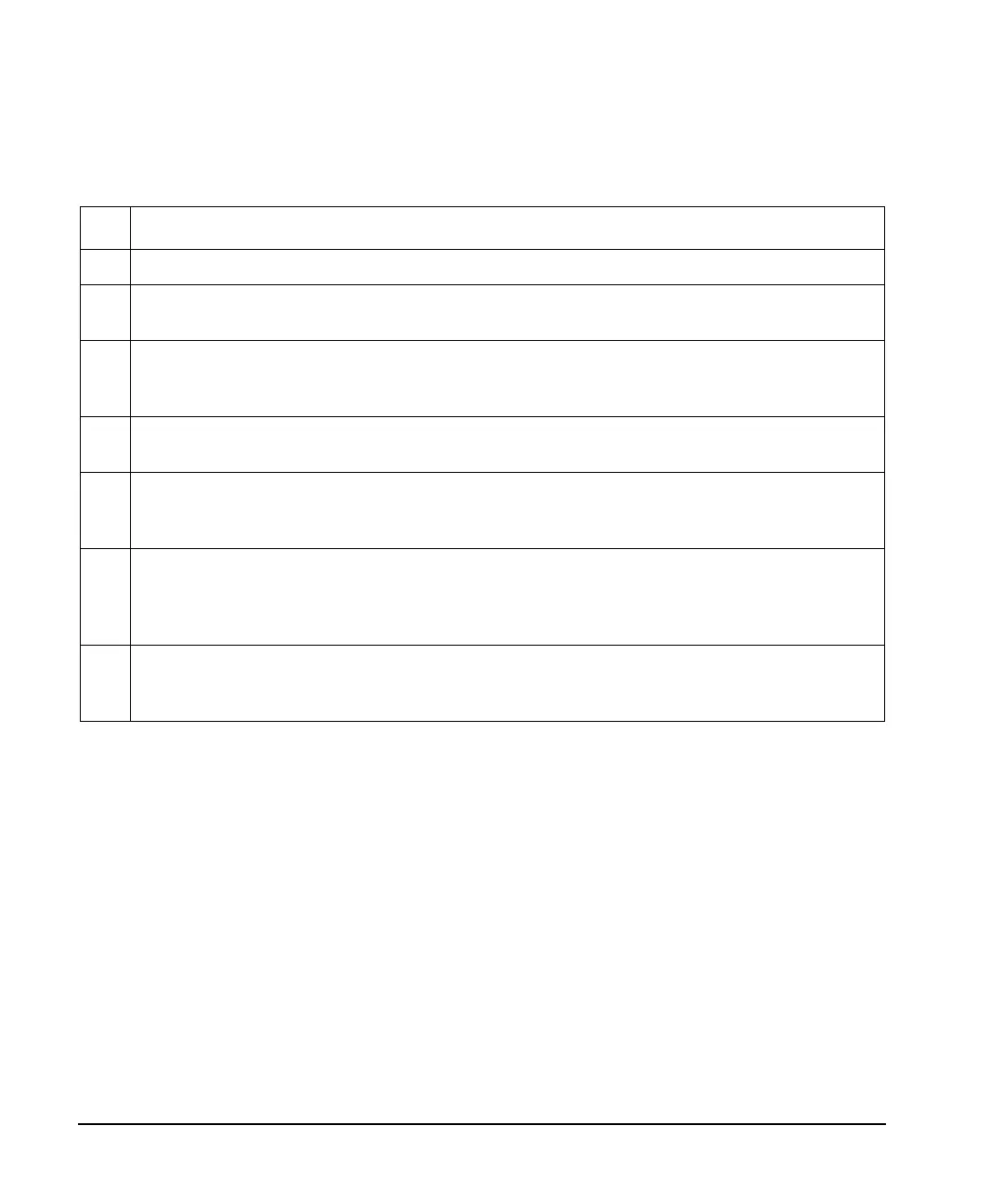
Table 3-3 Status Byte Register Bits
Bit Description
0,1 Unused. These bits are always set to 0.
2 Error/Event Queue Summary Bit. A 1 in this bit position indicates that the SCPI error queue is not empty;
the SCPI error queue contains at least one error message.
3 Data Questionable Status Summary Bit. A 1 in this bit position indicates that the Data Questionable
summary bit has been set. The Data Questionable Event Register can then be read to determine the specific
condition that caused this bit to be set.
4 Message Available. A 1 in this bit position indicates that the signal generator has data ready in the output
queue. There are no lower status groups that provide input to this bit.
5 Standard Event Status Summary Bit. A 1 in this bit position indicates that the Standard Event summary bit
has been set. The Standard Event Status Register can then be read to determine the specific event that caused
this bit to be set.
6 Request Service (RQS) Summary Bit. A 1 in this bit position indicates that the signal generator has at least
one reason to require service. This bit is also called the Master Summary Status bit (MSS). The individual bits
in the Status Byte are individually ANDed with their corresponding service request enable register, then each
individual bit value is ORed and input to this bit.
7 Standard Operation Status Summary Bit. A 1 in this bit position indicates that the Standard Operation
Status Group’s summary bit has been set. The Standard Operation Event Register can then be read to
determine the specific condition that caused this bit to be set.
Query: *STB?
Response: The decimal sum of the bits set to 1 including the master summary status bit (MSS) bit 6.
Example: The decimal value 136 is returned when the MSS bit is set low (0).
Decimal sum = 128 (bit 7) + 8 (bit 3)
The decimal value 200 is returned when the MSS bit is set high (1).
Decimal sum = 128 (bit 7) + 8 (bit 3) + 64 (MSS bit)

 Loading...
Loading...











