UG-1098 ADE9000 Technical Reference Manual
Rev. 0 | Page 16 of 86
It is recommended to set the voltage channel input so that the
nominal voltage (for example, 240 V rms) corresponds to one
half of the analog input signal range of the ADE9000. The
ADE9000 can support ±1 V peak, 0.707 V rms inputs; therefore,
it is recommended to scale the voltage channel inputs to
0.353 V rms. Then, with a nominal 240 V, the input signal is at
half of full scale and X is equal to 2. Write 574,042 (decimal) to
the VLEVEL register to configure this feature:
VLEVEL = 2 × 1,114,084 = 2,288,168
After configuring these two parameters, SELFREQ and
VLEVEL, the ADE9000 tracks the fundamental line frequency
within ±5 Hz of the 50 Hz or 60 Hz frequency selected in
SELFREQ. If a larger frequency range than ±5 Hz is required in
the application, monitor the line period, xPERIOD, and change
the SELFREQ selection accordingly. Note that the RUN register
must be set to zero before changing the SELFREQ setting and
then be set to one again.
Fundamental RMS
The ADE9000 offers fundamental current and voltage rms
measurements using the proprietary fundamental estimation
technique described in the Fundamental Measurements section.
The xIFRMSOS and xVFRMSOS registers allow the offset to be
calibrated for even better performance at low input signal levels.
Note that the xFRMS register does not read 0 with the xP and
xN inputs shorted together.
The fundamental rms calculations, one for each channel,
AIFRMS, BIFRMS, CIFRMS, AVFRMS, BVRMS, and CVRMS,
are updated every 8 ksps. Note that there the neutral current
channel does not have a fundamental rms measurement.
The xFRMS value at full scale is 52,702,092 (decimal).
For high performance at small input signals, below 1000:1, it is
recommended to calibrate the offset of this measurement using
the xFRMSOS register. It is recommended to calibrate the offset
at the smallest input signal which requires good performance;
do not calibrate this measurement with zero input signal.
The following equation indicates how the xFRMSOS register
value modifies the result in the xFRMS register.
xxFRMSOSxxFRMSxxFRMS ×+=
15
2
0
2
where xxFRMS
0
is the initial xFRMS register value before offset
calibration.
Fundamental Active Power
The ADE9000 offers fundamental active power measurements
using the proprietary fundamental estimation technique. The
fundamental active power is then gained by xPGAIN and offset
correction is applied according to the xFWATTOS register.
The xFWATTOS register allows offset calibration to provide
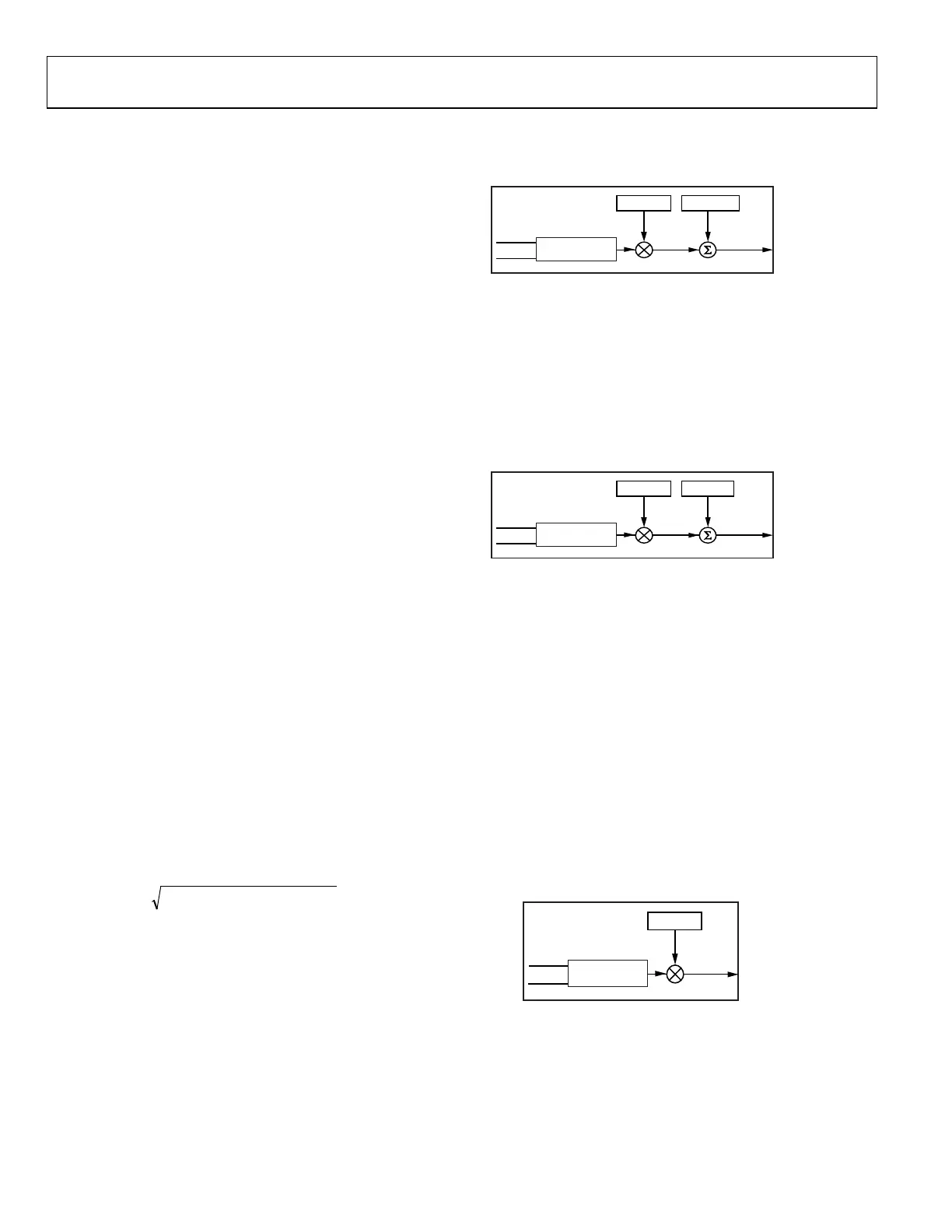
even better performance with low input signal levels. Figure 17
shows the signal chain for the AFWATT measurement.
APGAIN
AF
W
A
T
T
OS
AFWATT
AI_PCF
A
V_PCF
FUNDAMEN
TA
L
W
A
TT
ENERGY/
POWER/CF
ACCUMULATION
15523-017
Figure 17. Fundamental WATT, AFWATT Calculation
xFWATTOS has the same scaling as xFWATT; see the Tota l Ac tive
Power section to understand how to calculate this register value.
Fundamental Reactive Power
The ADE9000 offers fundamental reactive power measurements
using the proprietary fundamental estimation technique. This is
then gained by xPGAIN and offset correction is applied according
to the xFVAROS register. Figure 18 shows the signal chain for the
AFVAR measurement.
APGAIN
AFVAROS
AFVAR
AI_PCF
AV_PCF
FUNDAMENTAL
VAR
ENERGY/
POWER/CF
ACCUMULATION
15523-018
Figure 18. Fundamental Reactive Power, AFVAR
The fundamental reactive power at a power factor of 0 has a
similar ripple to the total active power at a power factor of 1
(see Figure 16).
xFVAROS has the same scaling as xFVA R; see the Total Active
Power section to understand how to calculate this register value.
Fundamental Apparent Power
The ADE9000 offers fundamental rms measurements using the
proprietary fundamental estimation technique described in the
Fundamental Measurements and Fundamental RMS sections.
The fundamental rms measurements, xIFRMS and xVFRMS,
are multiplied together to obtain fundamental apparent power.
This is then gained by xPGAIN and stored in the xFVA register.
Figure 19 shows the signal chain for the AFVA measurement.
Note that offset correction can be performed by calibrating the
AIFRMS and AVFRMS measurements.
APGAIN
AFVA
AIFRMS
AVFRMS
FUNDAMENTAL
VA
ENERGY/
POWER/CF
ACCUMULATION
15523-019
Figure 19. Fundamental Apparent Power, AFVA
 Loading...
Loading...