AT90S2313
40
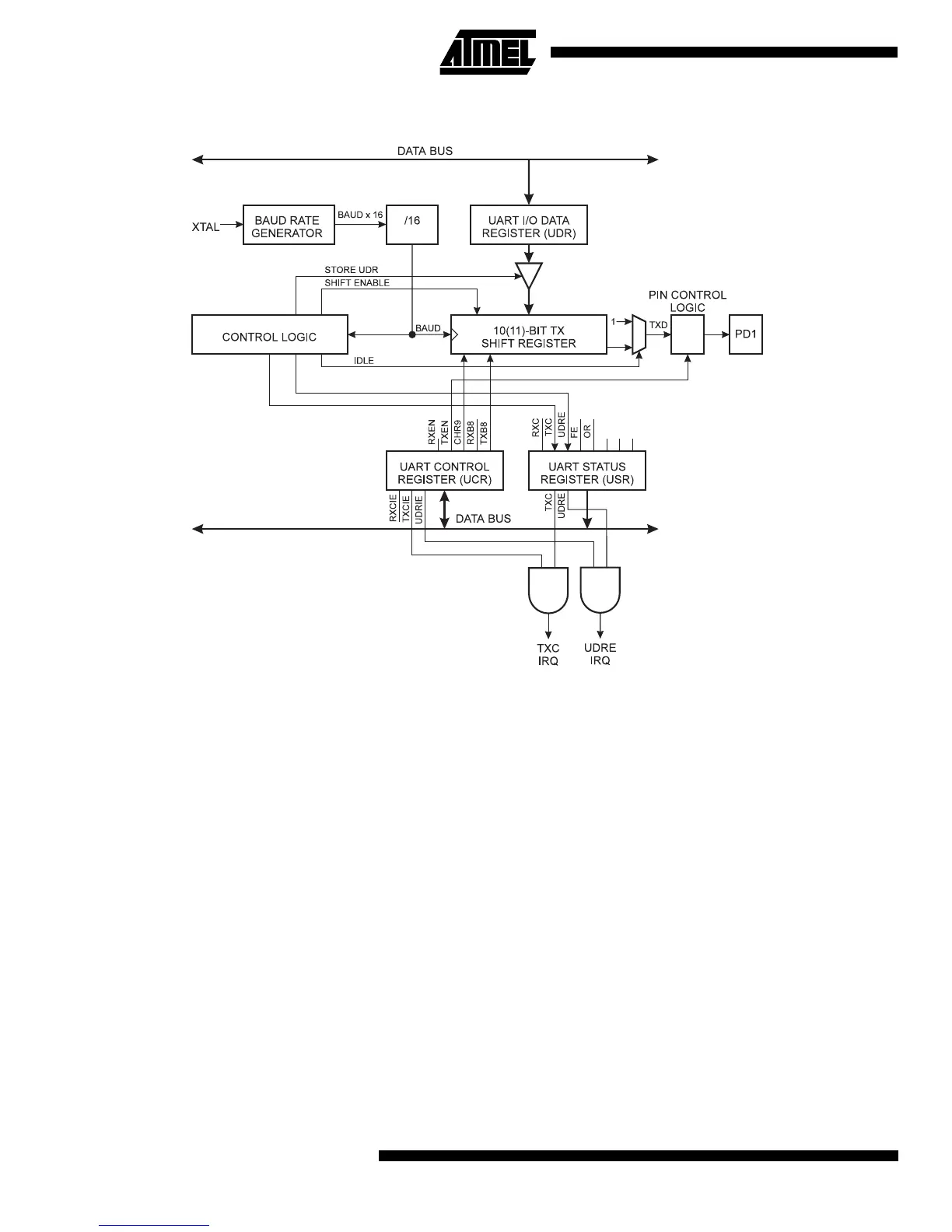
Figure 34. UART Transmitter
If the 10(11)-bit Transmitter shift register is empty, data is transferred from UDR to the shift register. At this time the UDRE
(UART Data Register Empty) bit in the UART Status Register, USR, is set. When this bit is set (one), the UART is ready to
receive the next character. At the same time as the data is transferred from UDR to the 10(11)-bit shift register, bit 0 of the
shift register is cleared (start bit) and bit 9 or 10 is set (stop bit). If 9 bit data word is selected (the CHR9 bit in the UART
Control Register, UCR is set), the TXB8 bit in UCR is transferred to bit 9 in the Transmit shift register.
On the Baud Rate clock following the transfer operation to the shift register, the start bit is shifted out on the TXD pin. Then
follows the data, LSB first. When the stop bit has been shifted out, the shift register is loaded if any new data has been
written to the UDR during the transmission. During loading, UDRE is set. If there is no new data in the UDR register to send
when the stop bit is shifted out, the UDRE flag will remain set until UDR is written again. When no new data has been
written, and the stop bit has been present on TXD for one bit length, the TX Complete Flag, TXC, in USR is set.
The TXEN bit in UCR enables the UART transmitter when set (one). When this bit is cleared (zero), the PD1 pin can be
used for general I/O. When TXEN is set, the UART Transmitter will be connected to PD1, which is forced to be an output
pin regardless of the setting of the DDD1 bit in DDRD.
 Loading...
Loading...