38 • Guide to Electrophysiological Recording
MultiClamp 700A Theory and Operation, Copyright 2000, 2001 Axon Instruments, Inc.
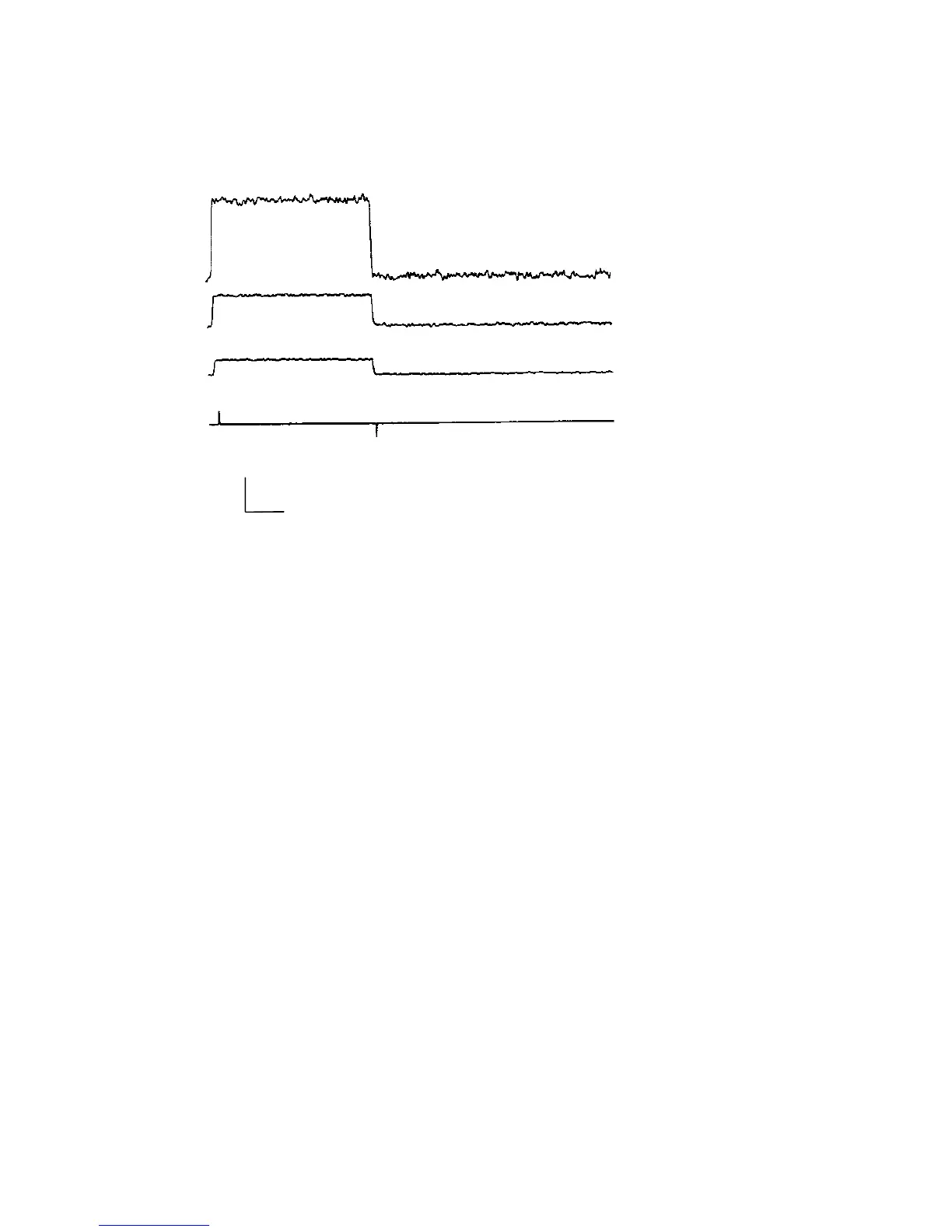
encountered a cell. A slow increase probably means the tip is becoming clogged, in
which case you can try blowing it out with high pressure before advancing again at
lower pressure.
2 ms
250 pA
IN BATH
PUSHED AGAINST CELL
MORE PRESSURE
AGAINST CELL
GIGOHM SEAL
Figure 3.1 Change in resistance while forming a seal.
When you are pushed up against a cell, apply 50-100 mbar of suction (negative
pressure) to the pipette holder. At the same time, steadily increase the holding
potential towards –60 or –70 mV; doing this usually helps seal formation. There
should be a rapid increase in the resistance. Release the suction when the resistance
reaches a gigohm. The resistance often continues to increase slowly over the next
several minutes.
The best gigaseals are those that form nearly instantaneously. If a seal does not form
within about a minute, continued suction is usually pointless. It is best to change
electrodes and try again.
 Loading...
Loading...