20010101
kk
kk
k Quadratic Differential Calculations [OPTN]-[CALC]-[d
2
/dx
2
]
After displaying the function analysis menu, you can input quadratic differentials using either of
the two following formats.
K4(CALC)c(d
2
/dx
2
) f(x),a,tol)
Quadratic differential calculations produce an approximate differential value using the following
second order differential formula, which is based on Newton’s polynomial interpretation.
2 f(a + 3h) – 27 f(a + 2h) + 270 f (a + h) – 490 f(a)+270 f(a – h) – 27 f(a – 2h) +2 f(a – 3h)
f''(a)
= –––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
180h
2
In this expression, values for “sufficiently small increments of h” are used to obtain a value that
approximates f ”(a).
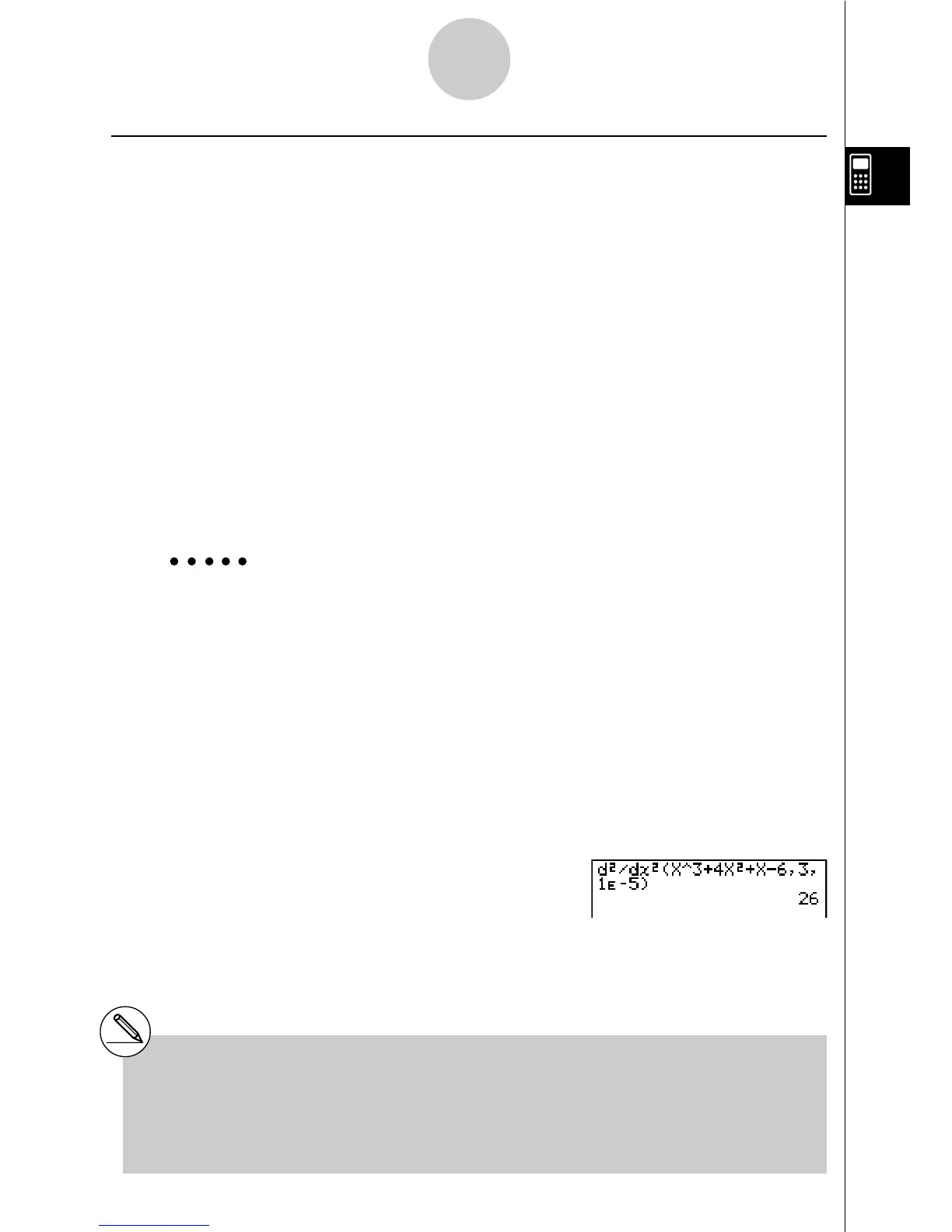
Example To determine the quadratic differential coefficient at the point where
x = 3 for the function y = x
3
+ 4x
2
+ x – 6
Here we will use a tolerance tol = 1E – 5
Input the function f(x).
AK4(CALC)c(d
2
/dx
2
) vMd+
evx+v-g,
Input 3 as point a, which is the differential coefficient point.
d,
Input the tolerance value.
bE-f)
w
2-5-5
Numerical Calculations
# In the function f(x), only X can be used as a
variable in expressions. Other variables (A
through Z, r,
θ
) are treated as constants, and
the value currently assigned to that variable is
applied during the calculation.
#Input of the tolerance (tol) value and the closing
parenthesis can be omitted.
#Discontinuous points or sections with drastic
fluctuation can adversely affect precision or
even cause an error.
(a: differential coefficient point , tol: tolerance)
d
2
d
2
––– (f (x), a) ⇒ ––– f (a)
dx
2
dx
2
20011101
 Loading...
Loading...