2-16
k Trigonometric and Inverse Trigonometric Functions
• Be sure to set the angle unit before performing trigonometric function and inverse
trigonometric function calculations.
• Be sure to specify Comp for Mode in the Setup screen.
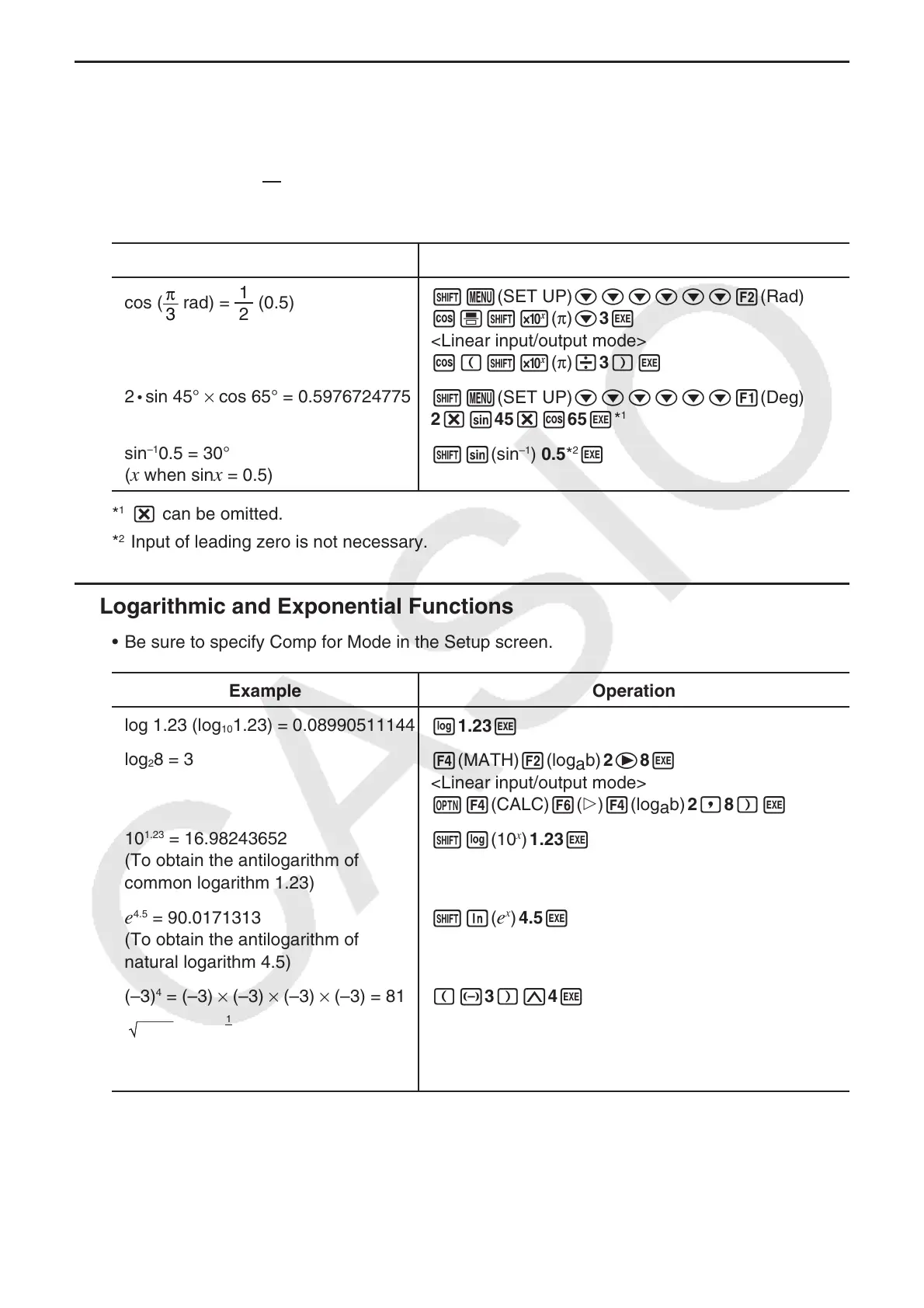
Example Operation
cos (
π
3
rad) =
2
1
(0.5)
!m(SET UP)cccccc2(Rad)J
c'!5(π)c3w
<Linear input/output mode>
c(!5(π)/3)w
2
•
sin 45° × cos 65° = 0.5976724775
!m(SET UP)cccccc1(Deg)J
2*s45*c65w*
1
sin
–1
0.5 = 30°
(x when sinx = 0.5)
!s(sin
–1
) 0.5*
2
w
*
1
* can be omitted.
*
2
Input of leading zero is not necessary.
k Logarithmic and Exponential Functions
• Be sure to specify Comp for Mode in the Setup screen.
Example Operation
log 1.23 (log
10
1.23) = 0.08990511144
l1.23w
log
2
8 = 3
4(MATH)2(log
a
b) 2e8w
<Linear input/output mode>
K4(CALC)6(g)4(log
a
b) 2,8)w
10
1.23
= 16.98243652
(To obtain the antilogarithm of
common logarithm 1.23)
!l(10
x
) 1.23w
e
4.5
= 90.0171313
(To obtain the antilogarithm of
natural logarithm 4.5)
!I(e
x
) 4.5w
(–3)
4
= (–3) × (–3) × (–3) × (–3) = 81
(-3)M4w
7
123 (= 123
1
7
) = 1.988647795
!M(
x
') 7e123w
<Linear input/output mode>
7!M(
x
')123w
• The Linear input/output mode and Math input/output mode produce different results when
two or more powers are input in series, like: 2 M 3 M 2.
Linear input/output mode: 2^3^2 = 64 Math input/output mode:
2
3
2
= 512
This is because the Math input/output mode internally treats the above input as: 2^(3^(2)).
(90° = radians = 100 grads)
π
2
(90° = radians = 100 grads)
π
2
 Loading...
Loading...
















