ENGLISH
27
Installation and control elements
• CEDIMA
®
• Technical Documentation • All rights reserved as per ISO 16016 • Subject to modications due to progressive development •
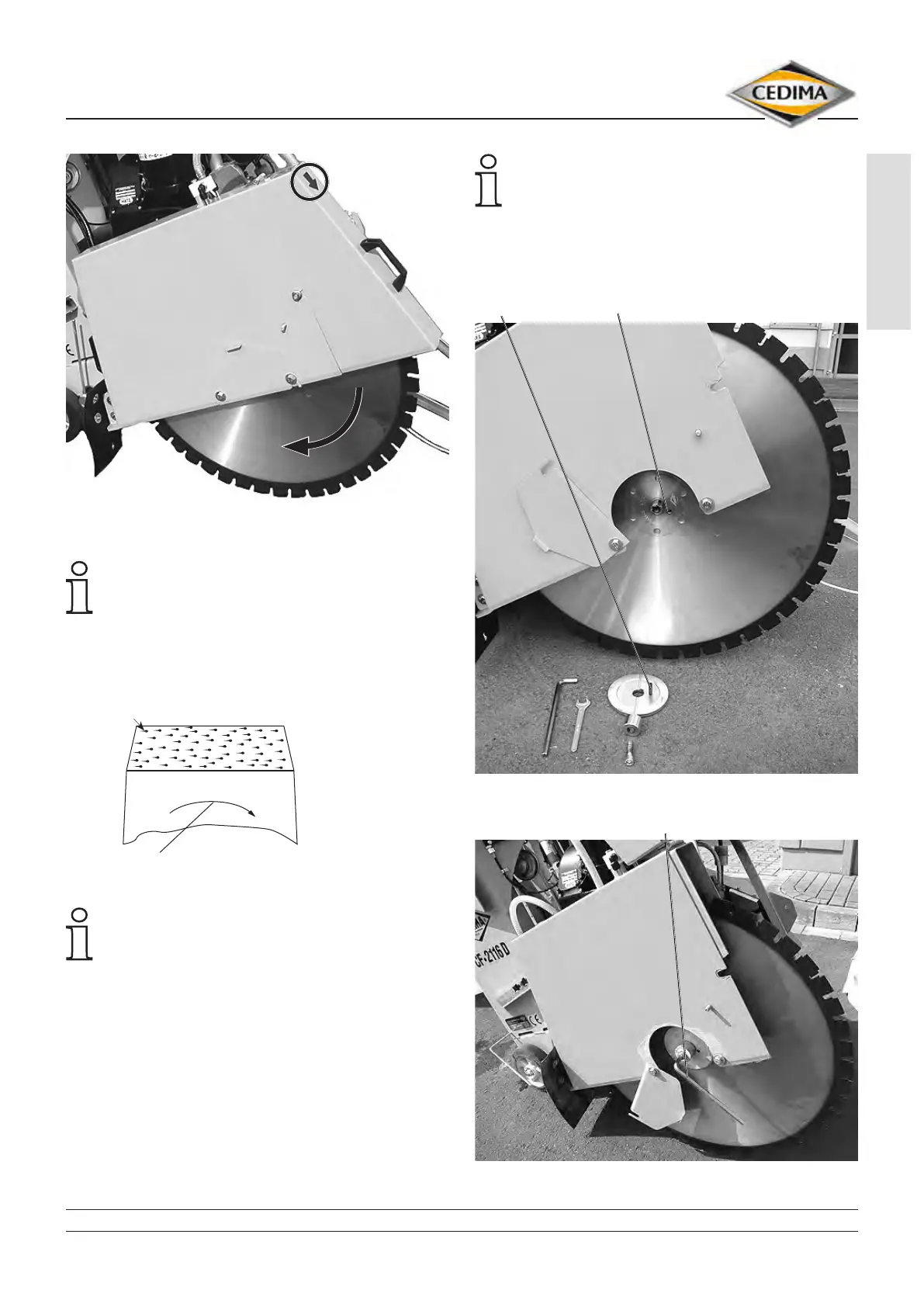
Directional arrows on the CF-2116 D blade guard and the
diamond saw blade Fig. 4.20
Determining the blade’s rotational sense
If the arrow is not visible, the cutting direction of
the saw blade can be determined in the following
way: A “tail” forms behind the diamond during cutting,
so the diamond will always be to the front in relation to
the direction of rotation!
segment
diamond “tail”
direction of rotation
Fig. 4.21
Re-sharpening blunt diamond saw blades
Diamond saw blades are designed to re-sharpen
themselves during cutting operation. They can
become blunt by frequent cutting in heavy steel
armouring or in hard material, which is only slightly
abrasive. Blades can be re-sharpened by cutting in an
abrasive material such as chalky sand stone or asphalt!
8. Fit the blade clamping ange with the sealing ring
and screw drive pin on to the blade shaft and screw
the blade shaft screw tight (left-hand thread, g. 4.19,
4.22 and 4.23)!
Make sure that the drive pin extends through the
bore hole into the blade mounting ange.
9. Put the clamping ange onto the cutting shaft and
re-screw the cutting shaft screw (left-hand thread, g.
4.23).
CF-2116 D standard, mounted saw blade Fig. 4.22
drive pin bore holes for drive pin (ange, saw blade)
CF-2116 D standard, tensioning the saw blade Fig. 4.23
Allen key
 Loading...
Loading...