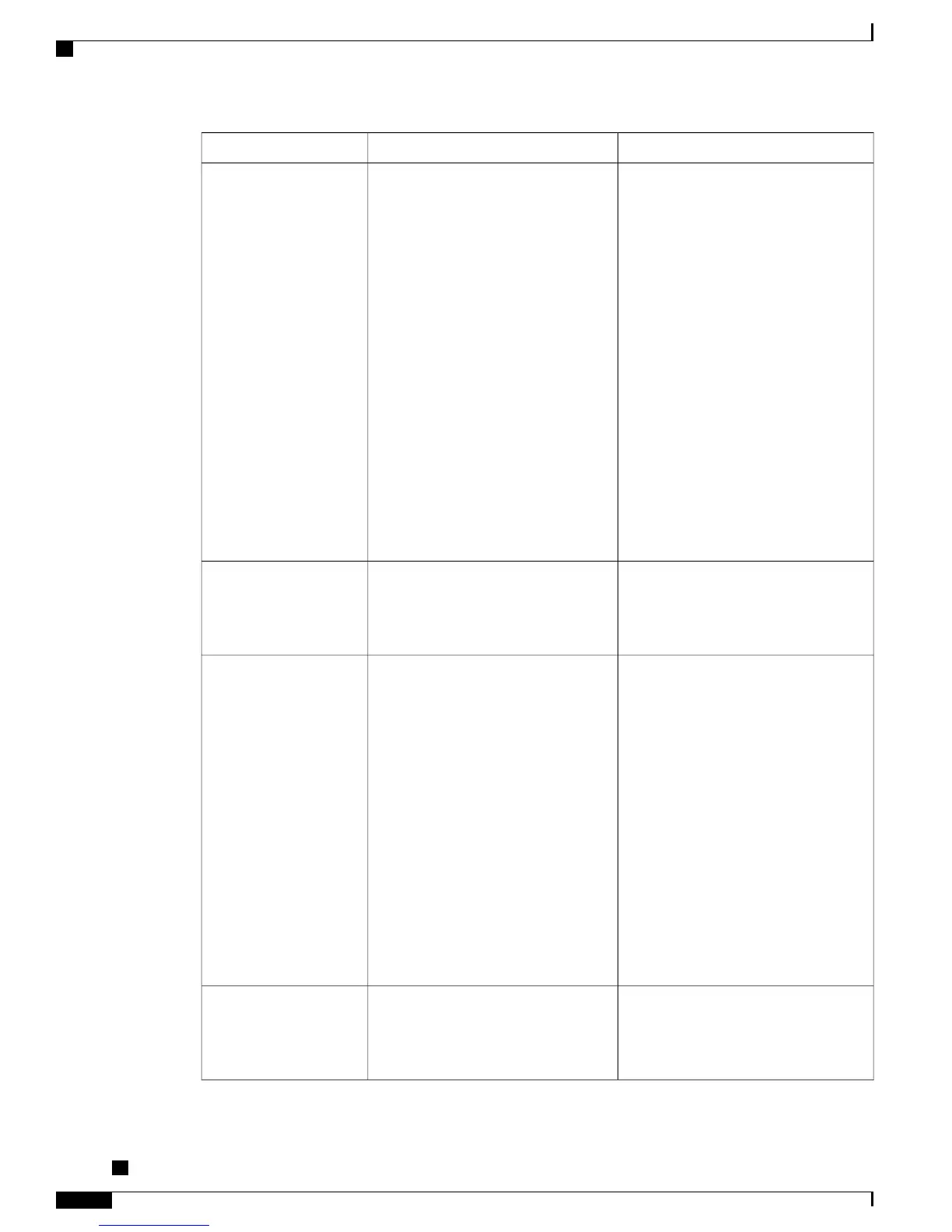
Usage notesPurposeNetworking Protocol
To communicate using IP, network
devices must have an assigned IP
address, subnet, and gateway.
IP addresses, subnets, and gateways
identifications are assigned
automatically if you are using the phone
with DHCP. If you are not using DHCP,
you must assign these properties
manually to each local phone.
The Cisco Unified IP Phone supports
concurrent IPv4 and IPv6 addresses.
Configure the IP addressing mode (IPv4
only, IPv6 only, and both IPv4 and IPv6)
in Cisco Unified Communications
Manager Administration.
For more information, see the Cisco
Unified Communications Manager
Features and Services Guide, “Internet
Protocol Version 6 (IPv6)” chapter.
IP is a messaging protocol that
addresses and sends packets across the
network.
Internet Protocol (IP)
The Cisco Unified IP Phone supports
LLDP on the PC port.
LLDP is a standardized network
discovery protocol (similar to CDP)
that some Cisco and third-party devices
support.
Link Layer Discovery
Protocol (LLDP)
The Cisco Unified IP Phone supports
LLDP-MED on the SW port to
communicate information such as:
•
Voice VLAN configuration
•
Device discovery
•
Power management
•
Inventory management
For more information about LLDP-MED
support, see the LLDP-MED and Cisco
Discovery Protocol white paper:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk652/
tk701/technologies_white_
paper0900aecd804cd46d.shtml
LLDP-MED is an extension of the
LLDP standard developed for voice
products.
Link Layer Discovery
Protocol-Media Endpoint
Devices (LLDP-MED)
The Cisco Unified IP Phone uses the
RTP protocol to send and receive
real-time voice traffic from other phones
and gateways.
RTP is a standard protocol for
transporting real-time data, such as
interactive voice and video, over data
networks.
Real-Time Transport
Protocol (RTP)
Cisco Unified IP Phone 7931G Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager 9.0 (SCCP
and SIP)
10
Cisco Unified IP Phone 7931G
Network Protocols

 Loading...
Loading...





