1-13
Cisco TrustSec Configuration Guide
OL-22192-01
Chapter 1 Cisco TrustSec Overview
Using Cisco TrustSec-Incapable Devices and Networks in a Cisco TrustSec Network
Using Cisco TrustSec-Incapable Devices and Networks in a
Cisco TrustSec Network
This section includes the following topics:
• SXP for SGT Propagation Across Legacy Access Networks, page 1-13
SXP for SGT Propagation Across Legacy Access Networks
Tagging packets with SGTs requires hardware support. You might have devices in your network that,
while capable of participating in Cisco TrustSec authentication, lack the hardware capability to tag
packets with SGTs. By using the SGT Exchange Protocol (SXP), these devices can pass
IP-address-to-SGT mappings to a Cisco TrustSec peer device that has Cisco TrustSec-capable hardware.
SXP typically operates between ingress access layer devices at the Cisco TrustSec domain edge and
distribution layer devices within the Cisco TrustSec domain. The access layer device performs Cisco
TrustSec authentication of external source devices to determine the appropriate SGTs for ingress
packets. The access layer device learns the IP addresses of the source devices using IP device tracking
and (optionally) DHCP snooping, then uses SXP to pass the IP addresses of the source devices along
with their SGTs to the distribution switches. Distribution switches with Cisco TrustSec-capable
hardware can use this IP-to-SGT mapping information to tag packets appropriately and to enforce
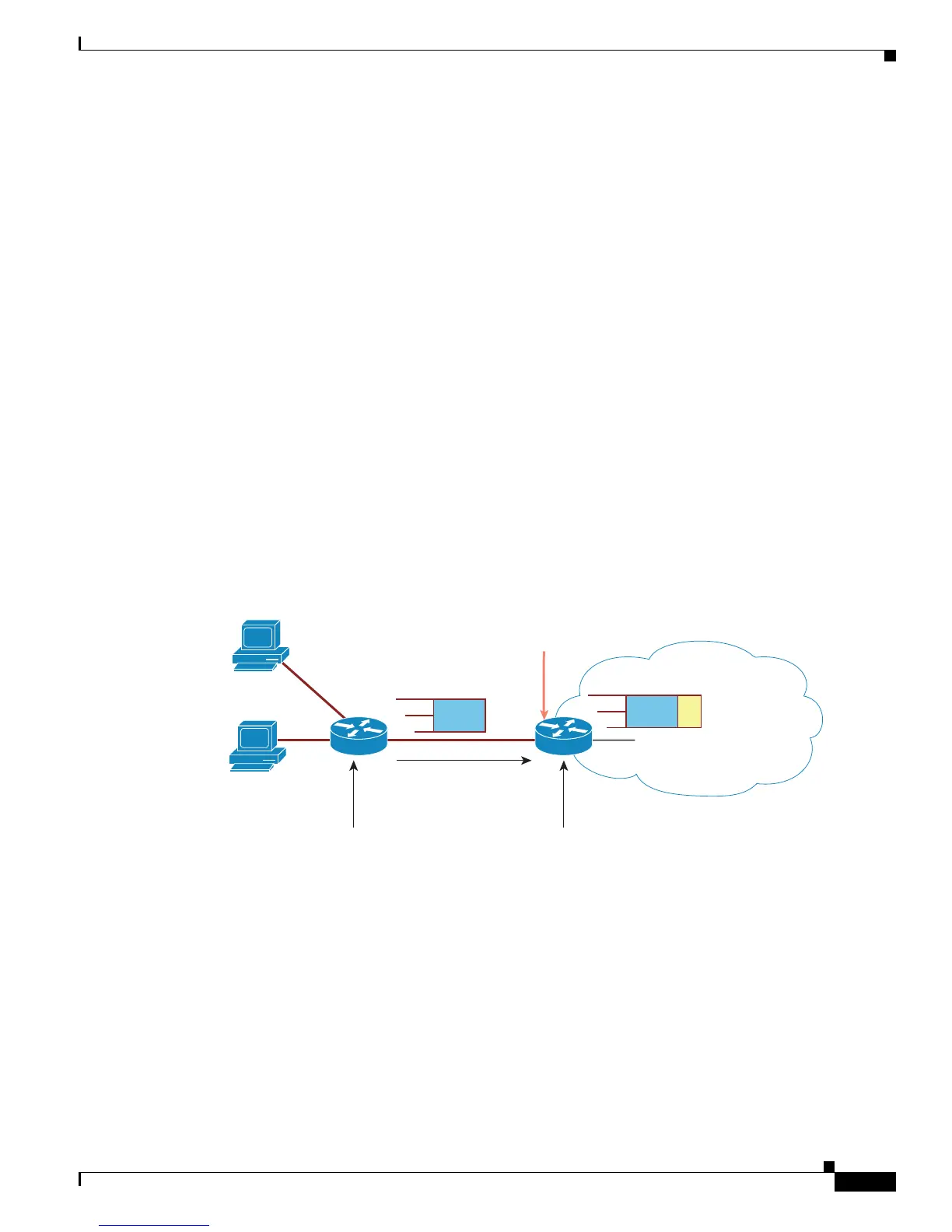
SGACL policies (see Figure 1-6).
Figure 1-6 SXP Protocol to Propagate SGT Information
Src IP=1.1.1.1/ SGT = 3
3
HostB
(1.1.1.1)
SGT tagging
Cisco TrustSec
Src IP =1.1.1.1
Cisco TrustSec capable software
Cisco TrustSec incapable hardware
SXP protocol exchange
IP:1.1.1.1: SGT:3
IP:1.1.1.2: SGT:5
Cisco TrustSec enabled software
and hardware
HostA
(1.1.1.2)
187011

 Loading...
Loading...











