The empty main IP rule set will now appear. Press the Add button at the top left and select IP
Rule from the menu.
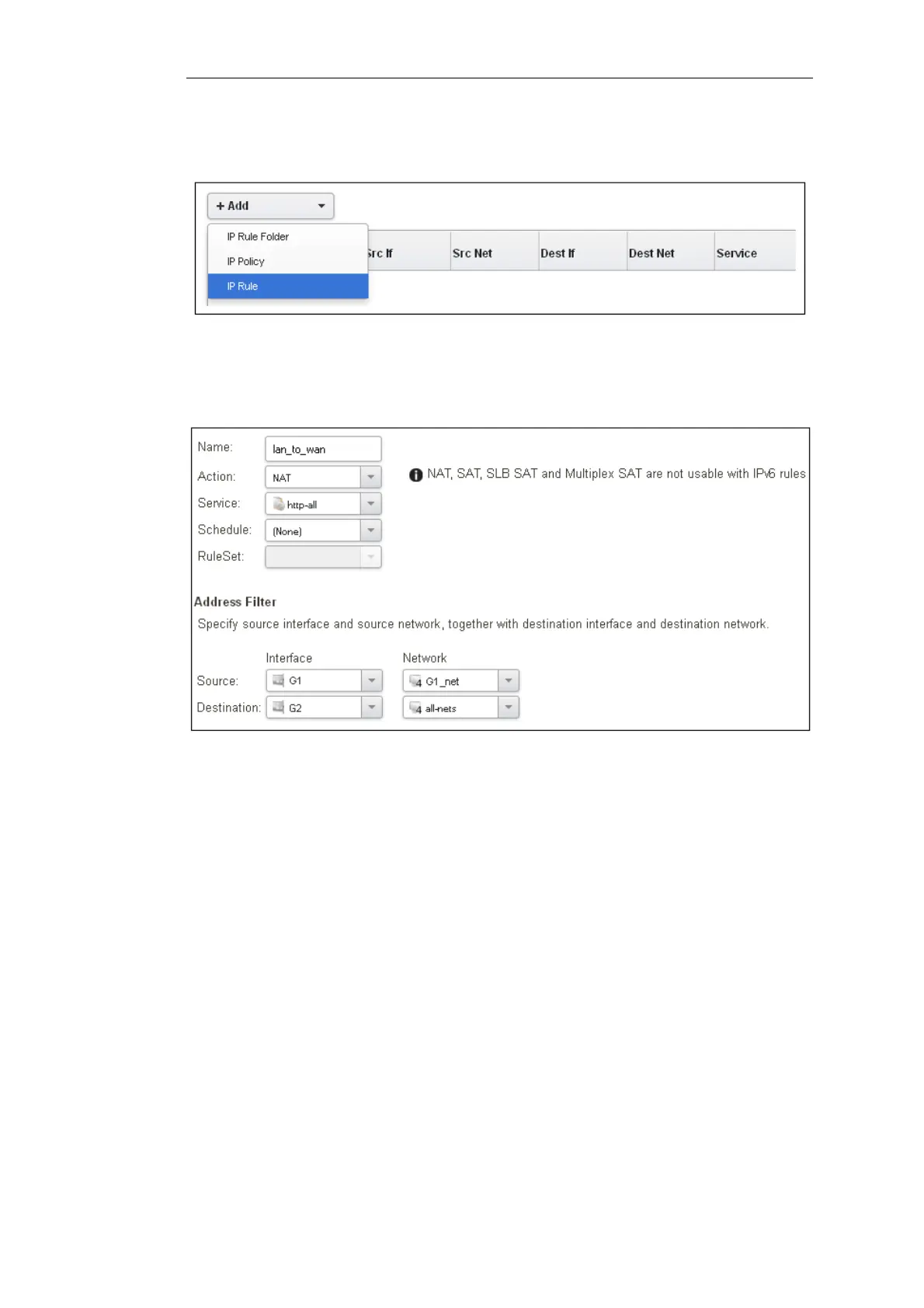
The properties for the new IP rule will appear. In this example, we will call the rule lan_to_wan.
The rule Action is set to NAT (this is explained further below) and the Service is set to http which is
suitable for most web browsing (it allows both HTTP and HTTPS connections). The interface and
network for the source and destinations are defined in the Address Filter section of the rule.
The destination network in the IP rule is specified as the predefined IP4 Address object all-nets.
This is used since it cannot be known in advance to which IP address web browsing will be
directed and all-nets allows browsing to any IP address. IP rules are processed in a top down
fashion, with the search ending at first matching rule. An all-nets rule like this should be placed
towards the bottom or at the end of the rule set since other rules with narrower destination
addresses should trigger before it does.
Only one rule is needed since any traffic controlled by a NAT rule will be controlled by the cOS
Core state engine. This means that the rule will allow connections that originate from the source
network/destination and also implicitly allow any returning traffic that results from those
connections.
In the above, the predefined service called http is the best service to use for web browsing (this
service includes HTTP and HTTPS but not DNS). It is advisable to always make the service in an IP
rule or IP policy as restrictive as possible to provide the best security possible. Custom service
objects can be created for specific protocols and existing service objects can also be combined
into a new, single service object.
The IP rule Action could have been specified as Allow, but only if all the hosts on the protected
local network have public IPv4 addresses. By using NAT, cOS Core will use the destination
interface's IP address as the source IP. This means that external hosts will send their responses
back to the interface IP and cOS Core will automatically forward the traffic back to the originating
local host. Only the outgoing interface therefore needs to have a public IPv4 address and the
internal network topology is hidden.
Chapter 4: cOS Core Configuration
43
 Loading...
Loading...