Byte 1
Byte 2
Byte 3
Parity
Command
2ms
300us
300us
Start
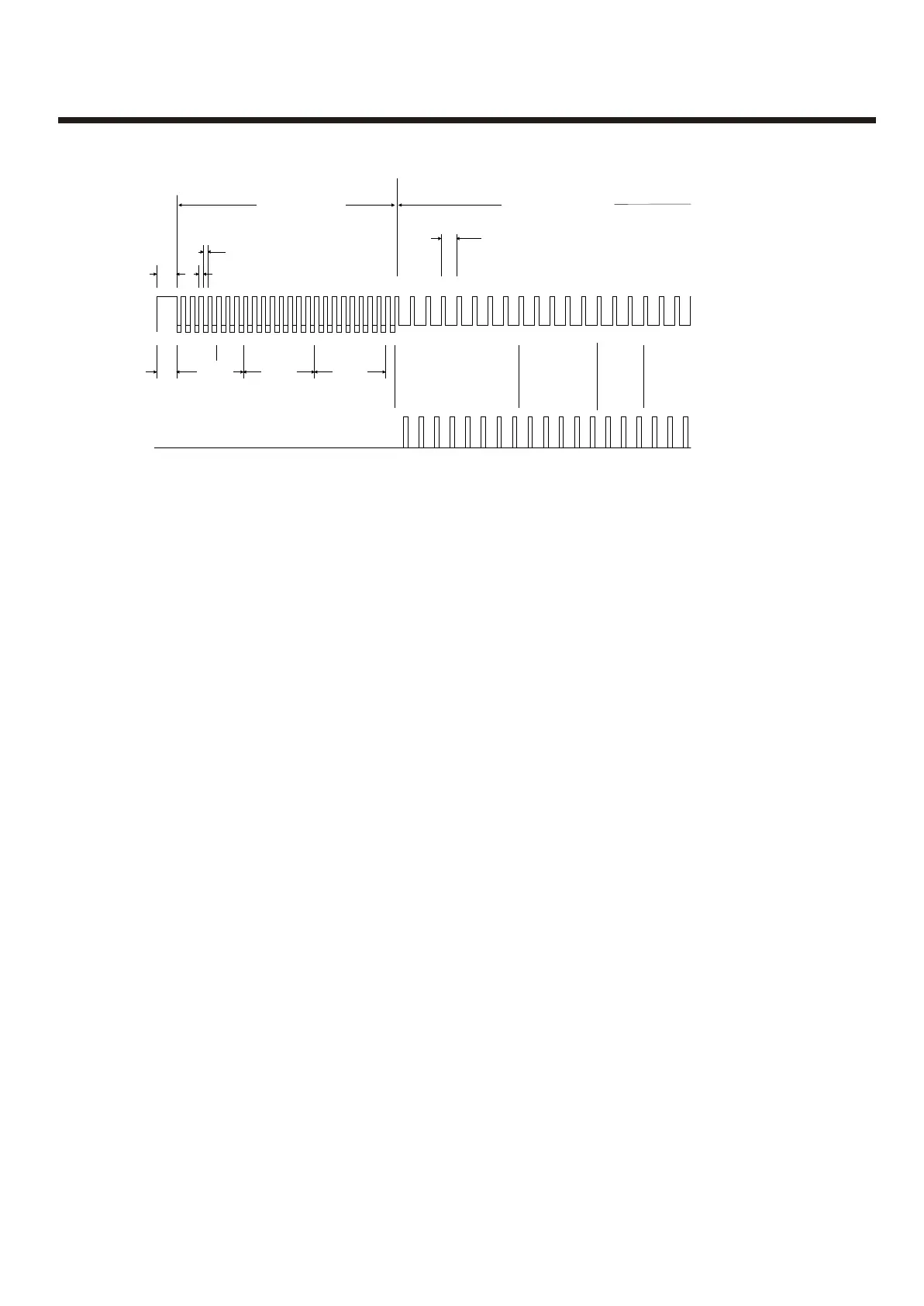
Fig. 1 Full Protocol Format (Not including Repeaters)
Panel to Device Device to Panel
Response
8 bits
ID
5 bits
Flags
3 bits
Address
8 bits
Loop Current
24v
typ
7.5v
0v
Mode
See Fig 4 for detail
1.1 ms
Each Packet of Comms above must be separated by a gap of 20ms minimum where the line is held at 24v
Last Bit Only
1.36 ms
Protocol FormatProtocol Format
Normal Communications to Devices:
With the command bits set for the 'Normal' command and the MSB of the three mode bits set
at 0, this shortened version of the Normal communications to each device allows the
analogue reply or status from each device to be read. This format of communication is
generally used throughout all background supervision of the addressable loop.
Alarm Interrogate Command:
This command is seen by all devices on the loop, so no address byte is required, and is
periodically sent out during normal communications. This command allows any device
experiencing an alarm condition to respond, with call points given the highest priority,
reporting their address. This causes the control panel to break off from general background
supervision of the loop and focus directly on the device in question.
Full Protocol Format:
With the command bits set for the 'Normal' command and the MSB of the three mode bits set
at 1, the long version of the Normal communications can be sent to any device. This would
normally be done by the panel following a response to the Alarm Interrogate command,
allowing the panel to check the device address, ID and confirm that the analogue reply, or
status, is truly an alarm condition before actioning the panel sounder outputs, for example.
Viewing the Voltage and Current waveforms at the panel:
Loop 1: Using a Digital Storage Oscilloscope, connect one channel to R34 on the Loop Driver
Card; probe 0V clip to the 'in-board' side of the resistor; I/P to the 'out-board' side. This will
display the loop current.
Connect the other channel to Loop 1, S+ terminal on the main mother board. DO NOT
connect the 0v clip of this probe.
Loop 2: Using a Digital Storage Oscilloscope, connect one channel to R?? on the Loop
Driver Card; probe 0V clip to the 'in-board' side of the resistor; I/P to the '????????' side. This
will display the loop current.
Connect the other channel to Loop 2, S+ terminal on the main mother board. DO NOT
connect the 0v clip of this probe
31
 Loading...
Loading...