2 — INSTALLATION AND WIRING
pg. 11
Return to TOC Curtis 1353 CANopen Expansion Module Manual – June 2017
INPUT/OUTPUT SIGNAL SPECIFICATIONS
e input/output signals wired to the 23-pin connector can be grouped by type as follows; their
electrical characteristics are discussed below.
• driver outputs
• digital inputs
• analog inputs with virtual digital input
• encoder inputs
• serial port
• auxiliary power supplies
• CANbus interface
Driver Outputs
e 1353 contains nine identical driver outputs. ese outputs have all the features necessary to drive
proportional valves as well as many other inductive and non-inductive loads. A variable amount of
dither (xed frequency command “jitter”) can be added to the PWM to prevent proportional valves
from sticking in place.
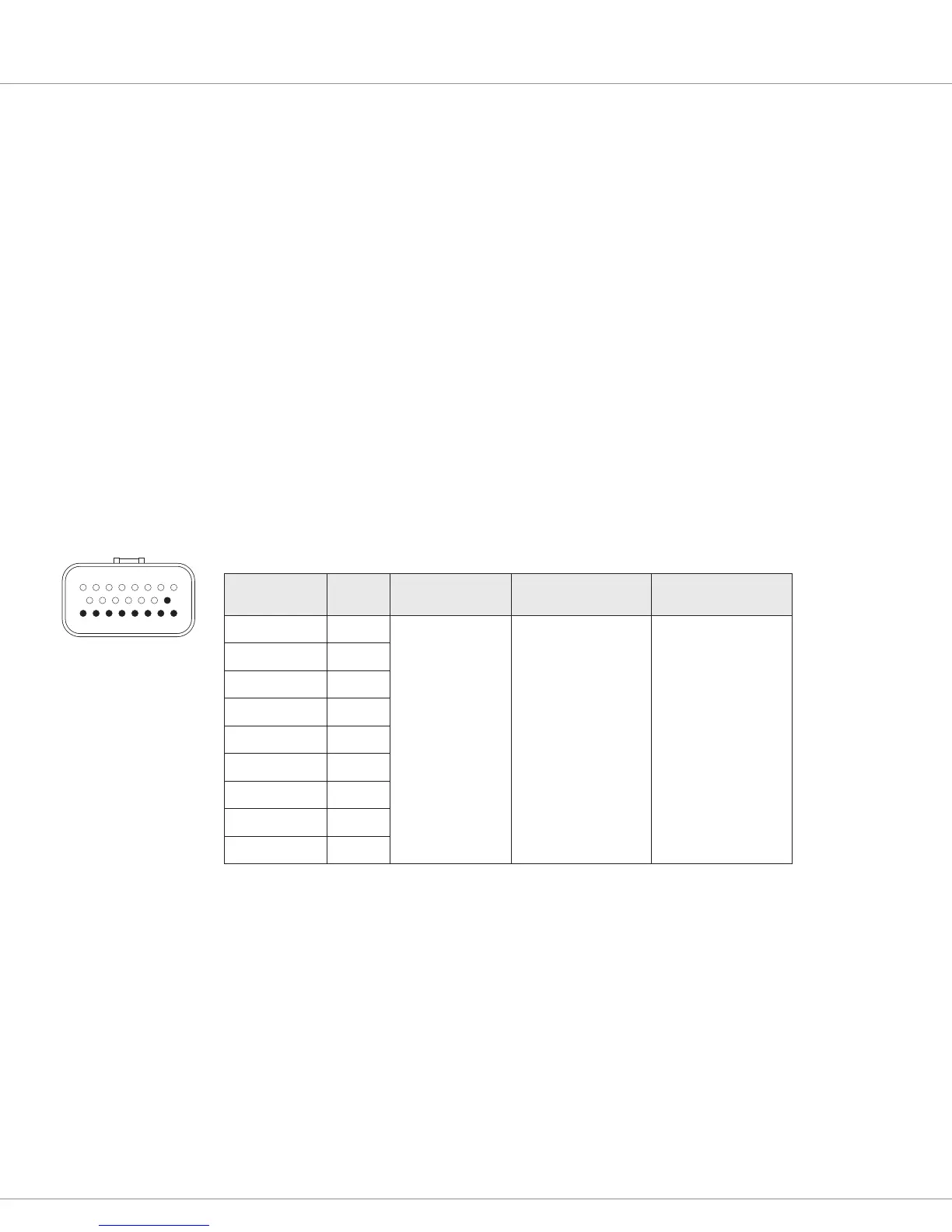
DRIVER OUTPUT SPECIFICATIONS
Signal Name Pin Max Current Impedance Frequency
Input/Output 9 15
Each driver:
3 amps
All 9 total:
18 amps
12 – 36 V models:
10 kΩ pulldown to B-
36 – 80 V models:
47 kΩ pulldown to B-
All models: 16 kHz
0–100% duty cycle
Input/Output 8 16
Input/Output 7 17
Input/Output 6 18
Input/Output 5 19
Input/Output 4 20
Input/Output 3 21
Input/Output 2 22
Input/Output 1 23
e drivers can be set for Constant Current, Constant Voltage, or Direct PWM control mode.
In Constant Current mode, the driver command of 0 to 100% is interpreted as a current from 0 to
Max Output setting (up to 3 amps). Internal current shunts are measured and fed back to a closed
loop PI controller to provide a steady current over changing loads and supply voltages.
In Constant Voltage mode, the driver command of 0 to 100% is interpreted as a voltage from 0 to
Max Output (up to 80 volts). e battery voltage is constantly monitored and fed back to a closed
loop PI controller to provide a steady voltage, compensating for battery droop and discharge. If the
command is higher than the driver can output, the PWM will max out at 100%.
In Direct PWM mode, the driver command of 0 to 100% is directly output on the driver.
81
2316
9 15

 Loading...
Loading...