In the same way, net_2 could be published on the interface if1 so that there is a mirroring of routes
and ARP proxy publishing.
Route # Network Interface Proxy ARP Published
1 net_1 if1 if2
2 net_2 if2 if1
In this way there is complete separation of the sub-networks but the hosts are unaware of this. The
routes are a pair which are a mirror image of each other but there is no requirement that proxy ARP
is used in a pairing like this.
Keep in mind that if the host has an ARP request for an IP address outside of the local network then
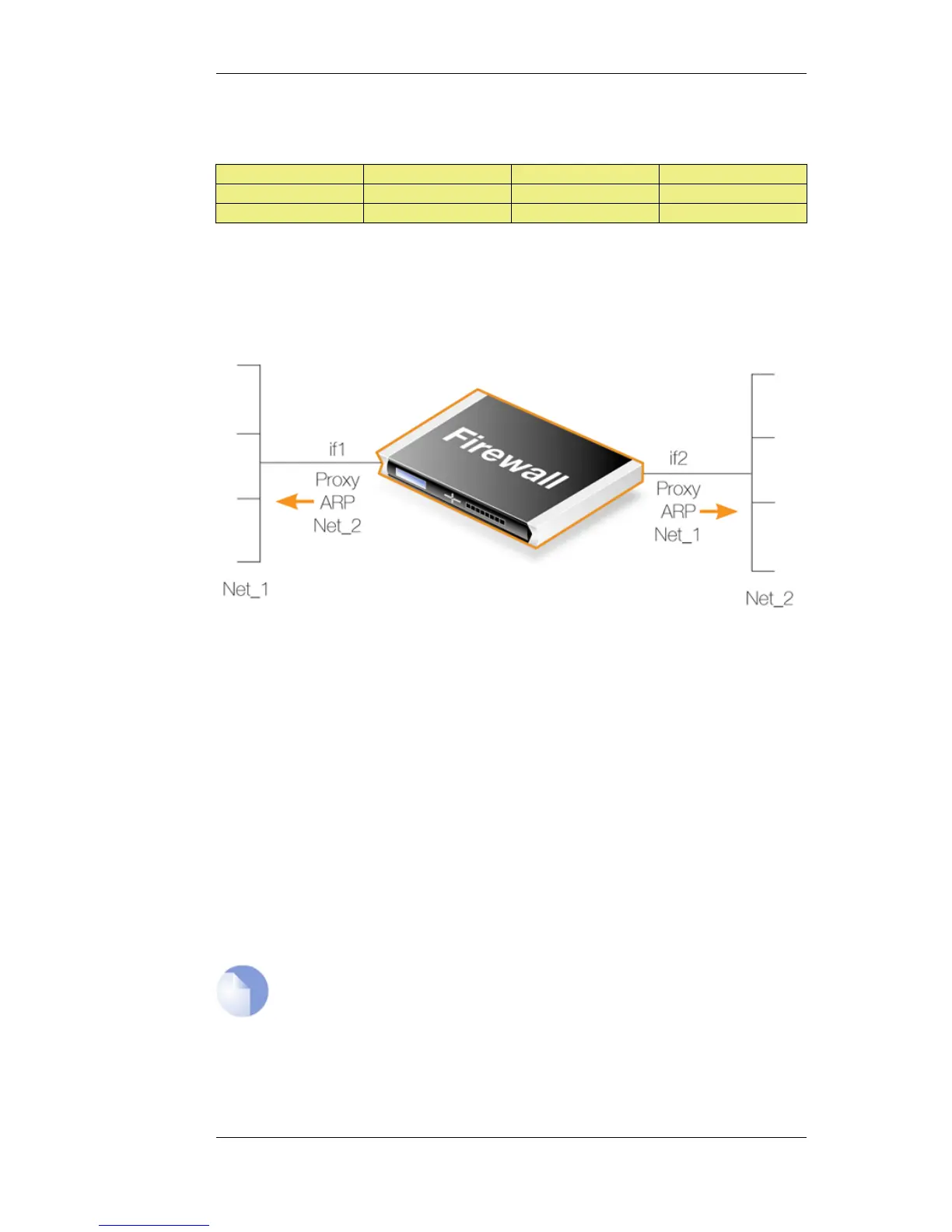
this will be sent to the gateway configured for that host. The entire example is illustrated below.
Figure 4.4. A Proxy ARP Example
Transparent Mode as an Alternative
Transparent Mode is an alternative and preferred way of splitting Ethernet networks. Setup is
simpler than using proxy ARP since only the appropriate switch routes need to be defined. Using
switch routes is fully explained in Section 4.7, “Transparent Mode”.
Proxy ARP depends on static routing where the location of networks on interfaces are known and
usually fixed. Transparent mode is more suited to networks whose interface location can change.
Proxy ARP and High Availability Clusters
In HA clusters, switch routes cannot be used and transparent mode is therefore not an option.
However, proxy ARP does function with HA and is consequently the only way to implement
transparent mode functionality with a cluster.
Note: Not all interfaces can make use of Proxy ARP
It is only possible to have Proxy ARP functioning for Ethernet and VLAN interfaces.
Proxy ARP is not relevant for other types of NetDefendOS interfaces since ARP is not
involved.
Automatically Added Routes
4.2.6. Proxy ARP Chapter 4. Routing
184
 Loading...
Loading...